Everyone knows about the dangers of pneumonia in the adult and child age, but sometimes a special state associated with the neonatal period. It is a congenital pneumonia, which manifests itself immediately after birth or during the first three days.
Pathology can occur in full-term babies and preterm children of different time, of course, that the more pronounced prematurity, the harder it is the more dangerous pneumonia and its prognosis.
It is important to recognize this condition immediately and actively treat the baby, otherwise, such condition is threatening his life and future.
Features of congenital pneumonia
Based on data from the statistics on cases of congenital lung lesions, the most frequent cases is a birth from mothers who had severe and complicated course of pregnancy, signs of infection, including intrauterine infection of the fetus. In addition, it is also possible infection of the lung tissue of premature babies or those babies who are born with aspiration of meconium or amniotic fluid (swallowing them due to too early the first breath). According to statistics, these children congenital pneumonia occurs almost two times more likely than those born at term, healthy babies.
The name “congenital pneumonia” is used because the pathogenic agents of infection and inflammation is formed by the child during the pregnancy or during delivery, so external factors play in its formation very little value.
The main reason for such pneumonia is an infectious agent that was initially present in the female body and intensified in the period of pregnancy or its activity became significant for the infection during childbearing.
In this regard, all congenital pneumonia infants divided by the time of their formation into two large groups:
- antenatal infection, that is, the pulmonary system is affected and inflamed before birth, in utero.
- intrapartum infection, pathogenic objects penetrate into lung tissue of a baby in childbirth, usually a prolonged or complicated.
For each episode of pneumonia typical of its causative agent, which may be microbial or viral in origin, and it is important to accurately and quickly identify that remedial measures were correct and effective.
Causes of congenital pneumonia in newborn
The most common causes of congenital pneumonia are viral infection, as children in utero and immediately after birth are the most vulnerable to their influence. To develop infectious inflammation of the lung tissue, you need to hit the virus in the third trimester. If it is activated earlier is the risk of congenital malformations, termination of pregnancy or intrauterine fetal death.
The most common causative agents of pneumonia in this group of children are considered to be TORCH-infections. This group is the most detected pathogens capable of provoking malformations, intrauterine infections, including lesions of the lung tissue. It’s such pathogens as herpes, cytomegalovirus, rubella and Toxoplasma gondii. Also possible influence of other agents, which have their peculiarities in the structure and formation of the infectious process, and treatment.
Features of infections of TORCH-complex
If we talk about the toxoplasmosis, it is triggered by a particular pathogen, Toxoplasma (a group of protozoa). The infection transmitted through Pets, mostly cats, often in the form of asymptomatic carriers. It is also possible flow Toxoplasma into the body from undercooked meat. If the infection is formed for the first time during pregnancy, especially in her last weeks, the pathogen can cause lesions of the lung tissue of the fetus and congenital pneumonia.

If a woman contracted toxoplasmosis before pregnancy she already has antibodies to the pathogen, in this case, this infection is not a danger to herself or her baby.
Clinic of the acute toxoplasmosis in women nonspecific, so often taken for a cold or fatigue.
The development of the rubella is dangerous in the absence of antibodies to it in the mother (if a woman before pregnancy and not had the disease). Is an acute viral infection transmitted by airborne droplets, bearing a potential threat to the fetus from early gestation because of the high risk of congenital malformations. The virus can lead to the formation and pneumonia in the fetus if infection occurred in the last weeks of pregnancy.
The defeat of cytomegalovirus infection is also dangerous. This airborne viral infection which can get into the body of a woman sexually and by contact. About 60% of the adult population is infected with the virus, but the hospital infection is manifested only in isolated cases. If infection occurs the mother, the virus is able to penetrate through the placenta with induction of inflammatory processes in many tissues and organs of the fetus like brain, liver or lungs.
The formation of herpes is possible in any pregnancy, a particle that has affinity for nerve cells, but it can affect the skin and internal organs, including the lung tissue with pneumonia. There are two types of herpes, are dangerous to women – the first and second type (labially and genital). The first type is transmitted mainly by airborne droplets or by kissing, close contact, shared utensils. The second primarily is transmitted through sexual contact (of any type).
Herpes of the first type most often can form of antenatal pneumonia (intrauterine infection), and the second type often affects during childbirth (intrapartum). This is because during birth the infant passes through infected genitalia of the mother, on which surface may be a herpes virus.
A group of TORCH-infections is most dangerous against provocations like pneumonia, especially if we are talking about the last stages of gestation or childbirth. But this is not the only cause of pneumonia in infants.
Features of intrauterine pneumonias of other etiology
Perhaps the influence and many other pathogens having a viral or microbial nature, related to fungi or protozoa. Often can cause congenital pneumonia, candidal infection, chlamydia or Mycoplasma, the possible role of Listeria, Ureaplasma, or Trichomonas. They are mainly influenced before the birth, in recent weeks or in the process of the birth of the baby.

Trichomoniasis and ureaplasmosis belong to the group of genital infections, they rarely cause pneumonia among quite healthy and full-term infants. Usually the infection, along with Candida, is formed in premature babies or with congenital immunodeficiency.
Infection with chlamydia or Mycoplasma, as intracellular pathogens, typically for children immediately after birth and in the first hours after birth. But you need a confluence of special circumstances.
Generally speaking, for congenital pneumonia is a big role in how viruses and microbes, protozoa, but typically for such problems is necessary and the presence of additional factors. In healthy term infants of similar lesions not typical.
The mechanism of pneumonia in each case depends not only on the causes affecting the baby, but also many additional factors.
Special conditions for the provocation of congenital pneumonia
Any pathogen needs for the formation of pneumonia in utero to penetrate through the placental barrier to have a certain affinity for lung tissue and enter the bloodstream in the lung area of the fetus. Before birth the lung tissue of the infant has its peculiarities, the alveoli are in the sleeping state, and can become a breeding ground for viruses or microbes. Formed the inflammatory process, which only after birth, at the beginning of pulmonary respiration manifests itself by symptoms of pulmonary insufficiency, incomplete disclosure of all sites, the formation of silent zones. Usually the inflammatory process on the background of pulmonary respiration aktiviziruyutsya, and to generate additional symptoms.
There are several factors that can increase the likelihood of infection in the baby. These include:
- Hard progressing pregnancy and illness of the mother, which led to the defects in the structure of the placenta and its protective role
- infection of the mother, especially belonging to the group of TORCH-complex. They increase the risk of infection of the placenta, and penetrating through it agents in the tissue of the fetus.
- the prematurity, the weakening of the immune protection against it.
- the course of labor and complications in them, the long dry period, prolonged labor, and various medical intervention with the purpose of childbirth.
How does congenital pneumonia?
For congenital pneumonia typically the onset of symptoms immediately after birth or during the first three days. If symptoms occurred during the first days – we are talking about the infection at birth if it is during pregnancy.
In the formation of pneumonia, caused by certain viruses of the group of TORCH, often on the background respiratory symptoms are formed and symptoms of other systems and organs. It is important to consider the doctors in the diagnosis of lung injuries and approach to the treatment of pneumonia and other manifestations.
It is also important to identify viral or microbial nature of infection, symptoms and treatment approaches vary greatly.
The first signs appear after birth, the overall condition of the crumbs can be very difficult due to the developing immediately after the first breath the respiratory disorders. Babies can be born with blue or gray, pale skin color on the body and face, possible rash red spots and hemorrhages due to intoxication. The cry of the baby will be weak, depressed reflexes on the background of deficiency of oxygen, nourishing the nervous system in infectious process. In the end, assess Apgar score will be low, and children are immediately taken by the neonatologists in the NICU Department.

In some situations, they need intubation and artificial ventilation, and oxygen therapy to saturate the oxygen to the body organs and normalize metabolic processes. This is especially important on the background of severe respiratory failure.
The main symptoms of pneumonia is a respiratory distress with shortness of breath, retraction of spaces between ribs and areas under the sternum and above the clavicles, with the active participation in the breathing of the abdomen. Amid the shortness of breath is rapid breathing and heartbeat, exceeding the norm by 20-30% or more. It tells about the problems with his lungs and needs immediate examination.
For children not the typical stages, which is formed for pneumonia in adults, it is important to know that the inflammation spreads rapidly, and infection, for example influenza virus, Pneumocystis or Staphylococcus, leads to necrosis of lung tissue.
Pneumonia congenital plan differ in form of the pathogen to microbial, viral, fungal and caused by atypical flora, can also be divided into non-specific specific, complicated. It is important for the diagnosis and selection of proper treatment.
The clinic is the specific TORCH-pneumonia and bacterial
If pneumonia provoke pathogens from the group of TORCH-infections, possible presence of generalized infection on a background of pulmonary symptoms. Doctors know about it, simultaneously with the treatment of pneumonia, surveying the child aiming to damage other systems and organs.
So, if cytomegalovirus is formed and the lesions in the brain and liver, which increases the overall course of the disease. When exposed to the fetus the virus causes serious brain damage with the formation of zones of ischemia and cystic formations, enlargement of the liver with the development strongly pronounced jaundice, increase in bilirubin with the development of encephalopathy. Therefore, the pneumonia is just one of the symptoms of a viral infection.
Pneumonia when congenital rubella is accompanied by rashes on the body and defeats all the other divisions of the respiratory tract.
Special properties differ and microbial pneumonia, as the nature of the inflammation is purulent. They often develop within the first three days, with a sharp deterioration of the child, evolving literally by the hour. On the background of a sharp shortness of breath are formed symptoms of intoxication, a fever, or prematurity paradoxical lowering the temperature to severe hypothermia. There is a rejection of breast or bottle, weight loss and sudden anxiety, cyanosis or sudden pallor, regurgitation, wheezing when breathing.
The consequences of congenital pneumonia
Such processes are for babies more dangerous than adults, complications depend on the types of pathogens and have both immediate and delayed. If the expense is formed of the pathogen destruction in the field of pulmonary tissue, it threatens to spread beyond the respiratory tissue. It threatens to breakout of an infectious agent in the blood vessels and the formation of sepsis with bacteremia (germs in the blood) and the formation of secondary purulent foci in the tissues and organs.
Sepsis at this age has a high percentage of mortality.
If we talk about other immediate complications include forming of bleeding in virtue of hemorrhagic syndrome, or DIC, circulatory disturbances and tissue hypoxia, the development on the background of respiratory failure and even cardiovascular failure. If to speak about purely pulmonary complications, these include the formation of lesions of the pleura (acute pleurisy) and pneumothorax (air in chest) and lung atelectasis (portions wears off).
Among the delayed complications can be called brain damage with the suffering of intellect in different degree of expressiveness, chronic infection, impaired growth and development, malformation of organs and tissues.
Methods of diagnosis of congenital pneumonia
A relatively quick diagnosis of congenital pneumonia always presents some difficulties. This is due to the fact that respiratory failure in this age is typical not only for pneumonia but also of many other States. It is important for suspected pneumonia also accurately identify its pathogen, as haemorrhage protozoa, viruses, and germs different, and the range select drugs.
Important data, obtained from the mother or her the card exchange – how was the pregnancy, childbirth and if complications whether there were signs of infection in the third trimester, did her research on a group of TORCH-infections what were the results.
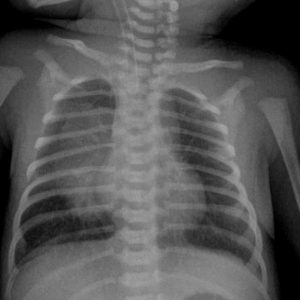
The peculiarity of congenital pneumonia, especially if we are talking about premature babies is fuzzy objective data, difficulty of listening to the rattling and noise, similar data as on the background of pneumonia and respiratory distress syndrome. Very important in this case, data of laboratory and instrumental diagnostics.
Due to instrumental examinations can accurately determine the damage to the lungs and to clarify where it is localized. Especially important are x-rays of the lungs of the newborn, when the typical signs of inflammation – reducing airiness of the lungs with a strengthening of the pattern of blood vessels at the beginning of pneumonia, and then the manifestation of inflammatory infiltrative changes with their tendency to merge. In prematurity of the child radiography cannot accurately give information – whether it’s pneumonia or hyaline membrane disease. The changes are very similar to the background of both pathologies, so the necessary tests.
Features of the infant with suspected pneumonia
In the diagnosis of pneumonia in newborns carried out a series of tests, but they have their own characteristics due to the physiological peculiarities connected with the birth. So, the infant typically increase in white blood cells and red blood cells to enhance tissue respiration, and by the 5th day occurs physiological crossing of leucocytes and lymphocytes.
These data can confuse the doctor, to disguise the features of inflammation. It is important to note changes in the dynamics of spirit daily, there will be a noticeable increase in leukocytes, and perhaps the lack of physiological chiasm.
According to the level of white blood cells and lymphocytes determine the nature of pneumonia – viral or microbial, but may also mixed infection with the simultaneous influence of viral and microbial associations.
If there is no effect of treatment crumbs, conducted a survey of mothers, which revealed the presence of specific pathogen. This is due to the fact that the mother will be the main source of infection to the fetus and newborn, and antibodies the child to infection is not yet formed and to determine their impossible.
Mothers serological diagnosis, determining antibodies to certain infections with a level of immunoglobulin G and M. the level of antibodies to the most likely types of infections, and when the level of antibodies of class G this pathogen is not dangerous in terms of pneumonia, as it is evidence of chronic infection or immunity. But the presence of the M-class may indicate an acute process, and that the pathogen probably caused the pneumonia.
Can be shown smears from the vagina to sexually transmitted infections, especially when bacterial pneumonia of the child, it is possible to determine the sensitivity of pathogens to antibiotics.
How to treat congenital pneumonia in a child?
It is necessary to treat the child immediately after diagnosis, and apply complex scheme of treatment taking into account the type of pathogen and the peculiarities of its development, in parallel with the methods of care for your child and security measures.
Children with pneumonia are placed in incubators to provide them with optimal temperature and humidity is 32-34 degrees with 80-90% humidity, it is also important to exercise oxygen therapy is often right in the conditions of the incubator.
If possible, children are fed breast milk of the mother or donor, it is important to reduce total caloric intake, but increase the frequency of feedings.
Obligatorily oxygen therapy, it is selected taking into account the capabilities and condition of the child. This is important in order to correct metabolic disorders and to support the work of the cardiovascular system. In terms of the incubator it can be a direct supply or use of masks, with weakness and premature crumbs, a correction of the respiratory act with the connecting oxygen supply (constant positive pressure), and if necessary – transfer the crumbs to a ventilator. Amid all these events is being held for drug exposure.
It is important to establish the exact nature of the pathogen, under his chosen therapy:
- When viral origin shown antiviral agents in parallel with antimicrobial therapy.
- On the background cytomegalovirus has a particular drug – an anti-cytomegalovirus immunoglobulin in combination with interferons. May be prescribed drugs from the group of stimulators of interferon synthesis in the form of solutions, suppositories or other forms.
- The detection of toxoplasmosis applicable drugs of specific actions – antibiotic spiramycin, specifically tailored to the dose per kilogram of body weight. In the treatment of control blood tests and liver function in order to avoid complications in treatment.
- In bacterial pneumonia of newborn antibiotics as one of the leading drugs used immediately two drugs by injecting them intravenously or intramuscularly, pick up the drugs from the group of seed funds, with their inefficiency – reserve drugs.
- It is especially difficult to pick up drugs subject to infection by opportunistic flora, including Staphylococcus aureus, it may have resistance to many antibiotics.
The therapy of powerful antibiotics, suffering intestinal microflora, and it is important for its correction, especially in light of the fact that the intestines have not had time to be populated by microbes. Shown taking probiotics in the form of formulations with lactic acid bacteria and bifidoflora. Pick up the drugs so that they are not exposed to antibiotics and prizivlenie in the gut.
With the improvement of the condition shown vitamin therapy and physiotherapy, the transition to feeding breast milk and care for the mother and child that improves the prognosis about his recovery.
What are the predictions for babies?
If the pneumonia is recognized at the very beginning and precisely determined its causative agents started active treatment, organized a full-fledged care of the baby and conducted all activities, the chances of recovery are high. But often congenital pneumonia occurs in utero, combined with multiple lesions of tissues and organs, the nervous system can lead to problems. Often severe and atypical pathogens can cause residual effects or disability.



