Amyloidosis of the liver is a chronic disease in which the liver parenchyma is deposited amyloid – specific protein-polysaccharide complex.
Often this pathology develops simultaneously with amyloidosis of other organs and tissues – liver, kidneys, adrenals, spleen, intestine and others.
The issue is that the amyloid displaces parenchyma cells of the liver, its working tissue, causing the functionality of the body deteriorating and when critical development of amyloidosis and completely lost.
Disease also called amyloid degeneration
In 1844 the Austrian pathologist Karl Rokitansky in the autopsy of dead people found in their internal organs peculiar change bodies had “greasy”, “oily” appearance.

Of these internal organs (including the liver) after 15 years, another eminent scientist, the German pathologist Rudolf Virchow allocated previously described substance which under the influence of acid and iodine, became blue. Rudolf mistakenly thought it was a starch, and a substance called “amyloid” (“amylon” in Greek means “starch”), and the pathology was called amyloidosis. The liver was one of the organs most commonly affected by amyloidosis.
It was later revealed that the substance “zasalamel” with amyloidosis of the liver, is a specific insoluble protein-polysaccharide complex with a high concentration of protein, which in normal cells is not produced.
Reasons
The immediate reason that triggered the production of amyloid, is unknown so far.
Amyloidosis of the liver is:
- primary – occurs in people with neskondensirovannyh liver;
- secondary – develops in the liver and other organs.
Most often the background for the development of secondary amyloidosis of the liver be the next group of diseases and pathological conditions:
- chronic infectious disease;
- fungal disease;
- long current inflammatory disease with purulent component;
- endocrine pathology;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- systemic pathology of the connective tissue;
- protracted chronic disease of the digestive tract;
- neoplastic lesions;
- bad habits – particularly “experienced”.
Amyloidosis of the liver often develops on the background of these pathologies with an infectious component, such as:
- syphilis – a sexually transmitted disease caused by a pale Treponema;
- malaria – a group of pathologies that are provoked by the parasites and occur after being bitten by malarial mosquitoes;
- tuberculosis – the defeat of the organism Mycobacterium tuberculosis (tubercle Bacillus);
- viral hepatitis is a viral infection of the liver.
Of fungal infections of the body most often the background for the emergence of amyloidosis of the liver becomes lumpy – the defeat of radiant fungi.
Noticed more frequent occurrence of amyloidosis of the liver on the background of such diseases with purulent component, such as:
- purulent peritonitis – purulent-inflammatory lesions of the sheets of the peritoneum;
- purulent pleurisy – focal suppurative process in the pleural layers;
- empyema of pleura – diffuse purulent pleural;
- osteomyelitis – purulent fusion of bone tissue.
Endocrine pathology contributing to the development of amyloidosis of the liver is:
- diabetes – a violation of the breakdown of carbohydrates due to the lack of insulin;
- deficiency of thyroid hormones T3 and T4;
- violation of the production of protein hormones of the islets of Langerhans of the pancreas;
- pathology of the adrenal cortex.
The last three pathology directly influences protein metabolism, therefore, play a critical role in the development of amyloidosis.
The emergence of the described pathology contribute to the following cardiovascular diseases:
- hypertension – persistent high blood pressure;
- ischemic heart disease – oxygen starvation of the myocardium provoked by the pathology of the coronary vessels (they provide blood flow to the heart);
- protracted septic endocarditis – inflammation of the endocardium (the inner lining that lines the ventricles and Atria)
and others.
Background for the development of amyloidosis of the liver most often these are systemic diseases of connective tissue:
- rheumatoid arthritis – connective tissue mainly in the small joints;
- psoriatic arthritis – joint inflammation in patients with psoriasis.

Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, often provoking the development of amyloidosis of the liver is:
- hepatitis – inflammation of the parenchyma of the liver;
- steatosis degenerative (associated with impaired nutrition of the cells) the defeat of the liver tissue;
- portal hypertension – increased pressure in the portal vein (the main vessel in the liver);
- ulcerative colitis is the occurrence of multiple ulcerations in the colonic mucosa;
- Crohn’s disease is the formation of small tubercles-granulomas in the bowel wall throughout.
It is revealed that the development of amyloidosis of the liver contribute to oncological diseases (mainly malignant) – not only the liver, but and other structures. This:
- fibroma of the liver, a connective tissue tumor;
- liver cancer – malignancy of epithelial cells;
- myeloma – a malignant bone marrow lesion;
- meningioma is a neoplasm that has developed from cells of the arachnoid of the meninges.
Bad habits, especially “experienced” and contribute to the violation of the metabolism (metabolism) in the cells – the incidence of amyloidosis of the liver in smokers and people who abuse alcohol, above.
The development of the disease
Primary amyloidosis is diagnosed less often secondary.
Primary amyloidosis of the liver develops mainly in combination with amyloid lesion of bodies such as:
- language;
- skin;
- thyroid gland;
- the liver;
- light;
- stomach;
- small intestine;
- the colon;
- spleen;
- pericardium;
- heart.
The secondary form of amyloidosis of the liver is diagnosed more often in combination with amyloidosis:
- blood vessels;
- lymph nodes;
- lymphatic vessels;
- kidneys.
Been several theories of the development of amyloidosis of the liver:
- immunological – according to this theory, due to exposure to precipitating factors to develop disorders of the immune system that contribute to the failure of tissue metabolism – as a result of such violation, and starts generation of amyloid;
- mutation – according to this theory, under the influence of various pathological factors start mutation of cells, their altered structures begin to develop a “perverse” protein-polysaccharide complex;
- the hypothesis of local cell synthesis adherents of this theory believe that the body’s cells don’t mutate and work as usual, but in parallel, begin to develop amyloid.
There are five types of renal amyloidosis:
- idiopathic – its causes and mechanisms of development are unknown;
- senile – it affects patients in the age group older than 80 years. Some clinicians see this form of amyloidosis as a sign of aging;
- family hereditary amyloidosis is of genetic nature. In the Mediterranean countries is diagnosed more often than in other regions;
- acquired – this form of amyloidosis that develops immunological disorders, which, in turn, lead to chronic infectious processes and diseases of rheumatic character, became the backdrop for the development of described pathology;
- local tumor develops in the liver in the form of lesions, the mechanism of its development is unknown yet.
Different types of amyloidosis are indicated by abbreviations:
- AA-type secondary. In amyloid a serum a-globulin;
- AL-type – idiopathic. To detect amyloid antibodies, which indicates the relationship of this type of amyloidosis, immune system;
- АTTR-type – familial, senile. In the specific amyloid protein is detected transthyretin
and several others.
Idiopathic, familial, senile and local tumor types of amyloidosis of the liver are considered as individual diseases. Secondary renal amyloidosis is not as a separate disease, as a complication of various pathologies as tuberculosis, psoriatic arthritis, and others.
The development of amyloidosis at the cellular level is as follows. First, in the blood plasma accumulate abnormal proteins. They normally are not produced, so the body reacts to them as foreign structures – in fact, such proteins are autoantigens and, therefore, provoke the production of antibodies. Is a typical interaction of antigen with antibody that leads to the deposition of particulate proteins involved in the formation of amyloid. It first accumulates in the blood, then starts to settle in the tissues of the liver. The accumulated amyloid begins to displace normal proteins in the liver, which if neglected may lead to the death of larger or smaller portion of the liver.
First, the amyloid is deposited in the center of the hepatic lobules, and then apply to their region. If you develop a hereditary type of amyloidosis, amyloid can “settle” in the vessels and stroma (tissue that plays a pivotal role – it keeps the liver parenchyma).
Depending on how delayed the amyloid, there are three tissue-type hepatic amyloidosis:
- Type I is interlobular (intralobular);
- Type II – periportally (around the portal vein);
- Type III – perivascular (mokrousovsky).
Affected by amyloidosis liver morphologically as follows:
- surface – smooth;
- color – pale brown;
- the consistency is thick, like the consistency of wax.
Important is that substitution of even a large number of normal protein structures of the liver the amyloid pathology does not lead to cirrhosis of the liver (its the germination of the connective-tissue elements).
The pathological effects of amyloid is that he intralobular type begins to put pressure on the hepatic beams, this leads to their deformation (breaking the mold) and atrophy (eating disorders).
Separate groups of hepatocytes (liver cells) is literally “walled up” the amyloid in a single monolithic unit and then destroyed.
In the second and third types described diseases of the liver slices is stored in normal form, as amyloid deposits in the blood vessels and connective tissue-based portal tracts.
Symptoms of amyloidosis of the liver
Clinical signs of amyloidosis of the liver are:
Hepatosplenomegaly – at the same time, the observed increase in liver and spleen. This is the most frequent symptom of amyloidosis of the liver. In the later stages of the disease the liver may increase to such an extent that the patient is able to palpate her yourself.
Jaundice is a staining of the skin, visible mucous membranes and sclera in a characteristic yellow color. Jaundice in liver amyloidosis rarely observed – in those patients who asked for help with the symptoms of amyloidosis of the liver, she was diagnosed in 4.7%. Previously it was thought that jaundice develops due to the fact that amyloid accumulates around the bile ducts, presses on them and degrades the emergence of bile in the 12-duodenum. However, it was found that even with a large amount of amyloid in the liver jaundice may be absent or unexpressed. It is assumed that in amyloidosis of the liver jaundice develops due to beginning liver failure.
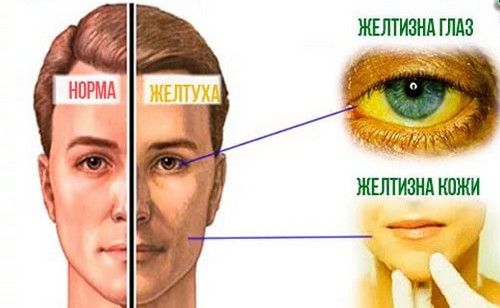
Characteristics of jaundice:
- color – a characteristic lemon color;
- intensity – unexpressed;
- on the origin – may be weakened.
Itchy skin appears when you have jaundice. Its appearance may indicate quite a marked accumulation of amyloid in the tissues of the liver in the region of the biliary tract.
Characteristics of pruritus:
- intensity – pronounced;
- on the basis of the frequency – constant, may increase night, which occurs in patients having trouble sleeping.
Bitter taste in the mouth may indicate about the compression of the biliary tract due to a significant accumulation of amyloid in the hepatic parenchyma.
Nausea may occur in a later period of development of pathology. It stems from the fact that due to the significant accumulation of amyloid in tissues and the violation of the outflow of bile on the bile pathways in the 12-duodenum violated the processes of digestion in intestine. Vomiting occurs rarely.
Discoloration of feces is observed simultaneously with the appearance of jaundice and pruritus. Its color is caused by absence of bile pigments in the feces – in case of violation of the outflow of bile in the 12-duodenum.
Pain syndrome in amyloidosis of the liver is not determinative in clinical symptoms, since it is rare. Characteristics of pain:
- localization in the right upper quadrant, sometimes in the epigastric (in the stomach);
- widespread irradiation is not observed;
- character – pressing;
- intensity – unexpressed, sometimes at the level of feelings of discomfort in the right upper quadrant;
- the occurrence – may occur in different periods of the course of amyloidosis of the liver.
Signs of violation of the General condition of the body develop in the late period and is caused by complex dysfunction of the liver. This symptoms such as:
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of amyloidosis of the liver only one of the complaints put difficult. Plays the role of the comprehensive diagnostics data of the anamnesis (medical history), the results of additional methods of examination (physical, instrumental, laboratory). The most informative is the laboratory detection of amyloid in the tissues of the liver. When enlarged liver and spleen without previous hepatic disease (diseases of liver) should be wary about amyloidosis of the liver. If the patient was previously diagnosed with amyloid lesions of the intestine, kidney and other organs, doubts about the diagnosis of amyloidosis of the liver.
Results of physical examination are as follows:
- on examination – pale skin, have a distinctive porcelain. In the presence of jaundice is determined by yellowish color of the skin, mucous membranes and sclera of the patient, as well as traces of brushes in the form of multiple small long surface scratches. May be identified this specific characteristic as macroglossia a large tongue;
- palpation (feeling) – the skin is dry to the touch. On palpation the abdomen is determined by enlargement of the liver (liver edge comes from under the costal arch), it is sealed and virtually painless. In the later stages of the disease enlargement of the liver is essential, determined, even at a superficial palpation;
- percussion (tapping) – percussion is confirmed by enlargement of the liver.

Instrumental methods of investigation used in the diagnosis of amyloidosis of the liver, the following:
- plain radiography of abdominal cavity – not a very informative method, but allows you to identify the fact of an increase the liver;
- ultrasound examination of the liver and spleen (ultrasound) – allows you to examine in more detail the structure of the liver and spleen;
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) – the same problem that the task of ultrasound, but informative above;
- liver biopsy – a puncture of the liver with a needle and sampling of fragments of its tissue for later examination under a microscope.
Laboratory methods, which are informative in the diagnosis of amyloidosis of the liver is:
- urinalysis – is defined by proteinuria (protein in urine). This analysis should be done regularly to monitor the dynamics of proteinuria;
- biochemical analysis of blood – has a value of determination of cholesterol and alkaline phosphatase (detected her increased activity). Also determine the amount of protein the blood total and fractions. To amyloidosis of the liver is characteristic of an ALPHA2-globulinemia (reduction алфа2 globulin);
- a blood test for bilirubin – the amount raised;
- IFA (immunofluorescence analysis) – this and other serological methods help to identify manifestations of immune shifts (in particular, the presence of autoantibodies);
- microscopic examination of biopsy material – amyloid is defined as inclusions in the liver tissue in the form of homogeneous (homogeneous) masses, which are colored with a special dye in pink. The most reliable method of diagnosis of amyloidosis of the liver.
Differential diagnosis of
Differential diagnosis of amyloidosis of the liver is mainly carried out with the pathologies that can lead to enlargement of the liver and spleen. This:
- cirrhosis – the replacement of liver parenchyma by connective tissue;
- steatosis – non-inflammatory degenerative (associated with malnutrition) defeat of the liver tissue;
- hepatitis – inflammation of the parenchyma of the liver;
- portal hypertension – increased pressure in the portal vein.
Complications
This files most often experience the following complications of amyloidosis of the liver:
- anasarca – edema of the soft tissues of the entire body;
- ascites – the presence of free fluid in the abdominal cavity;
- liver failure – a sharp deterioration of all liver functions (primarily detoxification);
- hepatic encephalopathy, the dementia that develops for the reason that a large amount of amyloid in the liver, it can not fully perform its detoxification role, the nitrogenous substances that are formed as a result of vital activity of the tissues, enter the brain and adversely affect it;
- hepatic coma is a late complication, which is a long-term lack of consciousness and evolving at the terminal stages of the disease.
Treatment of amyloidosis of the liver
Treatment of amyloidosis of the liver – conservative. It is based on the following assignments:
- diet. It is recommended that a fractional food 5-6 times a day small portions. Food should be rich in proteins, carbohydrates and vitamins. Excluded fatty meats, smoked fried, spicy dishes, alcohol, butter cakes;
- drugs whose action is aimed at halting the production of amyloid is hydrolysed liver, drugs aminohinolinovogo series, colchicine, corticosteroids;
- detoxification therapy – intravenously administered saline, electrolytes, glucose and so on;
- chelators – to regulate the activities of the digestive tract;
- medications to protect the liver;
- treatment of disease provocateurs – rheumatoid arthritis, tuberculosis and others.
Prevention
Specific prophylaxis of amyloidosis no. The risk can be mitigated through such recommendations as:
- prevention of liver disease, and other organs, which may trigger the development of liver amyloidosis, as if she had already developed her early detection and treatment;
- sanation of chronic infection foci;
- avoiding harmful habits;
- a healthy way of life.
Forecast
The prognosis amyloidosis of the liver different. Properly chosen treatment can stop the production of amyloid, and to support the liver. Are critical complications such as liver failure, encephalopathy and coma.




Thanks for your publication on this blog. From my very own experience, often times softening up a photograph may possibly provide the professional photographer with a bit of an artsy flare. Oftentimes however, the soft clouds isn’t what exactly you had in mind and can usually spoil an otherwise good picture, especially if you consider enlarging that.
I enjoyed this! good to read, but I am not sure where to start. Which of your posts can you recommend I read next?
Can I ask you to elaborate? Perhaps give another example? many thanks!
Thanks for your suggestions. One thing really noticed is that often banks as well as financial institutions have in mind the spending behavior of consumers and understand that the majority of people max out there their real credit cards around the breaks. They sensibly take advantage of this specific fact and start flooding the inbox as well as snail-mail box with hundreds of Zero APR card offers just after the holiday season finishes. Knowing that for anyone who is like 98 of all American public, you’ll leap at the chance to consolidate card debt and shift balances for 0 annual percentage rates credit cards.
My friends on FB would enjoy this article. Is it okay if I show it to them?
Hey there! I know this is somewhat off topic but I was wondering which blog platform are you using for this site? I’m getting sick and tired of WordPress because I’ve had problems with hackers and I’m looking at alternatives for another platform. I would be awesome if you could point me in the direction of a good platform.
Great article. It is extremely unfortunate that over the last one decade, the travel industry has already been able to to fight terrorism, SARS, tsunamis, bird flu, swine flu, along with the first ever real global downturn. Through it all the industry has really proven to be solid, resilient plus dynamic, discovering new ways to deal with difficulty. There are generally fresh troubles and opportunity to which the marketplace must all over again adapt and reply.