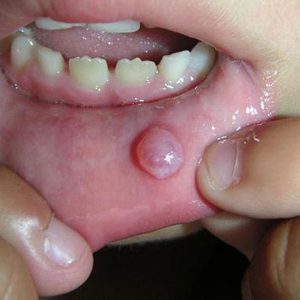
Papillomas of the oral cavity is tumors related to benign. They appear when the growth of the surface cells of stratified epithelium. Papillomas represent single or multiple soft, smooth growths on the leg.
The color of these painless tumors – whitish or pale pink.
Girls papillomas of the mouth are detected almost twice as often as boys.
Causes papillomas of the oral cavity
According to various sources, in 55-70% of cases the immediate cause of the proliferation of the epithelium becomes human papilloma virus – HPV-6 and 11. Transmission of an infectious agent is in direct contact with a carrier of the virus under the condition of neutralizing the activity of tumor suppressor genes.
Predisposing factors:
- microtrauma of the mucous membrane (to the basal layer);
- reduced synthesis of endogenous interferon;
- chronic injury is a chipped enamel or sharp edges of carious teeth.
- damage to the mucosa poorly polished basis removable orthopedic constructions.
If a child has tongue-tie, papilloma may be the result of regular injury to the frenulum of the lower front teeth.
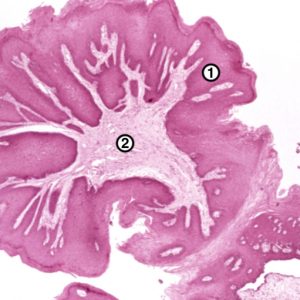
Microscopically, the papilloma of the oral cavity is a tumor consisting of highly differentiated squamous epithelium with signs of keratinization. Preserved the integrity of their own membrane, cell polarity and complexity. The broken relationship of the structural components of the epithelium and stroma. Places may be focal inflammatory infiltration.
Classification
Origin papillomas are divided into 3 main groups:
- True (caused by a fault in the mechanisms of division and growth of cellular elements). A typical localization of these growths – the retromolar area distal area of the cheeks.
- Virus. This type of papillomas develops with trauma to mucosal basal layer + direct contact with a carrier of the virus.
- Traumatic. They appear due to the influence of chemical and thermal stimuli. After the elimination of the etiological factor, the growth of such tumors is terminated.
Symptoms (appearance)
Form papilloma – always rounded, 0.2-2 cm, and the surface may be ridged, warty or fine-grained. External changes in the mucous membrane around the growth is not observed. The pain syndrome is absent. Base (leg) is both narrow and broad.
Papillomatosis (multiple papillomas) are often detected in the sky. After a random prokusyvanie the tumor begins to bleed, and later acquires a dark color due to hemorrhage into its cavity.
The skin of the patient in the projection of the papilloma – unchanged, and the mouth opening is free.
Diagnosis
Adult patients often are diagnosed solitary tumors, but in children multiple (papillomatosis).
Patients do not make complaints about the deterioration of General condition. Whitish nodules are detected during the General examination of the oral cavity. The basis for diagnosis are anamnesis and data obtained in the laboratory in the course of histological and cytological analysis of the tissue sample.
The localized growths of the epithelium is variable, but approximately every second patient papillomas are formed in the language.
In some cases, can be fixed focal inflammatory infiltration.
During microscopy revealed an increase in the number of capillaries in the connective tissue. Mitotic activity increases, i.e. the cell division is accelerated. For the detection of HPV 6 or 11 type that is used is PCR (polymerase chain reaction).
Differential diagnosis of papillomas is conducted with hyperplasia of the oral mucosa on the background of somatic diseases, as well as fibroids and warts.
The treatment of papillomas of the oral cavity
Conservative methods are ineffective. Papillomas are excised surgeon dentist within healthy tissue. If you identify a viral etiology of the disease, additionally appointed antiviral pharmacological agents and immunomodulators. Its high efficiency, in particular, proved the drug Inosine.

If time does not remove the papilloma, there is a risk of chronic trauma. As a result, on the surface of the formed nodule ulceration, which in turn may be considered as malignancy (malignancy) that already requires the consultation of an oncologist.
To cryotherapy and electrocautery is used very rarely, since the methods do not allow to obtain biological material for microscopy.
When papillomatosis it is possible to use combined techniques. The bulk of papillomas and remove the “classic” (with a scalpel), and single – cauterize.



Thanks for your practical advice on what is normally an overlooked topic. Is it okay to share this with my people?