About stomach cancer like many other diseases, not only cancer, there are a lot of misconceptions. We will understand where is the truth and how things really are.
Having the ideas of Russians about cancer as a disease of the 21st century nothing more than a myth. Of course, cancer incidence is increasing, however, evidence of malignant neoplasia was detected in fossil bones of the Neolithic (the period from the 8th to the 3rd Millennium BC), Egyptian mummies and in bones of American Indians who lived in the pre-Columbian era. The oldest find of a tumor in the spine of a dinosaur.
Describe malignant tumors are contained in Egyptian papyri, Babylonian cuneiform tablets, and ancient Indian manuscripts. They are repeatedly mentioned in ancient Greek medical literature. Hippocrates distinguished between benign and malignant tumors, Galen knew that a malignant tumor spread in the body.
Died from cancer of the Roman Emperor Galerius in 311, the Byzantine Empress Theodora in 548, and in the Hypatian Codex, a medieval monument of Russian literature, mentions the death from cancer in 1288, Volynsk Prince Vladimir Vasilkovich. It turns out that cancer plagued mankind throughout its history.
Stomach cancer is a widespread disease
Today in the world annually show about 15 000 000 new cases of cancer. Gastric cancer (GC) remains one of the most common diseases in the world. The leaders are Japan, Russia, Chile, Korea, China (40% of all cases).
In the Russian Federation in 2016 identified 38 thousand new cases of RJ, and died from this terrible disease 32 thousand patients. In Russia the highest incidence of this form of cancer accounts for Novgorod oblast and the Republic of Tuva, the minimum numbers in the North Caucasus region, the Magadan region and the Chukotka Autonomous district.
Nutrition affects the risk of developing stomach cancer
Research comparing regions with high and low incidence of gastric cancer found a correlation between dietary habits. The prevalence of food complex carbohydrates (potatoes, bread, flour products, more typical for Russia), rice (Asia, Japan) associated with reduced intake of vitamin C From fresh vegetables and fruits that contain ascorbic acid, an increased intake of salt, pickled, fried, smoked foods, spicy foods also increases the risk of developing stomach cancer.
For example, the national Korean dish, kimchi (a kind of sauerkraut), containing large quantities of salt and nitrates, was recognized as one of the reasons for the development of gastric cancer in Korea. Consumption of large amount of salted tea in Kashmir (Northern Pakistan) can be a major factor in the development of cancer of the stomach and esophagus in the region.
Nitrates and nitrites by prolonged consumption of have carcinogenic effect. The main source of their entry into the human body are nitrate and nitratsoderzhaschie vegetables, dried and smoked products, alcoholic products (beer, whisky) and spices.
2.5 times higher risk of developing gastric cancer in individuals daily consume animal oil, compared to those who prefer vegetable oil.
Excessive consumption of alcohol, especially vodka, also increases the risk of stomach cancer, the International Agency for research on cancer concluded that there is sufficient data to confirm the relationship of Smoking and cancer of the stomach.
The relative risk of disease in people who as infants less than one year were fed breast milk at 3-4 times higher than those who were breastfed for over a year. It is possible that this is due to the decrease in the protective function of the gastric mucosa due to the lack of immunoglobulin A, as well as the earlier infection of the gastric mucosa by the bacterium Helicobacter pylori.
Garlic reduces the likelihood of developing stomach cancer
Interesting information about the low incidence of stomach cancer in some regions of Southeast Asia and China, where the population is engaged in cultivation and sale of garlic. Have a protective effect fruits and vegetables (apparently, due to the content of ascorbic acid, tocopherol, b–carotene). However, this information requires confirmation on a larger sample of patients.
Stomach cancer is associated with infection of Helicobacter pylori
One of the important factors in the development of gastric cancer has an infectious component. In 1926, the Danish researcher Fibiger, Director of the Institute of anatomy, received the Nobel prize for the discovery of the infectious nature of stomach cancer. This was a prerequisite for discovery in 1983 of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori, causing stomach ulcer followed by its transformation into cancer.
Developed against this infection antiulcer antibiotic therapy has been so successful that in some developed countries, almost completely abandoned surgical treatment of gastric ulcer.
Currently, the infection Helicobacter pylori infection without adequate antibiotic therapy leads to the regeneration of ulcer into cancer, it is recognized carcinogen of the first order.
Other infectious agent, detected in gastric cancer is the Epstein–Barr (EBV), which infected more than 90% of the population. In Japan, the EBV–associated with Helicobacter pylori form of cancer found in 7%, US 16% Russia 9% of cases. However, data to confirm the relationship EBV and stomach cancer is not enough.
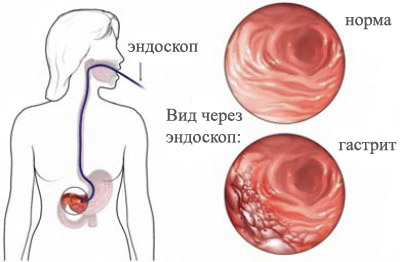
The vast majority of cases, RJ develops on the background of precancerous diseases, one of the most common of these is chronic atrophic gastritis in this group of patients is shown endoscopic screening after 40 years, at least 1 time in 3 years.
Genetic factors and risk of stomach cancer
The role of genetic factors in the development of gastric cancer was suspected due to the fact that individuals with blood group A(II) the incidence is higher by 20% than in individuals with group O(I) and B(III). The main contribution to the study of genetic factors has made the analysis of hereditary cancer of the stomach. In family cases of gastric cancer were identified a mutation in the gene E–cadherine.
Stomach cancer develops on the background of precancerous diseases
In most cases, stomach cancer develops on the background of long-existing precancerous conditions of the mucous. But the background and precancerous diseases does not necessarily lead to cancer.
The background diseases are: chronic atrophic hyperplastic gastritis, adenomatous polyps, pernicious anemia, post-gastrectomy, and menetrier disease (hypertrophic gastropathy, hyperplastic gigantology gastritis). Previously it was often stated that long-term current chronic stomach ulcers are pre-cancerous disease. Currently, most researchers recognized that “malosnezhnaja the plague” is the primary in a timely manner unspecified cancer.
The world health organization has ruled out a stomach ulcer from the list the background of precancerous diseases of the stomach. This fact does not mean that patients with stomach ulcers should not be under the scrutiny of doctors. On the contrary, regular gastroscopy with biopsy not only the edges of the ulcer, but other sections of the modified mucous membrane, should be mandatory.
Stomach cancer it is possible to identify at an early stage
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy with biopsy is the leading method for diagnosing early cancers. In recent years, to improve endoscopic inspection of the mucosa in routine practice introduced a comprehensive lookup method.
Endoscopes equipped with features narrow spectrum of light with optical zoom, more than 115 times, this technique allows to detect the tumor size of about 2-3 mm. Also used an endoscopic ultrasound. An innovative method of diagnosis – confocal laser endomicroscopy with an increase in 1000 times, is actually possible to see a group of 30-50 of tumor cells.
Over the past 10 years the diagnosis of early forms of gastric cancer in our country has almost doubled to 9% among all the identified forms. The figure is encouraging, however, is extremely low. In Western Europe it is around 20%. The world leader is Japan with 68% for early diagnosis. This is due to the introduction of screening programs. Every citizen after the age of 40 undergoing endoscopic examination of the upper gastrointestinal tract every year.