The renal pelvis is a kind of collector for collecting urine from large and small cups. The amount of education varies throughout a person’s life. It gradually increases with the kidneys in children.
Changes in the average sizes of the pelvis are possible in connection with its pathology caused by inflammation, stone formation, tumor.
Reducing the capacity of the renal pelvis cause abnormal development of the kidneys.
The structure and function
Calyx medulla parenchyma is connected with the natural drainage bag narrow formations – tails. Pelvis is a funnel with an extended side outwards, kidneys, and the drain – gate and the ureter.
To cumulative structures of the renal parenchyma include:
- small cups – the total number varies from 6 to 12;
- large calyx in the kidney of a person 2-4;
- pelvis.
Since smaller entities, calyx merge together and form larger structures. The role of the pelvis is reduced to the accumulation and promotion of the formed urine by the ureters.
In case of difficulty of outflow urinary tract abnormal enlargement occurs, then increase the size of the necks of the big cups. The process is called Kalimantsi.
Renal pelvis inside is covered with mucous membrane from the epithelial cells. This kind of refers to the double-layered epithelium with the basal and surface layers. Type of cells called transitional. They are able to vary depending on the degree of filling of the pelvis.
Histological study transitional epithelium are seen the nuclei of the cells, similar to vesicles, granules within the cytoplasm. Most often the cytoplasm is yellow because it is caused by the characteristic of the urine pigments.
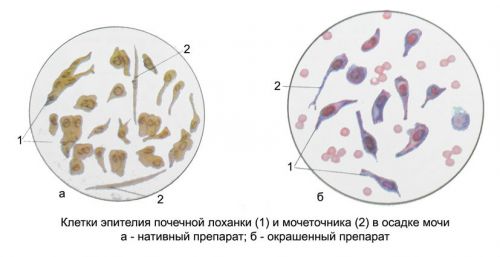
The shape of the epithelium of the renal pelvis can be in the form of cells:
- tailed,
- fusiform,
- pear-shaped,
- oval.
To determine exactly what type of epithelium are shed into the urine, it is important to diagnose the level of inflammation of the urinary organs. Typical cells are found in the catarrhal pyelitis, when the inflammation of the pelvis of the kidney does not affect the deeper layers.
In the case of suppurative pyelitis the epithelium undergoes degenerative changes, most commonly fatty degeneration
In the wall are smooth and transverse muscle bundles.
Such a structure allows to provide:
- reliable seal, complete isolation of the collected urine, it normally cannot go beyond the kidneys;
- to push the accumulated fluid in the ureters, causing peristaltic movement by reducing the longitudinal and transverse muscles.
What determines the size of the pelvis?
The size of the pelvis of an adult not more than 10 mm. in women during pregnancy may increase up to 18-27 mm, but this is considered physiologically normal and are due to pressure of the uterus on the ureters and difficult flow of urine.
In the absence of pregnancy should consider the following reasons:
- the probability of a tumor, compressing the urinary tract;
- the presence of calculi (stones) in the ureters;
- anomalies in the structure (bends or twists).
The renal pelvis of the child is visible even in the prenatal period of gestation of 17-20 weeks. To assume an abnormal development or pathology medical doctors can ultrasound study before the birth and to warn parents. An important difference is the absence of size changes in children before and after urination.
The table shows the maximum normal size of the pelvis in the fetus.
| The pregnancy | Size with ultrasound study in mm |
| up to 32 weeks | 4 |
| 36 weeks | 7 |
To determine how altered kidney and do I need to do anything, to help the pediatrician after examination and inspection of the newborn.
Common kidney disease affecting the pelvis area, consider from the perspective of the most likely causes.
Inflammation
The inflammatory process in the pelvis is called pyelitis. Occurs more often in girls aged 2-5 years, pregnant women, in men after surgical interventions on the prostate gland. Any stagnation of urine provokes the accession of infection. Dangerous pathogen is Escherichia coli, which is always present in the body.
Other agents are actively involved in the defeat of the urinary tract. This is especially important to consider when the presence of chronic infection (tonsillitis, sinusitis, cholecystitis). Hypothermia may be an additional factor of the disease.
Fetal anomalies
A doubling of the pelvis of the kidney is a rare anomaly. It is often combined with additional ureters. If kidney function in this case is not broken, the person does not feel the variance. In identifying the child is not considered the norm, treatment is expected only in the event of the accession of inflammation or other pathology.

Double ureters, kidney, pelvis arise in utero
Ectopia of the ureter – (violation location) when in girls, the ureter is attached to the vagina, and boys – to the urethra. Often combined with the doubling of the kidneys, causing inflammation of the renal pelvis and its increase.
Extension of the pelvis
Extension of the pelvis (pyeloectasia) in children is often congenital. His diagnosed in 2% of pregnant women. While boys suffer more often than girls 3 times. In identifying the “boundary” of size 8 mm is hoped that to leave the structure is normalized. But if the extension is 10 mm, the baby should be observed and treated after birth.
Boys in most cases to 6 months pyelectasis disappears on its own. And girls have evidence of additional pathology.
The main reasons lie in the difficulty of outflow of urine in the fetus: she is thrown back into the kidneys from the pressure of the expanding pelvis.
The fetus is possible:
- congenital malformations of the structure of the kidneys;
- blockage of the ureter or other narrowing of the lumen of the urinary tract;
- in boys the formation of the valve of the urethra.
Most changes occur when the expectant mother had suffered an inflammation of the kidneys, or chronic renal pathology, a possible repeat in future pregnancies. Some experts believe the pyeloectasia the initial stage of hydronephrosis.
In adults for the expansion of the pelvis, there are other reasons:
- kidney disease, if you stop the big stone at the mouth of the ureter, narrowing or complete overlap (urine can’t come down);
- tumors of the pelvis, if the growing site involves the pelvis or squeezes the way of urinary diversion.
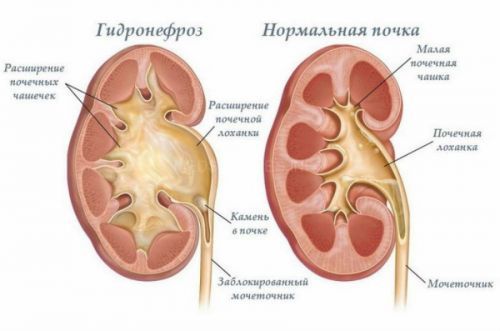
In adulthood the symptoms are determined not by the extension, and the main pathology. The process is gradual. Pelvis becomes funnel-shaped and reminiscent of a spherical cavity. Under the pressure of the parenchyma of the kidney is pushed to the edge. The nephrons die. Their place is filled by fibrous tissue. Kidney shrinks.
Alternatively, currents: permanent stagnation of urine leads to infection and development of chronic inflammation.
Hydronephrosis is followed by urolithiasis complicates it
What are the complications expected in advanced pelvis?
The gradual development of the enlargement process in the adult runs parallel with the main disease.
The consequences can be:
- hydronephrosis;
- urethrocele – at the confluence of the ureter into the bladder wall forms a globular extension, it is usually located on the part of pyeloectasia;
- vesicoureteral reflux is the backward reflux of urine from the bladder into the ureter and into the kidney, accompanied by infection and increasing pressure in the pelvis.
Cause reflux are:
- disturbed innervation of the bladder;
- mechanical obstruction for proper flow of urine in the neoplasm, stone in the renal pelvis.
Hydronephrosis
Hydronephrosis represents a significant expansion not only of the renal pelvis, and cups. Renal parenchyma is gradually atrophies and becomes thinner, the boundary between the cortical and medullary layer, killing the basic structural unit of the kidneys – the nephrons.
Are large sclerotic areas. The process can be one – and bilateral. The outcome is kidney failure.
According to the mechanism of development are distinguished:
- the acquired form;
- innate.
Congenital hydronephrosis is determined in 1.4% of newborns. Usually this is due to genetic predisposition.
Purchased a:
- if the tumor;
- if the kidney disease is accompanied by vesicoureteral reflux;
- urolithiasis.
Cancer processes in the pelvis
Tumors in the renal pelvis are rare localizations, considering only the isolated structure. Often tumor affects the whole kidney, including the renal pelvis-Cup segments. The source of malignant growth is the epithelium covering the inner surface. Such tumours are called adenocarcinomas. The type of epithelium they treat transitional cell.
Tumor long-term “masked” under inflammatory diseases. Pronounced symptoms manifested only at germination inside the walls of the pelvis.
The formation of stones
The cause of stone formation is the intake of chemical and biological substances in the body are broken down into insoluble salts.
These include:
- Urata,
- carbonates,
- phosphates,
- the oxalates.
A similar process takes place when disturbed metabolism and the impossibility of binding and neutralization of these components.
The deposition of salts occurs in the pelvis, ureter, bladder. Gradually, the stone in the pelvis of the kidney reaches a sufficient size. Due to a reduced useful volume. The shape of the stones replicate the structure of the kidney.
They can be:
- triangular,
- oval
- in the form of a cone,
- cylindrical.
Stationary stones dangerous the subsequent stagnation of urine, the development of hydronephrosis. Moving cause the destruction of the wall, a tear with effusion of urine into the peritoneal cavity.
What symptoms should pay attention to?
Malformations can be asymptomatic. Discovered by chance during the examination of chronic inflammation, in cases of suspected neoplasm. Symptoms of lesions of the pelvis are difficult to differentiate.

Patients complain of:
- pain acute or obtuse arching of the character in the lower back radiating to the perineum, the pubic region,
- frequent urination with sharp pains;
- bursting above the pubis, and the inability to urinate;
- the change of urine color (turbidity in excess of leukocytes caused by inflammation, presence of blood in the tumor, or after an attack of kidney stones);
- the temperature increase from low values up to a sharp rise depending on the nature of the inflammation.
The attacks of renal colic when moving the stone can lead to shocks, as
Common symptoms include:
- malaise and weakness;
- nausea;
- weight loss;
- headaches.
How to identify pathology of the pelvis?
Special diagnostic methods for detecting diseases of the pelvis not. In the Arsenal of a doctor, there are enough possibilities of research of kidney disease. To evaluate the level and localization of damage using a careful interpretation of the results.

Patients are prescribed:
- urinalysis with examination of the sediment;
- inoculation of pathological flora;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys;
- excretory urography with the introduction of the contrasting agent;
- computed tomography.
On the radiograph of the kidneys, conducted excretory method, seen left unfilled with contrast “spot”, maybe it’s the tumor
Treatment
Treatment of diseases of the pelvis are engaged in urology, the detection of the Oncology education, Oncology.
The inflammatory process requires antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs that concentrate in the kidneys. If congenital anomalies contribute to urinary retention, need for surgery, because without intervention it is impossible to deal with inflammation.
Hydronephrosis, stones and tumors are treated only by surgery. In special cases, tumors is chemotherapy with cytotoxic drugs, and radiation treatment. The operation always takes into account the state of the second kidney.
The usefulness of lithotripsy (crushing of stones) should be discussed in each case with a specialist. Not recommended acceptance of folk tinctures and herbal teas, heating pads and hot baths without consulting your doctor.
Therapy pathology pelvis long. You may need more than one course of treatment, selection and replacement of antibiotics, use of antifungal drugs. Patients should follow a proper diet. Exclude from food spicy dishes, condiments. The detection of anomalies in the development of the child must be protected from any infection, hypothermia. It is recommended that annual check-UPS.




I need to see more about this from you! Of course I will share this blog immediately. Thanks!