Arthroplasty is surgery on the joints (hip, knee, shoulder and others), in which one or both of its surfaces are preserved, thereby ensuring normal motor function.
Possible complications and potential risks
In the vast majority of cases, the arthroplasty gives excellent results. But we can not exclude possible complications as with any surgical intervention. Among these complications, you may experience a negative reaction to the anesthesia applied, can form scars or open to extensive bleeding.
But the most dangerous consequence of the arthroplasty can be a infection of the joint, the probability is getting higher with every next operation. If this happens, put the prosthesis will have to extract further repair or replacement.
Types of surgical intervention
There are several varieties arthroplasty:
- Modeling resection and osteotomy of the first metatarsal bone. This group includes the operation of Schede, cheilectomy, surgery Waterman and others. This intervention is based on the removal from the head of the first metatarsal bone and cartilaginous exostosis at the medial and dorsum of the. Sometimes it is carried out in parallel with Chevron shortening osteotomy of the first metatarsal bone, which is aimed at the expansion of the joint space.
- Resection arthroplasty. This operations such as: operation Keller, Trench-Brandes, and others. In this case, resection of one of the surfaces of the joint to introduce between them a complex of tissues, which includes ligaments and fascia. This makes it possible to prevent the development of ankylosis and provide motor function.
- Bone and cartilage plastic. This could include mosaic arthroplasty, a surgery Tychinkin and others.
The progress of the operation
The decision on necessity of surgical intervention is taken only by a doctor. Its feasibility depends primarily on the intensity of pain and the degree of limitation of motion.
Suppose that the patient cannot sleep because of the constant severe pain, all the tried methods of conservative treatment proved ineffective. In this situation it makes sense to resort to surgery. In taking this decision, it is important to consider the overall health of the patient and to evaluate the ability of the body to move planned surgery, as well as his desire and the possibility of the postoperative rehabilitation course of physical therapy.
During the arthroplasty joint on one side replaced by a prosthesis of metal, and the other is made of plastic. The most common are a similar operation on the knee and hip joints in patients suffering from severe form of rheumatoid arthritis or osteoarthritis.
If you hold a hip prosthesis, in this case, use special implants, consisting of the acetabular component (Cup), a femoral component (stem), and head. Each of them is made of titanium or steel. For the manufacture of Cup prosthesis used titanium with a liner or polyethylene. The head can be made of ceramics or steel, put her on the cone-shaped neck legs.
Depending on the type of fixation in all bone and joint implants are divided into three classes:
- with cementless fixation;
- with cement fixation;
- combined.
Cementless prostheses are usually installed in these young patients, but older people choose the second or the third variant of prosthesis. There are cases when patients put artificial prostheses which are made of anti-fouling over time, the living tissue materials.
The postoperative period
For some time (usually it takes a few days) after was performed a long surgery with spinal anesthesia or under General anesthesia, which was replaced by the joint, the patient should remain in the inpatient unit of the hospital. This time is necessary for the chemotherapy drug of anticoagulant therapy.
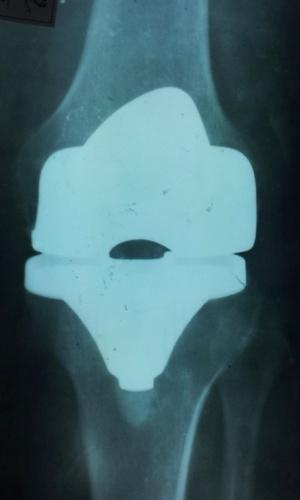
In addition, a very important part of postoperative treatment is physical therapy, lasted several months (up to six months). Subject to compliance with all regulations doctor at the end of the recovery period most patients who prior to surgery was able to walk, feeling with an intolerable pain, get rid of it completely. Many of the operated patients are able to return to normal life.
They can lead an active physical activity due to use in arthroplasty the most modern technologies. The service life of the delivered implants is around ten to fifteen years, and in many cases much more.