Trophoblastic disease (TB) is a disease that is always associated with pregnancy and due to proliferative neoplasia of the trophoblast (chorionic plate of the placenta).
In a group of diseases United by the term “trophoblastic disease” includes benign and malignant tumors: cystic skid (can be invasive), choriocarcinoma, trophoblastic teratoma and trophoblastic tumor of placental bed.
This pathology can develop during pregnancy, including ectopic, and after its completion.
Epidemiology
Trophoblastic disease is a rare gynecologic pathology and is 1 – 1.5% of all malignant tumors of female genital sphere. According to statistics, per 1000 births to 1 case of hydatidiform mole, and 100 thousand of all pregnancies ends in 2 cases of horionkartsinoma.
Molar pregnancy occurs more often in women 20 to 24 years. Invasive form of hydatidiform mole most often develops at the age of 40 – 49 years, and horionkartsinoma is diagnosed in 25 – 30 year old women.
The incidence of TB in different countries varies. In the United States in 2000 pregnancies account for only 1 case of this disease in Japan per 1,000 pregnancies, 2 cases, and in the Latin American and South-East countries 100 – 200 births and abortions have 1 case of trophoblastic disease.

Range and indicators of frequency of different forms of TB. Complete molar pregnancy was 72.2% of all TB cases, partial molar pregnancy – 5%, choriocarcinoma accounted for 17.5%, the share of other forms – 5%.
Causes and risk factors
All forms of TB cancers are considered as a single etiopatogenetice process. A distinctive feature of trophoblastic tumors is that the composition of the formations includes the cells of the maternal, paternal and genetic nature.
Trophoblast cells destroy the wall of blood vessels of the uterus, what is required to create messages of fetal blood with the mother’s blood. Therefore, cells trophoblastic tumors are quickly penetrating into the circulatory system of the woman and spread throughout the body, forming metastases in the near and distant organs (vagina, lungs, liver). A tendency to early metastasis and disintegration is characteristic of trophoblastic tumors.
Prerequisites pathology are:
- changes of the epithelium of the villi, caused by the proliferation of trophoblast cells and dystrophic processes in hormonally villi;
- changes the mother’s body, which consists in the development of decidual endometritis, which leads to secondary transformations of the villi;
- viral degeneration of the trophoblast (a molar pregnancy is diagnosed most often during the flu epidemic);
- the power shortage with the shortage of protein in food contributes to mutations in genes and chromosomes of a fertilized egg;
- high activity of hyaluronidase, which destroys the walls of blood vessels and promotes metastasis of atypical cells;
- immunologic factors – the fruit of the parent body is seen as foreign, which leads to the formation of antibodies against it.
The risk factors for TB include:
- age (women over 40 the likelihood of pathology increases 5 times);
- spontaneous abortions;
- medical abortion;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- consanguinity in marriages;
- childbirth;
- the lack of dietary retinol and fats of animal origin.
Classification
According to the International classification anabaena allocate the following histopathological forms of trophoblastic entities:
- molar pregnancy (PZ), which is divided into: full – pathological changes cover all chorionic villi and partial – regeneration comes only in part hormonally villi.
- invasive or destruirujushchego skid – education bubbles penetrate in the thickness of the uterine wall and spread throughout the body;
- choriocarcinoma (horionepitelioma) – usually occurs from cells of hydatidiform mole, in rare cases, is formed from the epithelium of the trophoblast, which remained after the completion of the pregnancy (abortion, childbirth);
- the combination of horionkartsinoma with teratoma or embryonal cancer;
- teratoma trophoblastic;
- trophoblastic tumor placental site.
Trophoblastic tumors can be:
- benign (molar pregnancy);
- cancer (all other forms): nemetstaticescoy education, metastatic tumor with a low or high degree of risk.
Classification of the stages of development of TB (international classification FIGO):
- Stage 1 – trophoblastic tumor is in the uterus, no metastasis;
- Stage 2 – the formation of metastases in the pelvis, vagina, and appendages;
- Stage 3 – the formation of metastases in the lungs;
- Stage 4 – the emergence of metastases in distant organs (digestive tract, liver, brain, kidney, spleen).
Clinical manifestations
TB begins to develop after a latent period which is the period of time from the date of completion of last pregnancy before the beginning of the formation of the trophoblastic education. The only exception is a simple molar pregnancy, which develops in the period of gestation.
Latent period about six months destruirujushchego characteristic of hydatidiform mole. When horionkartsinoma the latent period may be extended to 9 years, that is, TB can occur in women of perimenopausal age (menopause, premenopausal and menopause).
Simple molar pregnancy pregnancy
A characteristic symptom of this form of TB is the emergence of bleeding from the genital tract, sometimes with bubbling (modified chorionic villi) after 2 – 3 months of absence of menstruation.
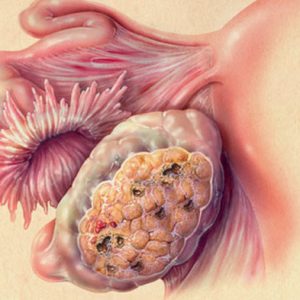
Also for simple PZ typical discrepancy between the size of the uterus to the term of delay of menstruation (uterus much more), severe early toxicity, early development of preeclampsia (18 weeks): arterial hypertension, preeclampsia. Uterine bleeding is preceded by the appearance of cramping pain in the abdomen. Conducting a pelvic examination allows to determine the uterus fugolastic consistency, the dimensions of which exceed the estimated gestational age and considerable size decalomainia cysts in the ovaries (40% patients).
Invasive molar pregnancy
This form of TB is characterized by infiltrative growth (by germination in the thickness of the uterus), high probability of conversion to horionepitelioma and 30 – 60% of cases with metastasis to the vulva, vagina, and lungs. Pathognomonic a symptom of destruirujushchego drift is uterine bleeding. The growth of education of the uterine wall collapses more, which leads to serious complication – perforation of the uterus and intra-abdominal bleeding. The second common symptom of invasive PZ are pain in the lumbar region and the abdomen, the intensity of which increases rapidly. Increased pain indicates either about the threat of uterine rupture or break occurred.
Horionepitelioma
Horionepitelioma often develops after removal of the PP. This tumor is accompanied by a triad of symptoms: subinwalucia of the uterus, persistent blood discharge caused by disintegration of the tumor and stabilization of high levels of HCG or its increase. The tumor is localized most often in the fallopian or uterine bottom in the corners.
A formidable sign of horionkartsinoma is the occurrence of profuse uterine bleeding, which may appear at different times: immediately after curettage of the uterus (abortion or miscarriage), gestational period, after childbirth or after evacuation of hydatidiform mole. The occurrence of bleeding in the menopausal period also may indicate the presence of chorionepithelioma.
In addition to bleeding take place serous, and later hoevenii highlight color of meat slops, due to the destruction of the tumor and the presence of vaginal metastases. Prolonged bleeding leads to anemizatsii patient. Pain in the lower abdomen and in the lumbar region and is due to the irregular germination of the education to the serous membrane of the uterus or the formation of metastases in the pelvis, and intestines.
Signs of metastases
The formation of metastases in TB is accompanied by signs of damage to the relevant authorities:
- brain damage: severe headaches, vomiting due to increased intracranial pressure, paralysis, paresthesia and other neurological symptoms;
- metastases to lung: chest pain, shortness of breath, cough and expectoration of sputum streaked blood;
- vaginal metastasis: detection of dark-red knots on the vaginal walls when viewed in a mirror, spotting them from the destruction of the walls of blood vessels.
Progression of TB and further metastases in patients have common symptoms characteristic of malignant tumors: sudden weight loss, weakness, fatigue, reduced work capacity.
Diagnosis
Preliminary diagnosis of TB will be done after a careful study of the history of collecting complaints and conducting a pelvic examination. In history, the doctor draws attention to the recent termination of pregnancy (occurring abortion or miscarriage, childbirth, removal of the fallopian tube).
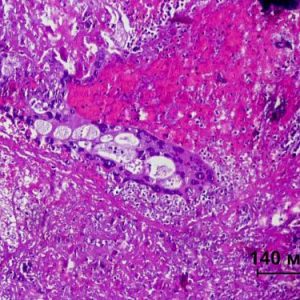
The main complaints of the patients include: lack of menstruation, the appearance of acyclic bleeding and menorrhagia, abdominal, headaches and chest pain, cough with expectoration of blood. Gynecological examination revealed cyanotic mucous vaginal and cervical metastatic foci crimson color on the vaginal walls. Palpation determined enlarged, uterus mogolistana bumpy surface and limited mobility. While probing the uterus possible pain, indicating that the germination of the tumor in the tissue of the pelvis. In half of the cases palpable bilateral ovarian cysts.
Additional methods of examination:
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs. Ultrasound examination is performed with a transvaginal transducer, the information content of the method is 90%. Allows you to define the size of the uterus, to detect decalomainia ovarian cysts, with the PP to detect the absence of the fetus and melkokolepnuju homogeneous fabric in the form of botryoidal conglomerate. When trophoblastic tumors are determined by the size, localization and structure (solid, mixed, vascular) nodes.
- Chest x-ray. Allows to detect metastases in the lung tissue, their number and localization.
- Ultrasound of abdominal organs, liver, kidneys. The purpose of this is exclusion/confirmation of metastases.
- CT, MRI of the brain.
- Pelvic angiography. Is performed for suspected horionepitelioma and destruirujushchego PZ. Allows you to identify the intramural and submucosal nodes trophoblastic education, their location and size.
- Hormonal studies Determines the content of HCG in the blood and urine, in the case of TB as its level increases several times. Also performed identification of trophoblastic β-globulin that allows early diagnosis of a potentially progressive forms of TB even at low values of HCG. Reduction of placental lactogen in the blood of the patient confirmed the presence of PZ in the background of the low content of HG. Progressive decline in placental lactogen talks about the possibility of malignant degeneration of the PZ.
Treatment
Tactics of treatment depends on the type and stage of TB. When molar undergoing evacuation (vacuum aspiration followed by curettage). After removal of PZ is controlled by the level of HCG every 2 weeks, until normalization, then tests for HCG should be repeated after 2, 4, 8 months for two years.
Chemotherapy after removal of the PP is assigned to the case:
- a high HCG level for 4 – 8 weeks after the evacuation of PZ;
- a permanent increase in the levels of HCG at any time after removal of PZ (held three times a study within one month);
- histological confirmation of chorionepithelioma after the evacuation of PZ or the detection of metastases.
In the event of horionepitelioma receive chemotherapy. Can be used as a single drug, and several (methotrexate, methotrexate in combination with 6-mercaptopurine, methotrexate and actinomycin D and other schemes). The effectiveness of treatment with cytostatics is estimated by the level of HCG (twice normal the concentrations of HCG in the urine). Treatment duration is 2 – 3 years.
Indications for surgical treatment:
- profuse bleeding;
- perforation of the uterus;
- the ineffectiveness of chemotherapy (rezistentnosti tumors to cytotoxic agents);
- significant uterine size (more than 10 weeks of pregnancy).
Surgical treatment involves removal of the uterus (hysterectomy without appendages).
Of the patient after the treatment of TB should be at the dispensary for 5 years and every six months to perform an ultrasound of the pelvic organs and to be tested for HCG to undergo annual x-ray examination of the lungs, according to the testimony of MRI of the brain.
Forecast
The prognosis for timely and adequate treatment of TB is favorable. Chemotherapy in patients with nemetstaticescoy form leads to a 100% cure, and in patients with metastatic course of disease cure occurs in 70% of cases. Recurrence of TB is possible in 4 – 8% of cases.




Thanx for the effort, keep up the good work Great work, I am going to start a small Blog Engine course work using your site I hope you enjoy blogging with the popular BlogEngine.Thethoughts you express are really awesome. Hope you will right some more posts.
Hi, I do believe this is a great web site. I stumbledupon it 😉 I may revisit once again since i have book-marked it. Money and freedom is the best way to change, may you be rich and continue to help other people.