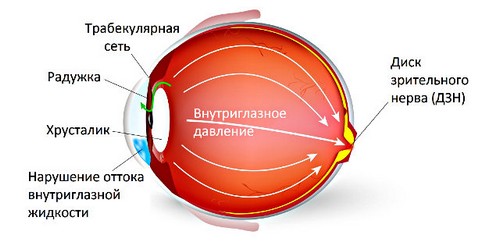
The eye is a globular body with elastic membranes filled with fluids. Maintaining a rounded eye provides intraocular pressure (IOP).
Normal intraocular pressure ophthalmologists consider figure 9-21 mm of mercury.St. If maximum figure is talking about the increased intraocular pressure.
The increased intraocular pressure depends on the volume of intraocular fluid (water moisture).
Reasons for the increase in IOP
This fluid is produced by epithelial cells of the ciliary body of the eye. The excess fluid drained from the eye through a special drainage system. Normally, these two processes, namely the synthesis of aqueous humor and its outflow are balanced.
When fluid is produced too much or when the violation of its outflow -the intraocular pressure increases. Increased IOP is observed in diseases such as glaucoma and ocular hypertension.
Glaucoma is a dangerous eye disease that leads to blindness. The reason for the development of the disease is elevated IOP. On the back of high eye pressure in glaucoma develops atrophy of the optic nerve and impaired vision. Glaucoma happens:
- Primary (independent disorder);
- Secondary (develops on the background of already existing diseases).

Ophthalmologists separately allocate such a pathological condition as ocular hypertension. The term “ocular hypertension” refers to elevation of IOP, in which there is no threat of those changes, characteristic for primary glaucoma (optic nerve atrophy, visual disturbances). There are such kinds of ocular hypertension:
- Essential;
- Symptomatic.
Essential form ocular hypertension occurs in people of Mature age, and the reason for its occurrence are age-related changes in processes of synthesis and outflow of intraocular fluid. Essential for ocular hypertension characteristic of a moderate rise of IOP.
Symptomatic ocular hypertension is formed on the background of existing disease or the adverse effects of drugs, toxic substances. So, symptomatic ocular hypertension can be the consequence of inflammatory eye diseases (uveitis, iridocyclitis), endocrine diseases (thyroid disease, syndrome of Itsenko-Kushinga), hormonal changes (menopause, pregnancy). Increased IOP may be periodically or constantly, depending on the duration of exposure of the pathological factor. Intraocular pressure may also increase occasionally due to severe anxiety, stresses.
Ocular hypertension is a benign disease. However, in some cases, this pathological condition may fail secondary glaucoma. Therefore, people with elevated IOP need to undergo regular examinations by an ophthalmologist.
The symptoms of high IOP
The patient may not even realize that he is high intraocular pressure. Indeed, the ocular hypertension is often asymptomatic. In some cases, a person concerned about the feeling of bloating, pain in the eyes can be a headache. But it certainly does not mean that every pain in the eyes is a manifestation of ocular hypertension. Because this symptom is also a companion of diseases such as migraine, hypertension, COPD, various ophthalmic pathologies.
If a person suffers from glaucoma, it can be distressing in addition to pain in the eye symptoms such as blurred vision, appearance of bright circles of light before the eyes, contraction of the visual fields. Acute glaucoma attack is very pronounced. Man complains of sudden nausea, vomiting, headache, redness of the eyes, lacrimation. If you feel the eyeball through the closed eyelid, you may find that it is very solid.
Diagnosis
As already mentioned, increased intraocular pressure often goes unnoticed due to scarce symptomatology. Given this fact, ophthalmologists are advised to undergo regular diagnosis of all men over forty years old. And even more need to undergo diagnostic testing as soon as possible, if a man began to bother narrowing of visual fields, clouding, decreased visual acuity.
A set of diagnostic procedures for suspected elevated IOP is as follows:
- The measurement of visual acuity using visiometry;
- Measurement of visual field by perimetry;
- The measurement of the IOP using tonometry;
- The study of the hydrodynamics of the eye during tonography;
- A study of the anterior chamber angle during gonioscopy;
- A fundus examination with ophthalmoscopy (performed to identify changes of optic nerve disc).
Principles of treatment
Before proceeding to the correction of intraocular pressure, it is necessary to determine the cause of the increase in pressure. Struggle with elevated IOP will be simply ineffective if the cause is not eliminated. If the cause of ocular hypertension is, for example, hyperthyroidism, the doctor prescribes treatment – receiving antithyroid drugs. Against the background of the treatment of the disease IOP is normalized by itself.
To reduce IOP ophthalmologists prescribed antihypertensive therapy. This diverse group of drugs which reduce either the production of intraocular fluid or its outflow. The steady increase of IOP glaucomatous origin can be surgical treatment.