Hookworm disease – parasitic infestation caused by the parasite in the human intestine roundworms (hookworm or hookworms) belonging to the family Ancylostomatidae.
Hookworm disease is clinically evident papules, vesicular rash, cough, shortness of breath, loss of appetite, nausea, abdominal pain, diarrhea, iron deficiency anemia.
Diagnosis of hookworm disease is confirmed by the detection of helminth eggs in feces and duodenal contents. Treatment of hookworm disease is to conduct deworming and correction of anemia with subsequent triple control research of faeces.
Hookworm disease
The hookworm – helminthiasis (hookworm and necatoroz) caused by parasitic round worms – Ancylostoma. Hookworm and necatoroz merged into one group based on biological similarities of pathogens, their common joint of parasitism in the body, as well as the similarity of clinical and epidemiological signs of infestation.
Both helminthiasis in the early stages flowing with allergic skin lesions and respiratory tract, and the later – with dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract and the development of iron deficiency anemia. Ankilostomidoz – common parasitic diseases, which affected 25% of the world population, mainly in the regions with low level of sanitary culture. The frequency of infection ankilostomidoz second only to that of enterobiasis and ascariasis.
Reasons and ways of infection with hookworm
The causative agents of hookworm (Ancylostoma – Ancylostoma duodenale) and necatorosis (necator – Necator amencanus) belong to a single family Ancylostomatidae. They share a common morphology, development cycles and actions exerted on the host organism. Both species of worms belong to the class of roundworms (Nematoda) and character development is related to geohelminths.
The causative agents of hookworm disease have a pinkish-yellowish color and small sizes: female hookworm in the 10-13 mm in length and males 8-10 mm; necator – 9-10 mm and 5-8 mm, respectively. At the head end individuals is the oral capsule, which the parasites attach to the wall of the small intestine. In the oral suction Cup hookworm has 2 dorsal and 4 ventral cutting teeth, necator – 2 cutting chitinous plates.
The eggs of Ancylostoma have the same structure: oval in shape, smooth colorless shell, size 66х38 microns. Each egg contains from 4 to 8 blastomere. The life cycle of the causative agents of hookworm disease, begins with the contact of helminth eggs with the feces into the external environment. Larval development occurs in the soil at a temperature of 14-40° C and humidity above 80%. After two molts, after about 7-10 days the larvae of Ancylostoma become invasive.
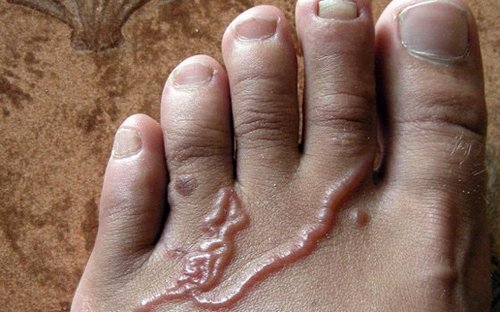
Human infection with hookworm disease may occur by two mechanisms – fecal-oral and percutaneous (percutaneous); water, food or contact ways. In the first case the larvae enter the body of the host through the mouth by drinking contamination of water, vegetables or fruit. Percutaneous route of infection involves active penetration of infective larvae through the skin during contact with contaminated soil (while walking barefoot, lying on the ground, excavation and agricultural work). Moreover, through the skin barrier, the larvae get into the blood stream, then migrate to the right parts of the heart and lungs, where Airways penetrate into the throat and swallowed again.
Once in the small intestine, after 5-6 weeks, larvae turn into adult worms capable of laying eggs. After oral infection with hookworm migration stage is missing – the larvae are immediately transferred to the small intestine. The life cycle of the hookworm is 7-8 years old, hookworms – up to 15 years. High risk groups exposed to infection with hookworm are agricultural workers, miners, gardeners, children.
The symptoms of hookworm
For hookworm disease distinguish 3 stages: invasive, migratory and intestinal. The first phase is associated with the introduction of larvae through the skin into the human body, accompanied by the clinic dermatitis or hives – rash (erythematous, papular, vezikuleznaya), local edema, burning, and itching of the skin, persist for 10-12 days.
During the second phase of hookworm disease (larval migration in the host organism) is sensitization of the organism with products of their vital activity with the development of allergic reactions. In addition, injury to capillaries of pulmonary alveoli and tissues of the respiratory tract clinically focal pneumonia, pleurisy, bronchitis, tracheitis, laryngitis. Patients with hookworm disease complain of cough, dyspnea, hoarseness, low-grade fever.
In the third (intestinal) phase of hookworm disease goes 30-60 days after infestation. This stage has a long, chronic course and is associated with parasitism of Ancylostoma in the intestine, where they are using teeth are attached to the mucous membrane, damaging it. In the place of fixation of the parasite are formed erosions and ulcers, which can be a long time to bleed, leading to the development of iron deficiency anemia. In addition, as hematophagy by way of supply, each individual of necator consumes per day is 0.03-0.05 ml of blood, hookworm – 0,16-0,34 ml, which also contributes to chronic blood loss. Intestinal phase of hookworm disease occurs with symptoms of duodenitis – a violation of appetite, taste perversion, nausea, vomiting, pain in epigastric region, diarrhea or constipation.
In the long hookworm or a massive infestation in children can experience decreased body weight, delayed physical and mental development. Adult patients can suffer from irritability, sleep disturbance, fatigue in women is often observed violation of the menstrual cycle. The development of anemia accompanied by weakness, dizziness, tachycardia, tinnitus.
Diagnosis and treatment of hookworm
In various phases of hookworm disease, the patient can seek medical help to the otolaryngologist, pulmonologist, gastroenterologist or physician. In the diagnosis of hookworm disease are taken into account clinical and epidemiological data. In the peripheral blood is iron-deficiency hypochromic anemia, increased ESR, eosinophilia, hypoalbuminemia. In the study a General analysis mokrotovarova a large number of eosinophils. In the phase of migration on the radiographs of the lungs can be detected eosinophilic inflammatory infiltrates; ECG – signs of myocardiodystrophy. Data radiography of the passage of barium indicate the hypotension of the intestine, impaired motility with signs of stagnation of feces.
Decisive for the confirmation of hookworm disease are the results of the analysis of a feces on eggs of worms or the contents of the duodenum 12, obtained by duodenal intubation. In addition, the use of serological diagnostic methods (the reaction of hemagglutination and latex agglutination). Since the eggs of Ancylostoma have the same structure, identification of helminths (hookworm and hookworms) is only possible after deworming and expulsion of faeces of adults. Hookworm disease requires a differential diagnosis with other helminth infections, and anemia of different etiology.
Causal treatment of hookworm disease carried out de-worming medications prescribed by a doctor with the infectious diseases (Parasitology). For deworming, you use the following drugs: Pyrantel, Beenie hydroxynaphthoate, levamisole, mebendazole. 3-4 weeks after antihelminthic treatment is control over the efficiency of treatment is 3-fold examination of feces at intervals of 1 month. Symptomatic and pathogenetic treatment of hookworm disease involves the administration of iron preparations, vitamin B12, folic acid, antihistamines, etc.
Forecast and prevention of hookworm disease
In most cases, with timely diagnosis and treatment of ankilostomidoz end in complete recovery. Subsequent clinical examination of patients with hookworm, are assessed annually for 4 years; after necatoroz – within 7 years. Severe complications and lethal forms of the hookworm develop in case of advanced disease.
Preventive measures consist in the observance of rules of personal hygiene – washing hands after visiting the toilet, the protection of the skin in contact with the ground, careful handling of fruit and vegetables, boiling water before drinking, etc. is Important sanitization of soils and environmental objects, presumably contaminated with larvae of Ancylostoma. High-risk groups on the incidence of hookworm disease need to undergo an annual medical examination.



Spot on with this write-up, I truly assume this web site wants way more consideration. I’ll probably be again to learn rather more, thanks for that info.