Alveococcosis is a parasitic disease caused by larvae of tape worms of alveoli and proceeding with the formation of the primary tumor in the liver. In uncomplicated stage alveococcosis symptoms include hives, itching, hepatomegaly, pain and heaviness in the right hypochondrium, bitter taste in the mouth, belching, nausea.
Complications of alveococcosis there may be suppuration of parasitic tumors, breakthrough of formation in the abdominal or pleural cavity, obstructive jaundice, portal hypertension, metastasis of alveoli in the brain and lungs.
To diagnose of alveococcosis used ultrasound and scintigraphy of the liver, angiography, x-rays/CT of the abdomen and thorax. Surgical treatment of alveococcosis is complemented by antiparasitic therapy.
Alveococcosis
Alveococcosis (alveolar echinococcosis or multi-camera) – cestodes, the causative agent of which is the larval stage of Alveococcus multilocularis helminth that causes a tumor-like lesion of the liver with subsequent infiltrative growth or metastasis in the lungs, brain and other organs. Alveococcosis person refers to the number of rare endemic helminth infections, the incidence of which in endemic areas is 0,01-0,08%.
Cases of alveococcosis is found in Canada, USA, Europe (Germany, Austria, France, Switzerland), Asia, Russia (Yakutia, Kamchatka, Chukotka and Western Siberia, the Volga region). A alveococcosis most infected young and middle-aged, mainly engaged in hunting.
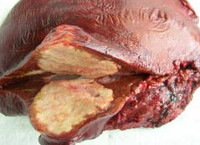
Causes of alveococcosis
For human risk is the larval stage of Alveococcus multilocularis worms, flat worms belonging to the subfamily Echinococcine. Mature forms of alveoli by building close to the Echinococcus, but differ in the number of hooks on the scolex (usually 28-32 units), absence of side branches in the uterus, location of the sexual openings in the front of the segment. The main difference between parasite lies in the structure of the Finns, which alveoli has the form of botryoidal bubbles filled with a gelatinous mass. Daughter vesicles are formed by budding and grow outward and not inward, as the Echinococcus.
Adult alveolar has a size of 1.6-4 mm, consists of a head with 4 suckers and hooks, 2-3 segments. In the last segment of the uterus is globular, containing about 400 eggs. Tape worms parasite in the intestine of the Fox, the wolf, foxes, dogs, cats, which are the main owners of alveoli. Mature eggs in the faeces of animals are released into the environment, where the fall in the body of the intermediate hosts (mice, muskrats, river beans, nutria and humans), where occurs the larval development of the parasite. The infection of human alveococcosis can happen when put into the mouth of the oncospheres of the helminth during the hunting and butchering of wild animals, removal and processing of skins, contact with Pets, consumption of wild berries and herbs contaminated with eggs of the helminth.
In the human body alionochka the larva emerges from the eggs and from the bloodstream is stored in the liver, which almost always delayed. Primary alveococcosis other organs is extremely rare. In the liver transformirovalsya the larva in a vial with a diameter of 2-4 mm, which starts to reproduce by exogenous budding. Gradually the connective tissue stroma of the liver is a dense, melkoporistaja parasitic tumor with a diameter of from 0.5 to 30 cm and more. In the context of a node alionochka has the form of porous glass (porous or fresh bread), consisting of a large number of chitinous bubbles. Similarly, malignant tumors, parasitic node is able to germinate in the surrounding tissue and organs (glands, diaphragm, pancreas, right kidney, adrenal gland, lung, etc.), lymphatic ways and blood vessels, spreading through the blood through the body and forming distant metastases, most often in the brain.
Symptoms of alveococcosis
In the development of alveococcosis allocate asymptomatic, uncomplicated and complicated stage. The nature of the flow of alveolar hydatid disease may be slowly progressive, actively progressive and malignant. Preclinical stage of alveococcosis can last for many years (5-10 years or more). At this time, patients concerned about the hives and itching. Identification of alveococcosis in this period usually occurs through an ultrasound performed for the other disease. Manifestou in the early stage symptoms of alveococcosis malespecific include hepatomegaly, heaviness and dull pain in the right hypochondrium, pressure in the epigastrium, bitter taste in the mouth, nausea. At inspection often found enlargement and asymmetry of the abdomen; palpation of the liver is defined by a dense knot with a rough bumpy surface. Patients feel weakness, poor appetite, weight loss. When alveococcosis occasional bouts of biliary colic, dyspepsia.
The most frequent complication of generalized alveolar disease is jaundice, caused by compression of the biliary tract. In the case of secondary bacterial infection may develop liver abscess, which is accompanied by increased pain in the right hypochondrium, the appearance of hectic fever, chills, heavy sweats. The breakout of parasitic cavity can develop suppurative cholangitis, peritonitis, empyema, pericarditis, and pleurotaceae bronchopneumonia fistula, aspiration pneumonia. In the case of compression of the tumor conglomerate Porta hepatic portal hypertension occurs, accompanied by varicose veins of the esophagus, esophageal and gastric bleeding, splenomegaly, ascites. In the interest of developing kidney proteinuria, hematuria, pyuria, associated infection of the urinary tract. The consequence of immunopathological processes is the formation of chronic glomerulonephritis, amyloidosis and chronic renal failure.
Metastasis of alveoli most often occurs in the brain; in this case there are focal and General cerebral symptoms (Jacksonian seizures, mono – and hemiparesis, dizziness, headaches, vomiting). Severe and transient for alveococcosis observed in patients with immunodeficiency, pregnant women, persons suffering from severe concomitant diseases. Alveolar hydatid disease often ends in death.
Diagnosis and treatment of alveococcosis
During examination of patients with suspected alveococcosis it turns out epidemiological history data (stay in endemic areas, hunting, gathering wild berries, the skins and carcasses of wild animals, professional risks, etc.). For early stages of typical positive allergic tests (eosinophilia, the casoni reaction with hydatid antigen). Specific methods of laboratory diagnosis of alveococcosis include immunological reactions (RIGA, RLA, ELISA), PCR. To identify alveolar echinococcosis of the liver, size and location of parasitic node using plain radiography of the abdomen, ultrasound and Doppler of the liver. A noninvasive alternative to arteriography and splenoportography is computed tomography. In complex situations, a scintigraphy of the liver, diagnostic laparoscopy.
In cases of suspected alveococcosis exclude other focal liver tumors, hemangioma, polycystic disease, cirrhosis, hydatid disease. For the detection of metastases is the chest x-ray, brain MRI, ultrasound of the kidneys and adrenal glands etc.
When alveococcosis liver, surgical treatment, supplemented with antiparasitic therapy. Most often the operation of choice is liver resection within healthy tissue (segmentectomy, lobectomy), but radical removal of a parasitic tumor is possible only in 15-25% of cases. At impossibility of radical resection of the node is partial resection, or husking and subsequent infiltration of chemotherapeutic drugs (trypaflavine solution, formalin) or the destruction of parasitic tissue using cryotherapy. In some cases, operation of marsupialization parasitic cavity, stenting of the bile ducts. Systemic antiparasitic therapy of alveococcosis is carried out by levamisole, mebendazole.
Forecast and prevention of alveococcosis
Slow and asymptomatic, the development of parasitic tumors leads to the fact that in most cases alveococcosis is diagnosed late, often does not allow for radical treatment. The prognosis of alveolar hydatid disease are quite serious: without treatment, 10-year survival rate does not exceed 10-20%. Death of patients comes as a result of septic complications, liver failure, profuse bleeding, germination of the tumor into nearby organs, with disorder of their functions, distant metastasis to the brain, etc.
Prevention of alveococcosis is to carry out deworming of domestic animals, veterinary supervision, safety precautions when interacting with wild animals, sanitary-educational work with the population of endemic areas. Persons at increased occupational risk of infection alveococcosis (shepherds, hunters, farm workers, etc.), are subject to regular screening.


Metastasis of alveoli most often occurs in the brain; in this case there are focal and General cerebral symptoms (Jacksonian seizures, mono – and hemiparesis, dizziness, headaches, vomiting). Severe and transient for alveococcosis observed in patients with immunodeficiency, pregnant women, persons suffering from severe concomitant diseases. Alveolar hydatid disease often ends in death.
You make some insightful arguments within this entry, but are you overlooking something crucial?
Hey this post abslutely made me think! TY-I hadn’t thought of things from your p.o.v otherwise.
Sincerely-thank you-Any chance you will clarify some things?
Hello there! I know this is kinda off topic but I was wondering if you knew where I could find a captcha plugin for my comment form? I’m using the same blog platform as yours and I’m having problems finding one? Thanks a lot!
Excuse, I can help nothing. But it is assured, that you will find the correct decision.