Arthritis is an inflammatory process of the knee joint. The disease is slow, prone to progression, and is accompanied by pain and discomfort when performing movements. It is important to notice the symptoms of arthritis to refer to specialists for treatment.
The symptoms and priznaki
Most often the disease begins to affect people from the age of 30 years. More susceptible female half of the population because arthritis is genetically transmitted. In this regard, early diagnosis is very crucial. Pathological condition occurs in both acute and chronic disease with exacerbations.
To recognize the disease by its characteristic signs of arthritis knee joint:
- a decrease in range of motion in the affected knee;
- pain, increasing during active movements;
- redness and swelling in the affected area;
- swelling and increased temperature in the affected knee joint.
Depending on what stage the disease is, symptoms vary in degree of development.
For the prevention and treatment of ARTHRITIS our constant reader uses the increasingly popular NON-surgical method of treatment is recommended by leading German and Israeli orthopedists. Thoroughly acquainted with him, we decided to offer it to your attention.
1 degree
In the initial stage of the disease patients do not experience strong, painful phenomena do not make specific complaints characteristic of arthritis.
However, there are a number of symptoms, which indirectly judge about the origin of the pathological focus:

Stiffness
- in the morning, immediately after awakening, there is some stiffness, people need a little more exercise to bring yourself back to normal;
- observed pain in the affected joint. As the pain passes quickly enough, the patients blamed this phenomenon on the fatigue. For children in the early stages of arthritis is characteristic of the refusal of mobile games where you want to run an active movement.
The first degree of arthritis is not harmless. Already in this period the joints begins to thin. Body temperature in the affected reaches 37.5 degrees Celsius.
2 degree
Second, the degree of arthritis pathology is manifested by erosions on the knee joint.
A visual estimate is not possible, because the lesion is hidden in the soft tissues. Signs of progression of the disease vividly identified in the 2nd stage:
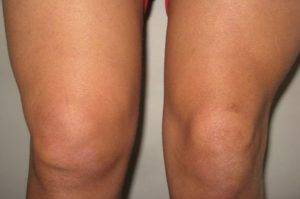
Swelling and redness in the area of kneecaps
- patient complains of swelling, redness of the knee cups;
- at objective examination revealed a crackle when bent leg;
- at night there is swelling in the knee;
- the body temperature rises to 38.5 degrees Celsius;
- begins the process of hardening cartilage, synovial manifest partition may have abscesses and capsule of the knee joint is thickened.
3 degree
The third degree of symptoms expressed. Morphologically bone tissue and joints are deformed.
As the progression of the process leads to sustained spasm of the muscular fibres, which further leads to atrophy. The symptoms intensified:
Recommend on the topic:
- the patient complains of meteosensitivity;
- body temperature can reach 39 degrees Celsius;
- patient increasing pain not able to perform basic active movement in the home;
- in the affected area is constantly observed redness and swelling;
- in the knee accumulates a pathological fluid, the cartilage is completely destroyed and in their place are formed osteophytes;
- in the result of irreversible changes in the lower limb can be lengthened and shortened.
3 the degree is an absolute indication for assigning to the patient disability.
Found effective remedy for pains and for the treatment of joints:
- natural composition,
- with no side effects
- efficiency, proven expert,
- a quick result.
In order to properly diagnose and identify the etiology of the disease, the patient is sent for consultation to the doctors. Rheumatologist needed to avoid reactive and rheumatoid arthritis. Phthisiatrician administered to exclude tuberculosis of the nature of arthritis. Trauma needs to define post-traumatic arthritis. Consultation of infectious disease necessary to exclude infectious diseases, complicated by arthritis, such as hepatitis or yersiniosis.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis begins with a General examination of the patient

Specialist when referring a patient collects detailed history of the disease. Finds out, when first appeared pain in the knee region with which they are connected. Further, it turns out, are there concomitant diseases, bad habits, and genetic predisposition.
Diagnostic measures begin with a General inspection. A clear sign of arthritis – the appearance of swelling in the affected area. The specialist offers the patient make several movements to determine the localization of the process and ways of distribution of pain.
An important technique is palpation. With its help, the doctor evaluates the external signs of the pathological process. Palpation allows you to find the rheumatic or rheumatoid nodules, to determine the condition of the joint capsule and the temperature of the affected area.
The above-mentioned methods is mandatory in cases of suspected arthritis. However, they are conducted without the use of technology that does not give the complete clinical picture.
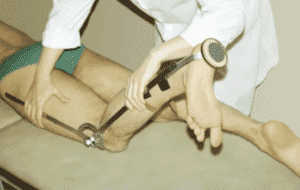
Goniometriia. The examination is carried out using a special apparatus – goniometer, which allows to evaluate the degree of mobility of the joint. In appearance it reminds a protractor. Patient the doctor performs a series of movements, the specialist records their amplitude and compares the results with the norm.
Laboratory studies. Laboratory methods are the most accurate in the diagnosis of “arthritis” and other pathological conditions.
Main ongoing studies:
- Biochemical analysis of blood. When interpreting the results pay great attention to the level of C-reactive protein, which is a parameter available in the inflammatory response in the body. In addition, pay attention to diphenylamine reaction, reflecting changes in the tissues. An important indicator is the rate of erythrocyte sedimentation. Its increase indicates inflammatory changes in the body. If you have arthritis, immunological analysis will show the contents of a large number of antinuclear antibodies. The last important parameters is the increase of urea level in the blood.
- The analysis of urine. Characteristic changes are observed in the final stages of arthritis. In the urine there is protein, which in norm should not be.

Thus, the main method of laboratory research is the biochemical analysis of blood.
Radiology. Research method it is necessary to conduct the patient to the appropriate treatment. Thanks to the x-ray and other devices it is possible to study in detail the joint and its surrounding structures.
Preliminary preparation study is not required.
- Absolute indication for prescription of x-ray examination is pain in the affected joint, swelling, and significant limitation of mobility. The study of x-rays on a special film project image. In order to protect other organs from exposure to the rays, they impose an apron of lead. The research results available in 15 minutes. It is forbidden to use x-rays in pregnant women and during lactation, since the minimum radiation is still present.
- Radiography in some respects largely inferior arthrography. Its use is advisable if the damage to the menisci and rupture of the capsule of the knee joint. When using arthrography is required in advance to enter the contrast agent into the joint cavity. The results of this method of study can be obtained in 10 minutes. Absolute contraindication is the presence of allergic reactions to iodine-containing drugs.
- CT. Allows you to accurately assess the structure of the joint and take a picture in any plane. Is held on a movable couch. The result of the study can be obtained within 2-3 minutes.
Computed tomography is an advanced method of diagnosis of all, with the exception of MRI.

MRI. This research method is also appropriate to apply at the stages of early diagnosis of arthritis. The machine’s action is based on the use of radio waves and magnetic radiation. During the test, the patient lies motionless, as it affects the quality of the picture.
MRI poses no threat to human health, therefore, has absolute and relative contraindications.
Ultrasound. This method of research is used as a diagnostic criterion, highly informative, safe, it can be used repeatedly. A special apparatus is required, allocates a frequency that interacts with the soft tissue.
The scanner captures outgoing sound waves and displays them on the monitor. If required, the can be printed. The gel, which lubricated the scanner used for the removal of air that may occur between the machine and the soft tissues. The specialist transducer over the area of the proposed localization process without causing the patient discomfort. Ultrasound is the safest method for diagnosis and allows for the application of the period of gestation and lactation.



