The Gardner syndrome is a hereditary disease in which develop polyposis of the colon and benign tumors of bone and soft tissue. In this pathology of disorders of the colon can be quite a long time to manifest, and patients diagnose only the visible tumor, unaware of the presence of colonic polyposis.
The Gardner’s syndrome were studied and described relatively recently – in the middle of the 20th century.
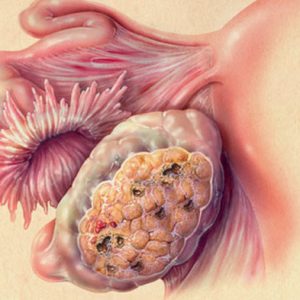
Polyps most often affects the direct and sigmoid colon, but in General they can grow in all departments of the colon.
Reasons
The Gardner syndrome is a congenital, genetically determined disease. Its main manifestation is a diffuse growth of polyps on the inner surface of the colon, which is combined with the appearance of benign tumors of skeleton and soft tissues:
- of osteomas and bone tumors;
- fibroids – tumors growing from connective tissue;
- neurofibroma – tumor that has developed from the sheath of nerve structures.
- epithelial cyst – cavitary mass with the wall of the epidermis
and some other tumors.

Pathology develops in an autosomal dominant – this means that of the two genes responsible for the development of fabrics, enough mutations, one of them that the violation is manifested in the form of congenital abnormalities.
From a practical point of view in this type of transmission is important is the following:
- the Gardner syndrome is passed down from generation to generation, and in each of them there are cases of birth of children with this pathology:
- the risk that the patient will be born a child with the described pathology, is 50%. In practice, this often looks as follows: healthy child will be born, younger brother or sister who will have a disease, or Vice versa;
- if the parents were not the syndrome identified by their appearance, it means that they will not transmit the disease by inheritance to their children;
- men and women are affected with equal frequency.
The development of the disease
In the classic version of the Gardner syndrome manifests as a triad of three diseases, developing at the same time. This:
- diffuse (widespread) polyposis parts of large intestine – mostly the lower, or distal (i.e., more close to the anus);
- osteoma of the tubular and flat bones;
- various benign tumors of soft tissues.
Morphological manifestation of Gardner’s syndrome is highly variable: some patients show only a few polyps in the colon and many benign tumors in bone or soft tissues, while the entire colon may be in the literal sense is dotted with prepoznati outgrowths and soft tissues hard to diagnose 1-2 inconspicuous tumors who do not progress and remain in the same state.
Also the variability of Gardner syndrome may manifest itself in the fact that in some cases, these patients in addition to colonic polyposis, tumors of bone and soft tissue can be detected polyphonie expansion:
- stomach;
- 12 duodenal ulcer;
- jejunum.
Polyps of the colon when Gardner syndrome can develop slowly, causing a long time clinically do not manifest themselves, therefore are often accidental findings during the diagnostic examination.
Osteomas in the development of Gardner’s syndrome is almost with the same frequency strike dice:
- flat are the bones of the cranial vault (forming the upper wall of the receptacle for the brain), pelvic bones, sternum, scapula, ribs;
- tubular is the femoral, tibial and fibular, humerus, ulna, radius, metacarpal and metatarsal bones, phalanges.
In most cases, after the appearance and increase in size of the osteoma, resulting in the Gardner syndrome, no longer continue to grow, however, they do not malignities.
The varieties of tumors that affect soft tissue in Gardner’s syndrome, more.
Often with Gardner’s syndrome develop such soft tissue tumors as:
- lipoma develop from fat tissue;
- dermatofibroma is formed from connective tissue and epithelial cells of the skin;
- neurofibromas – are formed from the membranes of the nerve endings;
- epithelial cysts are formed from the epidermis, which is the surface layer of the skin (most often of the hair follicles).
Less likely to be diagnosed:
- atheroma – cysts of the sebaceous glands, resulting in the blockage of their duct and, as a consequence, violations of the outflow of them secret;
- leiomyoma – benign tumor from smooth muscle elements.
All of these soft tissue tumors during the development of Gardner’s syndrome, and bone, characterized by benign growth, their malignant degeneration is not observed.
Diagnosis and treatment of this disease requires close attention: the risk of malignant transformation of polyps of the colon and formation of colorectal cancer in these patients is about 95%.
Treatment of patients with this pathology requires a comprehensive approach – they are engaged in the gastroenterologists, proctology, abdominal surgeons, oncologists, traumatologists-orthopedists, dentists and oral surgeons.
Symptoms of Gardner syndrome
Since morphologically the Gardner syndrome is highly variable (i.e., is manifested in different variants and combinations of colon polyps and tumors of bones and soft tissues), this means that the clinical picture of this disease, which consists of intestinal and extraintestinal manifestations, is also able to greatly vary.

In most cases the first clinical signs of Gardner syndrome occur in children older than 10 years. Often the first reason for going to the doctor is the appearance of benign tumors of bone structures and soft tissues. They grow slowly, so it is often about them first go to the doctor in adolescence, at least – the youth. Although in some cases may be a late start, and the first tumor formed above the age of 20 years.
Intestinal symptoms
For Gardner’s syndrome on the part of the large intestine there are three stages of his defeat:
- the first is easy;
- the second is moderate;
- third – heavy.
At the first stage of the Gardner syndrome are asymptomatic, as polyps, and they grow slowly. Sometimes the clinical picture is still present. However, she manifestoes mild discomfort in the stomach – but in General the clinic is expressed rather weakly, so does not attract attention of patients.
Symptoms, which appears on the second stage of development of described pathology is:
- abdominal discomfort;
- diarrhoeal phenomenon;
- changes in the feces.
Dyspeptic disorders are:
- flatulence (violation of flatus and bloating);
- recurrent violation of the chair in the form of constipation or diarrhea, and alternating constipation and diarrhea;
- the rumbling in the stomach – it is related to hyperperistaltic (increased intestinal activity).
Changes in the stool manifestirutaya in the form of constantly emerging contaminants – such as:
- blood;
- goo.
Pus in the stool are rare – only in the case of activation of pathogenic microflora and the emergence of superficial inflammatory lesions of the bowel wall.
In the third stage, patients with Gardner syndrome there is a pronounced clinical picture of the part of the large intestine:
- abdominal pain;
- flatulence (delayed flatus and bloating);
- pathological impurities in the stool;
- quite distinct violations of the General condition of the body.
Characteristics of pain:
- localization – in the area of education polyps;
- distribution mainly around the abdomen;
- by nature nouse-pressing;
- the intensity is expressed by meddling, with a significant progression of disease is unbearable;
- the appearance – because the polyps are often characterized by slow but persistent growth, pain syndrome is manifested first in the form of discomfort, then periodically appearing pain, which over time grow at the peak of the disease become regular and then permanent.
Flatulence develops from the fact that:
- long polyps when driving irritate the inner surface of the bowel wall, provoking failures in its peristaltic movements;
- the number of polyps may reach a critical level, they are on the large part of the inner surface of the colonic wall, causing the can not normally be reduced.
The number of pathological impurities in the form of mucus and blood in feces in comparison with the second stage of Gardner’s syndrome increases significantly.
Violations of the General state of the organism manifested by such signs as:
- the growing deterioration of appetite;
- slow but progressive weight loss;
- fatigue, which the patient is unable to overcome the usual amount of work in which problems had arisen;
- emotional lability – periods of bad mood are replaced by a manifestation of good mood, the patient may get upset over nothing and enjoy the little things of life;
- signs of anemia that develops because of repetitive bleeding from the tissues of polyps. It’s pale skin and visible mucous membranes, of almost constant weakness, drowsiness, fatigue, dizziness, occasional tinnitus, flashing “flies” before the eyes, tingling in the soft tissues of the upper and lower extremities, with the progression of anemia – shortness of breath, palpitations.
Tumor symptoms
Clinical symptoms at onset of tumors of bone and soft tissue depends on whether they impede the functions of the organs, which have arisen, or of neighboring organs.
In most cases of benign soft tissue tumors develop slowly, therefore physiological inconveniences does not cause.

The exceptions are the following cases:
- when joining the infectious agent the contents of a sebaceous cysts may suppurate;
- tumors of the soft tissues of the face lead to cosmetic defects;
- neurofibromas when it reaches a certain size can press on the nerve trunks, causing the development of neurological symptoms, often from the peripheral nerves. This may develop the feeling of “running ants” on the skin, and the more serious manifestations of paresthesias (particularly long expressed feelings of numbness of soft tissues).
Significant is the incidence of osteomas of facial bones – often it is accompanied by:
- his disfigurement;
- the misalignment of teeth;
- with further progression of the disease – their loss.
Diagnosis of Gardner syndrome
The presence of Gardner’s syndrome in a patient can be suspected:
- identified the triad – availability polyponic outgrowths of the colon, benign tumors of bone and soft tissues;
- on the basis of family history (of disease) – in particular, in the presence of the above described symptoms close relatives of the patient.
To detect polyposis of the colon and benign tumors need to attract additional diagnostic methods – physical, instrumental, laboratory.
Data of physical examination are as follows:
- when examination revealed the presence of multiple tumors that occur that deform soft tissue. Can visually determine osteomas that are close to the skin (tumors of the bones of the skull and extremities) and the superficial sebaceous cysts, leiomyomas, and so on. In the presence of osteomas of the facial skull often develops its deformation;
- palpation (feeling) tissues of the limbs, skull and torso – detected neoplasms of bones and more deeply located soft tissues. The tumor is small, their detection is difficult and requires careful probing of large volumes of soft tissues;
- on palpation the abdomen marked tenderness in the area of developing polyps;
- percussion (tapping) of the abdomen in case of bloating over the intestine is determined by the ringing sound, like knocking on empty containers;
- auscultation of the abdomen (listening with a stethoscope) – in the flatulence there is a weakening of peristaltic noise;
- when digital examination of the rectum – in the mucosa of the rectum can be detected by multiple sensing nodes.

Instrumental methods of investigation used in the diagnosis of Gardner’s syndrome is:
- review fluoroscopy and -graphy of the abdominal cavity – the study reveals distended bowel loops, areas of his spastic constriction, impaired motor skills and the presence of polyps. In some cases, determine the incidence of polyps of the individual sections of the large intestine, which alternate with its healthy portions;
- sigmoidoscopy – a sigmoidoscopy (a variety of endoscope) introduced into the cavity of the intestine, study the mucous membrane of rectum and sigmoid colon – it detects polyphonie growths, evaluate their number, size and other characteristics;
- colonoscopy – allows you to see the inside of a larger portion of the colon than sigmoidoscopy, is performed using the colonoscope – a long flexible probe with built-in lighting. Colonoscopy, and sigmoidoscopy reveals polyps of almost any size – even with a diameter of 1-2 mm;
- barium enema and –graphy – the colon is injected contrast agent, perform radiographic inspection on the screen and make x-ray images. Polyps identify because they stand out contrast. If the size polyponic outgrowths is less than 1 cm, then the information content of the method is reduced to solve this problem, attracting other diagnostic methods;
- radiography of the skull, upper and lower extremities enables to detect osteomas and solid tumors of the soft tissues;
- ultrasonography (USG) – to detect tumors of bone and soft tissues, to assess their size, contours, density;
- computed tomography (CT) – computer sections it is possible to obtain more accurate information about the characteristics of tumors of bone and soft tissues;
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) – its goals are the same as when performing a CT scan;
- biopsy – perform sampling of fragments of polyps and tumors for future study under the microscope. Biopsy of colon polyps carried out at the endoscopic methods of investigation.
Of laboratory methods of examination used in the diagnosis of Gardner’s syndrome, are most often used:
- General analysis of blood – with the development of intestinal bleeding is determined by the decrease in the number of erythrocytes and hemoglobin;
- microscopic examination of the biopsy confirms the diagnosis of polyps and benign tumors.
Differential diagnosis of
Differential (distinctive) diagnosis of Gardner’s syndrome is carried out with such diseases and pathological conditions, such as:
- the individual polyps of the large intestine;
- family polyposis – hereditary education 100 or more polyps in the colon;
- colorectal cancer;
- isolated benign tumors of bone and soft tissue – fibroids, fibroma, myofibrosis, lipomas, sebaceous cysts and so on;
- malignant tumors of bone and soft tissue – miosarkomy, fibromyalgia, skin cancer and so on.
Complications of Gardner syndrome

Often arise such complications of Gardner syndrome:
- malignant degeneration of polyps of the large intestine;
- perforation of the colonic wall associated with necrosis of the base of a polyp has undergone malignant transformation, and the subsequent release of intestinal contents into the pelvic cavity and the abdominal cavity;
- pelvioperitonit – inflammation of the sheets of peritoneum, which cover the wall of the small pelvis from the inside and envelop the pelvic organs. Develops as a consequence of the perforation of the colonic wall and the release of intestinal contents through the defect;
- peritonitis – inflammation of the sheets of the peritoneum lining the abdomen and covering the abdominal organs. Develops for the same reason that pelvioperitonit;
- intestinal bleeding – formed during the destruction of the walls of blood vessels located in the tissues of the polyp;
- intestinal obstruction is formed by the growth of polyps and their overlap of the lumen of the large intestine;
- suppuration atheroma.
Treatment of Gardner syndrome
Treatment of polyposis of the large intestine that occurs when Gardner syndrome, only operational, since the probability of regeneration of polyps in colorectal cancer is extremely high. The operation is performed:
- when a small number of polyps – endoscopic approach, with removed every polypoid growth individually;
- with a significant proliferation of polyps – an open method, in doing so, a resection (removal) of the part of the large intestine, which has grown polyps. In the case of extensive polyposis perform a total colectomy – complete removal of the colon.
To prevent malignant transformation of colon polyps formed in the Gardner syndrome, surgery is recommended to be in fact early detection of polyps at the age of 20-25 years. But it’s a crippling operation, so often patients refuse its execution – in this case, close monitoring of the growth of polyps, in particular, performing a colonoscopy with regularity every 6-8 months.
Tumors of bone and soft tissues in Gardner’s syndrome to malignant transformation are not inclined, therefore, their removal is carried out in case of aesthetic defect or functional disturbances.
Prevention
Specific prophylaxis of Gardner’s syndrome does not exist. The only 100 percent method, which is not the method of choice for ethical reasons, a failure to become pregnant and to give birth in the case of high probability of his Gardner’s syndrome. In any case, future parents, who have relatives with the described disease, when planning pregnancy should seek medical genetic counseling.
Prevention of malignant transformation of colon polyps is their early detection and removal.
Forecast
The prognosis of the syndrome Gardner’s controversial – primarily because of the high probability of malignant transformation of colon polyps. The deterioration of the forecast is possible with the development of complications in the first place:
Benign tumors of bone and soft tissues in most clinical cases to some severe discomfort does not lead. Complications that can develop due to the growth of these tumors, fairly well cropped. So, when festering atheroma carried out her autopsy, when the pressure of the soft tissue tumors on the nervous structure is removed, allowing neurological symptoms disappears.



I honor the logic in this article, however I would like to see extra insight from you at some point.
I find this totally interesting. Would it be ok to pose a question?