Calcification of the mammary glands is foci of calcification, which are formed in the soft tissue of the breast. Calcification may develop on the background of a number of diseases or at a later stage, as their complications.
Medical costs of the presence of these pathological entities is more of a psychological than physiological – women are feeling in the breast solid well rounded education and interpret them as a manifestation of malignant breast pathology.
The clinical picture of the disease can be scant or absent. The choice of treatment depends on the background of some diseases or pathological conditions in the mammary gland formed “stones”.
When the mass development of calcification affect the aesthetic appearance of the breast that brings women less suffering than the diseases of the glands, accompanied by severe clinical symptoms.

General data
This pathology is not too frequent. It is often diagnosed by accident – during the examination of women by a mammologist regarding the other diseases of the mammary glands or during routine inspections. Statistics that indicate a low prevalence can be misleading – in the absence of symptoms and any complaints from the side of the breast, many women still do not understand the role and significance of preventive examinations, do not pass examination by a mammologist for years (and sometimes up to the end of life), so the calcification of the mammary glands often remain unrecognized pathology. In some cases they are found during section (autopsy).

In this article we will talk about disease in women. Similar calcification can also occur in men, but in this case they are referred to as calcification of the breast. Developing this pathology in men is extremely rare.
The disease does not threaten neither the health nor the life of a woman – however, it may be indicative of previously transferred or available at the moment and pathological processes in the mammary glands.
Described asymptomatic cases of mammary glands, when due to the detection of calcification had any medical suspicion for other pathology at the woman, followed her diagnostic testing and was diagnosed of a disease.
It should be borne in mind that 20% of all diagnosed cases of calcification breast cause of their occurrence are tumors of malignant nature.
80% of the identified calcification have a different origin – namely:
- inflammatory;
- metabolic (associated with violation of exchange processes – but not only in the breast and throughout the body);
- dishormonal;
- involutive (developing in reverse the development of breast tissue, which is observed in aging women and aging);
- associated with the formation of benign tumors.
Despite some preventive irresponsibility of certain sections of the population, the number of running mammography in the last 5 years has increased several times, hence the increasing detection of this disease. Most often, the diagnosis of calcification of the mammary glands was posed during the survey of women with oncological problems of the mammary glands, because these diseases falls most number of mammography.
Reasons
In most cases, to the occurrence of calcification of the mammary glands leads not one cause but a combination of several etiological (causal) factors. Calcification in the soft tissues of the mammary glands quickly not grow – causal factors must act on mammary tissue for some time.
Most often it is the combined effect of these pathological factors as:
- inflammation;
- neoplasia (neoplasm);
- necrotic transformation of tissues;
- the high content of calcium.
Some clinicians believe that the deposition of calcium salts in the tissues of the mammary glands is not only the result (and value) their pathological condition, but a manifestation of the protective properties of the organism – a kind of fence damaged tissue from the healthy.
The most common causes that lead to the formation of calcification are:
- lactose – stagnation of milk in the lactation period (time period following childbirth during which the breast produces mother’s milk);
- diseases and pathological conditions of the mammary glands;
- involutive processes in them;
- hypercalcemia.
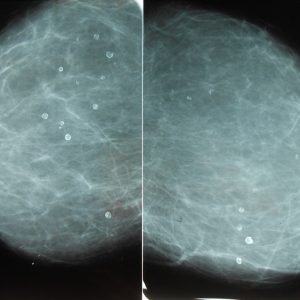
Lactose is one of the most common nonneoplastic causes of calcification of the breast. Normal in 100 g of breast milk contains 32 mg of calcium, and the pH (measure of acidity) is between 6.8 to 7.4 – this means that mother’s milk is an alkaline environment. If there is lactose, almost immediately begin to develop the process of lactic fermentation, which lead to a local acidosis – local oxidation of milk. This acidosis, in turn, leads to deposition in the tissues of calcium salts, which, accumulating in the form of conglomerates, form the centers of calcification.
Diseases of the mammary glands – the largest group of causes of calcification of the breast. In this case, all of them have in common is that in the soft tissues glands changes the metabolism (metabolism at the tissue level) environment becomes acidic, which leads to precipitation of calcium salts.
Most often it is such pathologies as:
- mastitis – an inflammatory breast lesion;
- mastitis is a violation of the structure of its tissues, which occurs due to hormonal imbalance;
- malignant neoplasms. Primarily, this is breast cancer is a malignant tumor that is formed from epithelial cells. In addition to the enhanced deposition of calcium salts, the formation of calcification of the breast if their cancer contributes to lose a sign of cancer as symptomatic hypercalcemia – increased calcium in the blood.
Not every involution of the mammary glands promotes the formation of calcification. Normal a gradual withering of the tissues of the glands passes without changes in these salt exchange. The importance of the so-called fibrocystic for involutive processes in the breast tissue when they form sacs of fluid inside.
Can develop two processes:
- in the walls of the cavities deposited calcium salts, which form foci of calcification;
- the contents of the cavities drops insoluble precipitate, which is based on calcium salts.
The high content of calcium in the blood (hypercalcemia) is fraught with the deposition of its salts in the tissues. Notice the following: in women with higher content of calcium in the blood calcification are not formed, in other women they can be formed insignificant increase his level. This confirms the hypothesis that the formation of calcification of the mammary glands in most cases depends not on one but several factors.
The content of calcium in the blood can rise in such pathological conditions as:
- endocrine diseases;
- pathology of the metabolism;
- some malignant tumors (particularly, cancer);
- uncontrolled intake of vitamins A and D;
- the abuse of drugs calcium.
Of all endocrine diseases background of the milking of the occurrence of calcification of the mammary glands often become:
- hyperparathyroidism – increased secretion of hormones of the parathyroid glands. This condition most often develops when hyperplasia (non-neoplastic growth of tissue) data glands or in the tumor (even limited) processes in them;
- hyperthyroidism – increased production of thyroid hormones.
The development of the pathology
Deposition of calcification in the breast tissue based on the fact that calcium salts are capable of deposition in terms of acidification of the tissues.
But it’s not a single link of the pathological process. The formation of calcification contribute to:
- the metabolism of carbohydrates and lipids;
- the depletion of the systems that do not allow tissues to zakislate – it develops in inflammatory processes.
Thus in the pathological focus occurs following violations:
- accumulate a lot of acids – primarily lactic, pyruvic, and keto;
- increases osmotic (interstitial) pressure.
As a result, this area retained fluid, which here rushes out of the cells and from the vascular bed. If the pathological focus the amount of calcium at the same time increased, the excess precipitates in the form of salts, of which then formed larger homes – calcification. They can be of different shapes and sizes.
For convenience, the calcification klassificeret according to their different characteristics. Most often it is the criteria:
- the number of outbreaks;
- the tissue distribution;
- origin;
- dimensions;
- form.
Basically calcification deposited in the form of multiple foci, rather than isolated, and are distributed in tissues of the breast more or less evenly. In most of the cases affects both Breasts.
Depending on the volume of the affected breast tissue calcification are:
- segmental – their identify in one lobe of the gland;
- regional – they capture the milky share.
- total – in this case in the pathological process of being drawn into the whole mammary gland, it is like a “Packed” foci of calcification. Total defeat occurs less frequently than lesions of the lobules and lobes of the breast.
Localization (location) calcifications of the breast are:
- ductal – formed in walls of ducts;
- lobular – formed in the glandular lobules;
- stromal are formed in the stroma of the mammary glands is its peculiar connective-tissue basis on which “fixed” the glandular tissue.
Ductal calcification in the majority of cases are formed in such diseases and pathological conditions, such as


Lobular calcifications are mostly diagnosed with such conditions as:
- fibrocystic mastopathy diffuse (widespread) changes in the mammary glands in the form of a proliferation of connective tissue and formation of cysts that are formed due to hormonal imbalance;
- adenos – a kind of mastopathy with a predominance of proliferation of glandular cells;
- calcification of the walls of the cysts that may develop during the pathological involution of the mammary glands.
Stromal calcifications are often formed under such pathological conditions, such as:
- fibroadenoma – a benign breast tumor formed of glandular and connective tissue;
- cyst;
- lipoma – a benign tumor of adipose tissue.
The shape and size of the calcification depends on the pathology that provoked their formation and location:
- ductal calcification are worm-like, linear (or needle), intermittent (spot);
- lobular have a Crescent shape, bowls or fragments of eggshells;
- stromal similar to cereals, popcorn, oval, and can also be formless.
The dimensions are distinguished:
- the microcalcifications, they are mostly formed in malignant tumors;
- microcalcite – formed in all other pathological processes causing their formation.
Symptoms of calcification of the breast
Quite often deposits of calcium salts in the tissues of the breast any symptoms appear and are detected by accident.
Can only manifest symptoms of the disease, against which there was calcification:
- pain;
- discomfort;
- discharge from the nipple;
- the presence of the seals
and so on.
The patient herself may feel at such foci of calcification (this is a dense painless formation) – usually happen if they have the following characteristics:
- size: large (greater than 1 cm in diameter);
- the location is close to the surface of the skin.
However, such calcifications are fairly rare.
Diagnosis
As the complaint of the patients in most cases do not exist, the diagnosis of calcification of the mammary glands put on the basis of history (revealed any disease, which are formed such formation), the results of additional methods of examination (physical, laboratory and instrumental).
When physical examination is important are the results obtained:
- during the inspection – the calcification is not visualized, but it is possible to identify changes in the breast that indicate the pathologies, against which arose the described pathology;
- palpation – assess location, size, shape, consistency of the calcification, the presence or absence of tenderness of breast tissue.
For diagnosis of calcification of the mammary glands involves the following instrumental methods of investigation:
- mammography – comprehensive breast examination. It includes the different methods – radiographic, ultrasonic, magnetic resonance and optical mammography, comosites;
- scintigraphy of the breast – the patient is administered intravenous pharmacological agents with radioisotopes, which at CT create a color image. It determines the condition of the tissues of the breast;
- ductography – radiography of the ducts of the mammary glands with the preliminary introduction of the contrast agent;
- biopsy – sampling of fragments of suspect tissue with a subsequent study in the laboratory under a microscope.
Laboratory methods used in diagnosis of the disease described it:
- cytological examination of biopsy material – it is made with the purpose of differential diagnosis of calcification and malignant tumors;
- immunohistochemistry – detection of specific antigens, which are characteristic of malignant tumors. The method is carried out for the differential diagnosis of calcification with malignant tumors;
- determination of tumor markers are specific compounds that appear in the formation of malignant tumors;
- the definition of total and ionized calcium;
- determining the amount of certain hormones – estrogen, follicle-stimulating (FSH), luteotrophic (LH).
In doubtful cases may require consultation of an oncologist, endocrinologist and other related professionals.
Differential diagnosis of
In most cases, diagnosis is not difficult, calzinoz mammary glands are recognized without any diagnostic difficulties. Sometimes because of the similarity of results of some instrumental methods of examination, it will be necessary to carry out differential diagnostics of this disease with fibrocystic mastopathy.
Complications
Calcification of the mammary glands are not a threat to the health or life of the woman. The possibility of complications arises if you plan the birth of a child and breastfed. In such cases, perhaps the development of complications such as:
- lactose;
- postpartum mastitis.
At the very impressionable women the detection in mammary gland seals may develop kantserofobiey – fear of death from cancer.

Treatment of calcification of the mammary glands, diet
Treatment of calcification of the mammary glands depends on the background of diseases and pathological conditions they appeared.
If there are clinical symptoms and signs of progression, assignments are limited only by the recommendation to consult with mammologist, even if the calcification is large in size.
If such education is combined with benign breast tumors, conducted a comprehensive conservative treatment.
It is based on the following assignments:
- correction of diet. You should limit or eliminate from the diet foods that contain large amounts of calcium is milk, dairy products, some species of sea fish (so, a lot of calcium in sardines), nuts, almonds, sesame seeds, beans;
- hormonal preparations – the choice depends on the results of the research of a hormonal background;
- phytoestrogen – appointed, if a woman consciously refuses hormonal therapy;
- nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) – are assigned when signs of inflammatory reactions.
Surgical removal of the calcification is not practiced. The reasons are as follows:
- low performance;
- the technical complexity of such an operation;
- a high degree of invasiveness – order to remove all obyzvestvleniya pockets, will have to do a lot of autopsy tissue.
If calcification of the breast formed on the background of malignant tumors, the appointments shall be made by the oncologist-mammolog – they depend on the specific type of pathology. Surgical treatment can also be assigned. As sparing surgery are not effective due to the spread of calcification throughout the breast, mastectomy is recommended for full removal of the gland. In the postoperative period according to the testimony used hormone-, chemo – and/or radiotherapy.
Prevention
Preventive measures are very diverse, as calcification of the breast can occur due to many diseases and pathological conditions.

The main ones are the following recommendations:
- compliance with the rules of breastfeeding;
- if the patient takes drugs to calcium and vitamin D – an exception to a long stay in the sun, if there is such a need – the use of sunscreen;
- the rejection of the Solarium;
- the prevention of pathologies that can lead to the formation of the described pathology, and if they have any – their timely diagnosis and adequate treatment;
- adherence to a healthy lifestyle – namely the regime of work, rest, sleep, nutrition, and sexual intercourse;
- the rejection of bad habits.
Forecast
The prognosis depends on underlying disease that caused the appearance of calcification of the breast. With regard to the effects purely of calcification – the prognosis is favorable.
To prevent psychological discomfort women and its consequences in the form of emotional reactions, the doctor should explain to the patient that the calcification of the mammary glands are not a critical condition and in the presence of foci of calcification in the breast, the woman is not at risk for health and life.




80% of the identified calcification have a different origin – namely:
Would you be interested in exchanging links?
This is super informative! I’m glad I found your post because it’s an improvement on similar blogs I’ve seen from most other bloggers about this subject. Can I ask you to elaborate? Maybe give another example? Thanks 🙂
hey there and thank you in your information – I’ve certainly picked up something new from proper here. I did on the other hand expertise a few technical issues the use of this site, since I experienced to reload the site lots of times prior to I may just get it to load correctly. I had been puzzling over in case your web hosting is OK?
I was looking at some of your articles on this site and I believe this internet site is really instructive! Keep on posting .