To provide the body a constant composition of the blood requires the formation of waste substances (toxins). This process involves the kidneys with the urinary organs, intestines, lungs, skin.
The structure of the human kidney the most adapted for the removal of excess fluid, and cull unnecessary harmful substances and preserve the useful components of the blood.
Kidney – paired bean-shaped organ. Each weighs 150-200 g are Located on both sides of the spine, in the area from the third lumbar vertebra to the twelfth thoracic.
A little anatomy
The upper and lower bounds referred to as “poles”. Vertical upper pole lie somewhat closer to the vertebrae. Horizontal level on the right body 2 cm below the left.
The inner side of the concave surface forms a “gate” through which the kidney is composed of:
- artery;
- the nerve trunks.
Overlook:
- Vienna;
- the ureter;
- the lymphatic duct.
Outside is the kidney covered by the dense capsule of fibrous tissue, followed by fat and fascia. Two pieces of fascia connects on the outer edge. It protects the body like the scales of the buds of plants, attaches it to the abdominal wall, creates a fixed receptacle for the vessels and nerves.
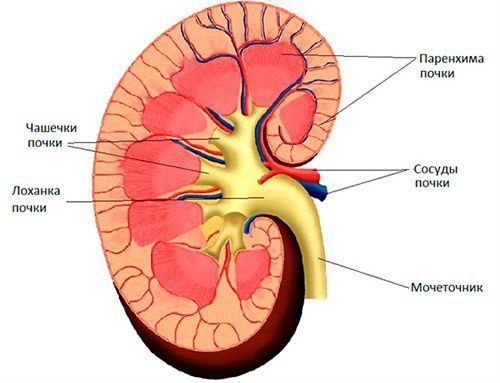
The cut is visible macrostructure of the body.
Stand 2 layers that work together to form the renal parenchyma:
- the outer, darker – cortical;
- inner, light – brain.
The substance of bark wedged in the underlying tissue. These areas are referred to as “pillars”, and between them from the medulla of the renal pyramids are formed. Every pyramid in the narrow part has a nipple with small holes, which is connected with the initial structure of the excretion of urine – renal calyx.
Small cups (to 10 in number) are merged into a larger (4-5) and transferred to the pelvis, lesion near to the gate from which the ureter comes out
From here the urine flows into the lower urinary organs: bladder and urethral canal.
The location of the kidneys
Special section – topographic anatomy – determines the location of the organs relative to the adjacent formations, muscles, blood vessels, bones, nerve branches. We would call this as a 3D image.
It is especially important to know the ratio of kidney to the adjacent organs operating surgeons-urology. People who surgery responsible for patient safety, careful approach to the changed body and minimal trauma.
The kidneys are extraperitoneal, although in contact with her on the front and back surface.
Front from the right are:
- the liver;
- the duodenum and colon.
Before the left kidney lie:
- stomach;
- pancreas;
- spleen;
- part of the small intestine;
- poperechnopolostah downward Department of the colon.
To the upper poles closely adjacent the adrenal glands, covered with fatty tissue. Still above is dense diaphragmatic muscle that separates the abdominal and thoracic cavity. Behind kidney abdominal wall is strengthened to large spinal muscles (lumbar and square).
Blood supply
Blood flow to the kidney arterial blood originates from the abdominal aorta. Through the renal artery for 4-5 minutes passes entire blood volume of the human body. Moving away from her to both bodies left and right renal artery.
Then they break up into a network of branches:
- vessels of the first row are divided into 5 segments;
- the second row presents the interlobar arteries;
- the third row consists of curved branches;
- fourth of interlobular.
Interlobular arterioles are essentially generating components of the capillary network of glomeruli.
After the merger of the efferent vessels form venules. In the cortical layer of the kidneys in humans are stellate veins. They collect blood from brain matter in the interlobular vessels then in the arc, same with the arteries. Blood flow goes to the renal vein, it flows into the lower hollow. In relation to the same mass of the cortical layer receives 20-40 times more arterial blood than brain.
Lymphatic vessels go from the renal gate and sent to regional lymph nodes:
- kidney;
- retrocaval (so called because are for Vena cava);
- Prearalie (located in front of abdominal aorta);
- para-aortic (along the vessel).
Features of innervation
Renal nerves form the renal plexus. They get “information” from Central departments through the branches of the vagus nerve and paravertebral nodes. In the tissue of a large number of receptors. The irritation sends impulses via the afferent (going from the periphery to the center) fibers in the spinal cord. They are composed of the sympathetic splanchnic nerves.
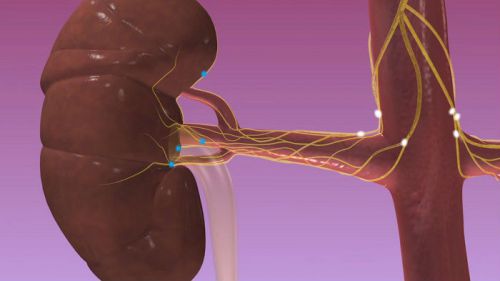
Reverse (efferent) fibers are directed by branches of sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves:
- The sympathetic innervation comes from neurons located in the lateral horns of the spinal cord in the lower thoracic and upper lumbar segments.
- Parasympathetic – is of less importance, is carried out by branches of vagus nerves and General pelvic plexus.
Innervation of the nephron is intertwined with nerve endings, arterioles, glomerular capillary, venules
Maximum developed a network of nerve fibers in cells yukstaglomerulyarnogo zone.
The microstructure of the kidney
Smooth operation for the removal of toxins in the urine provide a structural unit of the kidney – the nephrons. In each kidney there are about one million such entities. In the case of the decrement part of the nephron, the remaining take a high functional load. Therefore, renal pathology long runs secretly and asymptomatic.
2/3 of the nephrons lie in the cortical layer, 1/3 on the border of cortex and medulla, called juxtaglomerular area.
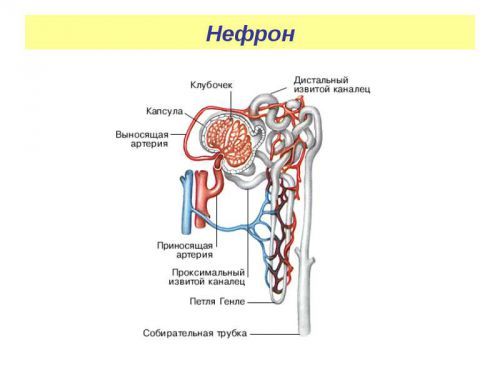
Each nephron consists of:
- capillary glomeruli, in them comes from the blood causing arteries;
- the basal membrane;
- capsules from two lobes with a cavity inside, surrounding the glomeruli (Shumlyansky-Bowman);
- system tubular (straight, coiled), accompanied by a discharge of blood vessels.
It is estimated that the total length of all tubules of the kidney reaches to 100 km
Collective tubules for the coupling of nephrons with small cups of histology does not relate to the structure of the nephron.
The basement membrane outside the capillary wall is covered with special cells. They are called “podocytes”, have characteristic protuberances, and gaps (space between them). The inside of the vessel are endothelial cells, which form between themselves small holes, “slits”. Such a structure similar to a sponge, it provides filtration of water from the plasma.
How do the nephrons?
The nephron as the main structural and functional unit of the kidney takes blood from the renal artery under high pressure and with a high concentration of dissolved substances. Inside the glomerulus, these figures are much less. Due to the differential transition occurs between a liquid and molecules of small and medium size through the basement membrane formed by endothelial cells of blood vessels, and kidney epithelium.

Past the barrier fluid between the sheets of the capsule. It is called primary urine.
It comprises in addition to water:
- nitrogenous substances (urea, creatinine);
- dissolved salt;
- other toxins;
- glucose;
- amino acids;
- vitamins;
- low molecular weight components.
Proteins due to the large dimensions normally do not pass through the basal membrane. Further, the process of reverse suction occurs in kanalzeva apparatus.
Reabsorption are:
- a larger volume of water;
- amino acids;
- glucose;
- trace elements;
- vitamins;
- electrolytes.
Primary urine moves along the tubules, renal epithelium which has the unique ability to determine the value and the optimal concentration for the organism of the solute. These cells can withdraw from the plasma portion of the excess glucose, urea, change of electrolyte composition due getting rid of acidic or alkaline components.

The epithelium of the tubules consists of cubic (marked with number 2) and cylindrical cells (figure 3), some of which have “brushes” on the surface
These formations are tiny growths that can increase in contact with the primary surface of urine from 6 m2 to 50 m2. The same mechanism have the cells of the intestinal wall.
Needed substances are returned to the bloodstream without the cost of energy for the synthesis or transport. Epithelial cells move into the surrounding tubules vessels due to osmotic pressure.
Secondary, the urine is directed into the collecting ducts and excreted into the holes of the pyramidal papillae (12-15 on each vertex). Thus it reaches the cups, where it comes into the pelvis and into the ureter.
The importance of the kidneys in the body
Physiology of the kidneys is closely connected with the activity of the whole organism, each organ separately. In General, the formation of urine and the removal of slag substances spend up to 10% of energy reserves.
Healthy the kidneys are self-sustaining body. They synthesize the energy your own cells, from glucose and vitamins, the necessary oxygen. The mass of the two kidneys represent about 0.5% of the total weight of the human body. And oxygen flow rate – 9%. It is proved that the cortical layer consumes more oxygen than the brain.
The study of the processes of damage of renal tissue under conditions of oxygen deficiency (hypoxia) showed how sensitive the camera for any violation of the blood supply. Ischemia due to thrombosis, atherosclerotic changes in major arteries leads to a loss of functional capacity of renal structures.
Paying maximum attention to urine output, we must not forget that the role of the kidneys in maintaining acid-base balance of the blood. Because the correct exchange of substances takes place only under conditions of optimal internal environment.
This task is performed by the epithelial cells of the tubules, which are capable of:
- to analyze the present composition of the liquid;
- to ascertain variations in chemical composition and reaction.

Balancing is carried out by accumulation or excretion of hydrogen ions of sodium and potassium, ammonium compounds. In the derivation of urine in the alkaline residue of the reaction of the blood becomes closer to sour and Vice versa. Delay of electrolytes is also associated with insufficient intake of food.
The kidneys perform the following objectives:
- the removal of toxins, unwanted waste products of cells metabolism;
- the elimination of foreign substances that have antigenic properties;
- maintaining the desired concentration is biologically important for the body components within the current needs;
- intra – and extracellular regulation of electrolytes, water and salts;
- support optimal acid-base balance to support all types of metabolism.
Urine – the result of kidney
How is the function of the kidneys?
One of the peculiarities of the physiology of the kidneys – production of hormone-like substances, which provide their participation in the overall activity of organs and systems.
Renin – is a proteolytic enzyme synthesized in the cells of the glomeruli, located in ukstaglomerulyarnogo area. From here it enters the bloodstream and lymph. Not actually considered a hormone because it has sensitive target cells. However, it contributes to the development of this hormonal substance, angiotensin II.

Its action consists in:
- the narrowing of the blood vessels;
- the increase in blood pressure (especially in the vessels of the internal organs and skin);
- strengthening the process of reabsorption in the tubules of sodium ions.
Other methods of regulation have cells of the medulla oblongata related to the hypothalamus. They produce the hormone vasopressin (an antidiuretic), which accumulates in the posterior lobe of the pituitary gland. When injected into the renal tissue vasopressin significantly increases the reabsorption of water in the convoluted tubules. This mechanism triggered large losses of water in the heat, bleeding, vomit.
The action of vasopressin is accompanied by a decrease of the volume of secondary urine, water retention in the body
Regulation has aldosterone, which is synthesized in the adrenal glands. You’ll be able to change their reabsorption in the tubules, increases retention of sodium and removes potassium.
The influence of the nervous system is to:
- the vasoconstriction of the kidneys and reducing the filtration under the influence of sympathetic impulses;
- the increase in blood flow in irritation of the parasympathetic nerves.
Features of the kidneys in children
After the birth of the formation of structures necessary for the implementation of all kidney functions, incomplete, although the number of nephrons is already equal to a full adult body. Morphologically the structure of a child’s kidney is ready to work for 3-6 years.
The epithelium basal membrane of the glomeruli consists of high cylindrical cells. Cubic are not yet available. Therefore greatly reduced filtering surface at the same time increased resistance.
Tubular device in infancy presents a narrow and short formations, the epithelium is not able to perform a secreting function, highlight the body of excess water.
The amount of produced urine increase with age from 750 ml in a one year old baby, up to 1.5 liters in 10 years.
The allocation of the waste substances in children is significantly limited. The regulatory function of aldosterone and antidiuretic hormone is reduced. The epithelium of the tubules is not responsible for the appearance of these substances.
The kidneys depend on the type of feeding an infant:
- “infants” are not required in the process of the reabsorption of all substances derived from breast milk is completely digested;
- “iskusstvennym” a required regulation of acid-base balance, because under the influence of foreign proteins formula blood zakislate and needs to be cleaned of toxins.
Secretion kanaltsevam epithelium alkaline and acidic components of urine in children is underdeveloped. This is a serious flaw – a tendency to increased formation of salts. In the urine of the child appear amorphous phosphates, and oxalates.
Since the acidic component is less alkaline than 2 times, the children tend to react acidosis in response to different diseases. Feeding mainly protein foods only increases this possibility.
The study of the structure and functions of kidneys allows to compare the work of healthy and modified on, to find a cure, supporting natural processes. Development of a method of hemodialysis that allows to save many patients based on the imitation of renal filtration.



Great blog! Is your theme custom made or did you download it from somewhere? A theme like yours with a few simple adjustements would really make my blog jump out. Please let me know where you got your design. Thanks
Hello, its nice paragгaph on the topic of media print, we all be aware of mediа is a impressive source of facts.
woh I love your posts, saved to my bookmarks! .
Why?
Very good post.Much thanks again. Keep writing.