The human spine is a bony and cartilaginous axis, composed of 33 – 34 vertebrae. Each division of the vertebral column has a certain number of vertebrae that performs a clear function.
Their structure is very similar, but depending on the spine, there are some differences. The human vertebrae are divided into seven parts: cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacrum, coccyx, Atlas, and transverse processes.
All vertebrae are made of a body and arch. It arcs and body are the basis of the spinal canal. The vertebral body consists of a plastic outer bone and inner cancellous playing the role of the bone rail.
Exactly spongy substance responsible for the strength. Inside of the body is red marrow, regulate the bleeding. All tissue covering the vertebrae of the person is updated periodically. With constant physical activity, these processes are much faster.
Types and characteristics
All the vertebrae that comprise the spine, as mentioned above, is divided into types. In the cervical spine consisting of 7 units, and the thoracic spine consisting of 12 vertebrae, is the spinal cord.
Whereas in the lumbar spine, has 5 links, are the spinal nerve roots. Intervertebral openings are formed by scrapbooks on the arc. Through them blood vessels and nerve fibers.
Transverse processes are on the vertebrae in pairs. The arc and the body constitute the spinal canal, but apart from them, are part and ligaments.
The main is yellow and posterior longitudinal ligament. Yellow ligament connects all the arcs of the spine, and the rear body of the vertebrae. Their function is to combine all parts into one system.
Each group has its own peculiarities in external form. Because the spine is not a single straight and twisted column, respectively, and the vertebrae are some differences:
- in the neck, Flex forwards (lordosis);
- in the chest, shifted backward (kyphosis);
- in the lumbar are of the deflection forwards (lordosis);
- sacral curves backward (kyphosis).
The vertebrae represent a kind of curve, but such a location involves the correct formation of the skeleton and the locomotor activity of the segment.
In the direction from the cervical to the sacrum, the vertebrae increase in size, and below, on the contrary – decrease. Form chest parts more like a triangle, in size they are smaller than the lumbar, having an oval, and the largest form.
Totally different neck structure. On top of the body is jelly-like and concave, and transverse processes are formed as a bump. Between the two tubercles is a transverse hole. The cervical vertebrae are the most mobile, thanks to its shape and jelly-like body.
This is one of the differences which divide them into types. In the vertebral column differs 6 and 7 vertebrae of the first branch.
Sixth distinguished by the presence of tubercle, and the seventh is a long process. One of the links of the office – Atlas, has no body.
It consists of two arcs, United by bone seals on the sides. From him and begins to leave the spine. The vertebrae in this part are small, because the load on them is minimal.
The adult sacrum consists of five bone-krasivaya links. The connection forms a massive triangular bone.
Sacral vertebrae represent the Foundation, upward, and departing from it five vertebrae.
In the place where the connection of the vertebrae, has rounded the Cape, heading up. For attaching to the pelvic bones on the sides of a lug surface.
By the end of the spine the vertebrae are narrowed. The connection of the vertebrae of this part is performed by means of intervertebral discs, joints and ligaments. The sacrum and coccyx form a fused vertebrae.
The coccyx is the last segment of the spine. It consists of 3-5 vertebrae fused together. Functions of the tip is the attachment of the muscle to adjust the physical load on the pelvic region. It has a pyramid shape.
Two adjacent vertebrae are motor pigment. In humans there are 24 segments, 12 thoracic, 7 cervical and 5 lumbar. This grouping features and functions. Through each segment are veins, arteries, and spinal nerve.
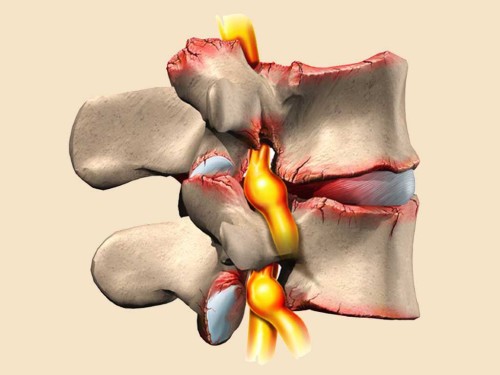
In the first three sections, between each two vertebrae is the intervertebral disc composed of fibrous ring with a gelatinous core.
Intervertebral discs
The right bond links of the spine, allow the person to move without any difficulty. Connection of vertebrae, as already mentioned, carries the intervertebral disc.
It is a fibrous cartilaginous plate, with layers of connective fibers at the periphery.
Components is the fibrous ring surrounding the plate, and purposee core, which is a jelly-like mass that regulates the amount of water that is isolated vertebrae. Trailing plates have an equally important role in the strength of the spine.
They protect the elements of the vertebrae from rubbing and possible bias. The intervertebral disc performs the function of flavour and takes all the load on yourself. And also provides the connection of the vertebrae.
In the interval between the first vertebra and the occipital bone, intervertebral disk is missing. So it is not between the first two coccygeal and sacral spine.
The compound represented by vertebrae fused elements. The size of the disks are different, depending on which division it is located.
The vertebrae are a major part component of the spine is the axis of the entire skeleton. Disorders in the back, always are the cause of the failure in the functionality of the population systems of the vertebrae. So, for example, may offset or the accretion or impairment of the function of the intervertebral discs.
In most cases, their structure and functionality depend on the person’s lifestyle. These violations can only be an adult, because all the bone of a child’s education are very different from adult bones. In the process of development, child’s spine is formed and changes shape.
So it has a special plasticity and ability to recover. The formation of the skeleton begins in utero.
Some elements undergo a process of ossification at the time of the fetus in the womb. Full completion of the process of agostinone is only 20 years because by this age, the person ceases to grow and is the final formation of the musculoskeletal apparatus.




What’s the purpose of this?
How can they do this?
How can this be done?
Hello there, You have done an excellent job. I will certainly digg it and personally suggest to my friends. I’m sure they’ll be benefited from this website.
Excellent read, I just passed this onto a friend who was doing some research on that. And he actually bought me lunch since I found it for him smile Thus let me rephrase that: Thank you for lunch!