Tracheobronchitis is a term describing an inflammatory lesion at the same time as the trachea and bronchi of a child. In view of their proximity to each other, as the trachea passes into the main bronchi, the inflammatory process often affects the mucous membranes of both organs, especially in childhood, when the immune system is still not working at full capacity and imperfect in comparison with the adult body.
Usually the process starts in the upper respiratory tract like SARS, without proper treatment “descending” below the area of the trachea and bronchi. In some cases, a lesion will occur with the involvement of more and of the larynx, or is formed immediately as a primary inflammatory process against the background of certain infections or pathologies.
Without treatment, bronchitis may threaten the health of children, and demanding full and diagnosis and therapy under strict medical supervision.
The cause of the inflammation
Most often, the inflammatory process in the trachea and bronchi formed because of the penetration to the surface of the mucous membranes of these the respiratory system viruses or bacteria. With strong immunity and adequate local protection of the mucous membranes of these infectious agents neytralizuya, if protective factors are not sufficient or infection has a high degree of aggressiveness, developing tracheobronchitis.

There are a number of predisposing factors and situations in which such pathology more likely. This should include:
- the frequent incidence of SARS and the recent influenza, which lead to the decrease in immune reactivity
- irrational use of antibiotics and immunomodulators, unreasonable prescription of antiviral drugs
- the presence of rickets, malnutrition, reducing the supply of vitamins, anemia, diabetes and other pathology exchange
- congenital immunodeficiency, pathology cell component and humoral
- the legs and feet, systemic hypothermia
- passive Smoking, if household members smoke in front of the child
- anatomical defects in the respiratory organs, bronchial spasm
- violation of the indoor climate (hot and dry air, dust, mould on the walls).

Bronchitis refers to a category of infectious diseases, the pathogens are transmitted from sick children to healthy (although infection may be different), and they often affects preschoolers and school children. It is important if you suspect the development of tracheobronchitis immediately isolating the child in order to treat and distribute microbial and viral particles among healthy children.
The vast majority of cases, bronchitis is considered as a complication of improperly treated colds or flu as well as pneumonia, sinusitis, tonsillitis or childhood infections (whooping cough, measles, chickenpox). Often, such complications are becoming infection on the background of the adenoids, when a child is forced to move due to nasal congestion mouth breathing. Similar breathing difficulties are possible on the background of congenital defects of the chest and nasal passages.
Perhaps as an option the development of allergic form of pathology when inhaled, cause-significant allergen with prior sensitization of the body. If on a background of allergies or mucous membrane to penetrate the virus or microbe is the most difficult to recognize and treat form of tracheobronchitis – infectious-allergic.
Children usually have the acute form of disease, chronic process occurs in a few cases, in the absence of treatment, nutrition and immunity issues.
In adolescents one of the risk factors can become bad habits: Smoking, including VAPI, and the consumption of alcohol, narcotic and psychotropic drugs.
Types of tracheobronchitis in children and their characteristics
In childhood the development of tracheobronchitis can have multiple forms with the typical changes in the affected areas.
They are divided according to the severity of the process, the duration of the course and nature of inflammation:
- Acute bronchitis is usually manifested by coughing fits at night, when it formed a diffuse inflammation in the trachea and bronchi at its various levels.
- Chronic bronchitis is characterized by periods of coughing and expectoration in the daytime and at night. With him on the background of long flowing inflammation are formed or atrophic processes or hypertrophy of the tracheal and bronchial walls.
- Allergic tracheobronchitis occurs in the form of sharp attacks during contact with allergens. It is typical for a sluggish manifested symptomatology and the absence of common symptoms typical of infections.
It is important that the doctor during the inspection and examination of the child accurately identified the cause of the inflammation, then the treatment will be maximally effective and quick. Symptoms of bronchitis in children vary depending on the shape and course, and should talk more about them.
Symptoms of acute tracheobronchitis
Symptoms in acute bronchitis in General similar to SARS in its initial period, there is weakness, lethargy and irritability of the child, fever, malaise and headaches, loss of appetite.
Also typically the manifestation of the local symptoms:
- Cough – dry, paroxysmal and Intrusive, increasing the night and sometimes culminating in a bout of nausea or vomiting.
- Pain in the chest in the course of the trachea and bronchi
- Mucous discharge from the nose is abundant in nature
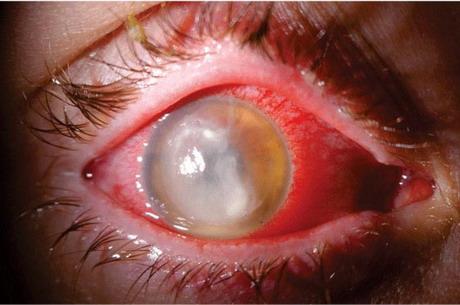
- Redness of the pharynx by the oral examination of the child, pain along the back wall and when swallowing, a sore, burning and dryness
- Shortness of breath, severe sweating, frequent pulse.
In severe condition and in the advanced form of the disease the child has hypoxia, which can turn blue lips and nasolabial triangle, it is more noticeable when you cough. If the process involves the larynx, the symptoms can be added a strong hoarse voice or osiplosti, the development of barking cough and sometimes suffocation because of laryngeal edema.
Usually the condition is particularly severe in the first two or three days of illness, as treatment and began liquefy and sputum discharge the child is feeling better, gradually, the cough abates and the inflammation goes away.
Manifestations of chronic bronchitis
In the absence of adequate treatment of acute tracheobronchitis or, when properly selected drugs on the background of various folk methods of self-medication, the symptoms become less clear and distinct, the process proceeds to chronic. Normally all symptoms not expressed so vividly and clearly how the sharp process, but manifest themselves on the background of banal colds, hypothermia if the body is affected by any stress factors.
Immediately arise:
- Profuse rhinitis mucous character
- Redness of the posterior pharyngeal wall with edema and friability of the mucous membranes and tonsils
- Soreness with the sore when swallowing, kreplin voice
- Typical coughing attacks, which is especially strong at night, develop pain in the chest, shortness of breath.
The temperature rise is small – from subfebrile values to febrile digits, and often it lasts a long time. On the background of chronic inflammatory process in the trachea and bronchial tree typically the development of progressive deformation of the bronchi, changes of the mucous membranes in the trachea, which can be a predisposing background for further pathologies by type of broncho-obstructive syndrome or asthma.
Features of symptoms and clinical diagnosis
Starts tracheobronchitis in children as a cold or flu, and often is a complication or clinical form. The main symptom of pathology is considered to be paroxysmal, dry cough, which occurs in the background crying, laughing or deep breathing, in the beginning it can be like laryngitis, in connection with which it is possible to confuse the condition.
It is important for parents called the doctor at home or were asked to accept in the presence of pain in the chest on the background of deep breaths or after a cough, with dry cough Intrusive attacks, the development of shortness of breath and hoarseness, paleness of the skin on the face and body with cyanosis on the fingers or around the mouth, with an increase in sweating amid the General symptoms of the disease – weakness and irritability, poor appetite, fever.

With the progression of the cough becomes wet cough sputum from the bronchi, usually greenish or yellowish. The severity of the condition depends on the age and characteristics of the immune response of the child.
Differences allergic form can be considered an aggravation of the fits at night or when going out on the street, the lack of temperature and common cold symptoms, a bad cold, and often conjunctivitis.
For additional diagnostics in the presence of such complaints, the doctor prescribes examination General blood and urine tests, biochemical analysis, and sometimes sputum with the definition of pathogens. Also swabs taken from the throat and nose to determine the cause of the infection, in the presence of allergic manifestations – estimated level of eosinophils the blood and are allergiesthe blood or skin. In the differential diagnosis to rule out pneumonia, shows the radiography of the chest.
General principles of treatment of bronchitis in children
It is important treatment only under the supervision of a physician, with monitoring of effectiveness and tolerability of chosen treatment. It must include both General procedures and local treatment. First of all, for all forms the basis of bed rest with a gradual transition to the home, a special diet with non-irritating products and dishes high in vitamins and minerals. Also shown medical treatment and physical therapy during the period of follow-up care folk methods of alternative therapy is applicable only in consultation with doctor if appropriate.
Acute bronchitis: treatment
The basis of the acute process is often a virus infection, therefore, the mainstay of therapy is antiviral treatment and immune protection. Apply the prescribed by a doctor in the age dosages in combination with General measures and symptomatic drugs.
Chronic bronchitis: treatment
Usually, when chronic bronchitis is formed secondary to microbial infection so it often requires antibiotics and immunotherapy to stimulate the body’s defenses. In order for treatment to have effect initially, the physician determines the nature of microbial agent and its sensitivity to particular antibiotics. In the treatment of chronic inflammation of the trachea and bronchi use protected penicillins and cephalosporins, and macrolides. They are applicable in oral form, injection is not required and does not have a higher efficiency. All regimens of antibiotics and additional drugs will paint doctor, shorten or lengthen the course to change the dosage on their own not.
Prohibited self-treatment with antibiotics, even if you previously gave them children and they are well tolerated. Not always chronic bronchitis requires of their reception, especially if it is the viral nature of inflammation or Allergy. When medications are contraindicated and will only hurt. The reaction can be more severe and pronounced.
Allergic tracheobronchitis: treatment tactics
In the presence of allergic lesions of the trachea and bronchi requires the use of desensitizing therapy and Allergy drugs. Banned antibiotics and antiviral drugs, they will only worsen the situation. Effective when allergies are oral forms of antihistamines, starting with the second generation without sedative and side effects. In the presence of bronchospasm or edema of the larynx shows the use of bronchodilators and hormonal drugs, injections, inhalation therapy with bronchodilators and corticosteroids, anti-inflammatory drugs.
Additional drugs and money in the treatment
Because of the availability of a painful cough, which disturbs the child, it is necessary to use drugs to thin mucus and ease the cough attacks. Used drugs antitussive series, which inhibit the activity of the cough center in the brain and lead to the suppression of attacks and obsessive dry cough in its poor tolerability. Applicable drugs is strictly limited, only on the background of dry cough.
In the presence of a productive cough this group of drugs is prohibited, they can threaten the development of stagnation and pneumonia.
For the relief of cough and thin mucus shows the use of mucolytic drugs and mucoregulatory. They suppress inflammation, liquefy phlegm, help her to cough up and make the cough nebraskensis and productive. It is important not to suppress the cough, and turn it from a painful and dry to productive cough up phlegm and get better.
Correction of diet and drinking regime
In the period of acute condition shows the change of diet and drinking regime to give the body a rest and unloading, to help in the excretion of metabolic products and toxins produced by the infectious agent.

Also need to drink plenty of alkaline nature, which helps in the separation and liquefaction of sputum, soothe irritated throat and relieve the breathing. Children useful compotes and fruit drinks, mineral water without gas in the form of heat, decoctions of lime blossom and rose hips, milk with butter and honey, raspberry tea. Banned strong black tea, coffee as well as soda and concentrated juices (diluted with water to 2/3 of its volume).
From food, especially if you suspect an allergic component of inflammation, should avoid such foods and dishes that can be potential allergens. These include bee products and chocolate, bright and exotic fruits, salmon, eggs and nuts. In predisposed children, they may increase swelling and spasm of the bronchi that causes coughing.
Necessary shown antipyretic, anti-inflammatory therapy, detoxification treatment and immunoassay therapy. Shown inhalation therapy with bronchodilators, drugs to thin mucus and stimulants of its origin. Using inhalation only with dry cough wet productive cough they should be lifted.
The use of physiotherapy in the treatment of
After the acute process gradually fades in the recovery period for the normalization of the ventilation functions of the respiratory system shown physiotherapy. Due to it improves blood flow to the affected mucous membranes, normalizes their work, stimulates expectoration and aktiviziruyutsya breathing, oxygenation of the tissues. In children’s practice apply massage, breathing exercises, and heat treatments, inhalation therapy with decoctions of herbs and drugs, electrophoresis with drugs.
All appointments are coordinated with physician and conducted at home or in the clinic only if there is no temperature on the background of normalization of the General condition. The course of treatment consists of several procedures carried out daily or every other day under the supervision of a physician.



The next time I read a blog, I hope that it doesnt disappoint me as much as this one. I mean, I know it was my choice to read, but I actually thought youd have something interesting to say. All I hear is a bunch of whining about something that you could fix if you werent too busy looking for attention.
I definitely wanted to develop a brief comment so as to express gratitude to you for the amazing guides you are giving on this site. My particularly long internet search has at the end of the day been compensated with brilliant knowledge to go over with my great friends. I ‘d declare that many of us site visitors are unequivocally lucky to exist in a fine website with very many brilliant individuals with great things. I feel somewhat fortunate to have discovered your site and look forward to plenty of more fabulous moments reading here. Thanks again for everything.
Ha, here from google, this is what i was looking for.