The disease is called postthrombotic syndrome (PTS). It is the responsibility of vascular surgeons in larger hospitals with greater specialization of medical specialists, phlebologists (physicians who deal with patients with diseases of the veins) and small hospitals the General surgeons.
Postthrombotic disease is changes in the soft tissues of the lower extremities that develop because of the constantly observed the difficulty of blood outflow, which is the result of suffering thrombosis (blockage of blood clots) or thrombophlebitis.
Pathology can develop in some years after the transfer of these diseases.
Causes and development of disease
Thrombosis in the lumen of the vessel is formed a thrombus (blood clot). If you assigned adequate treatment, the process of clot formation stops, the vessel is a blood clot with those sizes, which it managed to grow due to pathology of blood and the vessels.

After the relief of thrombosis the clot formed is subjected to:
- destruction;
- the substitution of connective-tissue elements.
The destruction of thrombotic masses is due to the so-called lizirovania process “corrosion” elements of a blood clot which is carried out lytic enzymes (biological compounds that can melt and/or dissolve tissue and other biological substrate).
Depending on prevailing process of destruction, or connective tissue substitution are changes in the veins:
- if lytic enzymes residual active, the clot is formed the tunnel. This is called recanalization of the vessel is resuming its patency;
- if the predominant formation of connective tissue elements (even in the background of the dissolution of the clot), the blood clot is gradually replaced by them. Developing occlusion – blockage of the lumen of the venous vessel, and in a literal understanding grows.
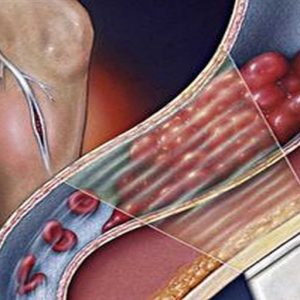
But even if the lumen of the affected vein is restored – in this place it will not possess the same physiological properties possessed until the thrombosis. Normal in Vienna there are valves through which the blood flows in only one direction. When blood clots and accession of the inflammatory process, they are destroyed and do not work properly.
The outcome of all these processes (whether dominated by the dissolution of thrombus or clogging of the lumen of the vessel connective tissue elements), is the failure of normal blood flow in the deep veins of the lower extremities. As the valve apparatus veins are not restored, such a failure is permanent.
Because of the violation of blood flow the following processes occur:
- the blood in the veins stagnates;
- the pressure in them rises;
- because of this expanded veins that connect the deep veins with the superficial.
Blood begins to be discharged in superficial veins – they are also involved in the pathological process, ceases to work correctly. In the end, because of a blood clot in a deep vein in the pathological process involved all the veins of the legs. In the tissues of the lower extremities in the literal sense, is deposited (accumulated) in the blood.
Failure of blood circulation leads to malnutrition of the tissues of the lower extremities. This leads to the formation of trophic ulcers – ulcerations of varying depth, upcoming because of “starvation” of the tissues.
Because of the described processes is the power of muscles, they weaken and become unable to provide the movement of blood through the veins. A vicious circle of pathological changes in the growing end result of developing venous insufficiency.
The process can be on one or both sides – depending on the blood clots formed in the veins of one or both lower extremities. It is often unilateral.
Symptoms
Tromboliticescoe the disease can develop in two forms:
- swollen;
- swollen-varicose.
Edematous form of PTS is characterized by the formation of persistent edema, which cover the soft tissue of the lower extremities.
When edematous form of varicose veins are formed not only swelling of the feet, but also pathological changes of the superficial veins.
Also there are three stages of the clinical course of this pathology:
- first – with the formation of transient swelling and development of “heavy legs syndrome”;
- second – with the formation of resistant edema and the formation of different trophic disorders, in addition to trophic ulcers;
- third – with the formation of stable, enduring edema and the formation of trophic ulcers.
Trophic disorders, which are observed in the second stage, lead to the development of such pathologies as:
- pigmentation (natural color) of the skin;
- eczema – damage to the skin that forms a rash in form of papules with serous fluid and swelling, worried about itching the affected skin fragments;
- lipodermatosclerosis (or indurative cellulitis) – cicatricial degeneration of the skin and subcutaneous fat.
Trophic ulcers, which are formed in the third stage of this disease, it is a violation of the integrity of the skin with the following characteristics:
- localization – develop in the projection of the affected veins, with further progression of the disease spread outside of this projection;
- size – initially, venous ulcers can be small in size, from 0.5 cm, and with the progression of the disease to increase. In advanced cases, when decompensation or inadequate treatment of an ulcer can cover most of the skin of the lower limb. In some patients venous disorders are marked from over a relatively large area of skin that is associated with a significant defeat of deep and subcutaneous veins;
- form – the form of trophic ulcers in the initial stages can remotely come close to round, then ulceration can acquire a different irregular shape as the ulcerative process extends over large areas of skin;
- depth is often shallow, up to 0.5 cm in depth;
- number – single or multiple. With simultaneous formation of multiple sores they are in the early stages of the disease exist in isolation, and then as more can merge into one large ulcer surface;
- color – saturated red;
- content – at the bottom of the ulcer may be a plaque dirty shade in the form of shreds.
The first indistinct signs of postthrombotic disease can appear a few months after suffering thrombosis of the lower extremities. But they are able to occur a few years after this illness, though, apparently, after the treatment came the physiological well-being from the affected limb.
The symptoms most characteristic of postthrombotic disease is to:
- pain;
- discomfort;
- swelling;
- convulsions.
Characteristics of pain:
- localization – first, the patient feels pain in the legs in the projection of the affected venous vessel. Further pain is affecting an increasing segment of the tibia until its coverage;
- widespread irradiation as such is not typical;
- feature – aching, pressing, in region formed trophic ulcers may be “burning” pain;
- according to the severity in the early stages of the disease tolerable, then increase;
- the occurrence – may occur before the formation of visible tissue changes in the affected lower extremity.
Discomfort in the legs manifests itself as:
- distension – patients often describe the sensation as follows: “If the leg is something is increases in size and presses from the inside”;
- severity – the patient seems that the affected leg tied some heavy object.
Pain, bloating and severity appear first in the load on the affected limb during walking, running or even standing. In the case of a non-running state, if the patient sits or lies, giving limb elevated position, the severity of the described symptoms is considerably reduced, there comes a sense of relief, but all the discomfort disappears. With the progression of the disease, such tricks do not lead to the expected relief of the patient.
Swelling of the soft tissues of the affected limb at PTFs may appear almost immediately with the development of this disease.
Their characteristics:
- localization – first can be local, in a place of passage of the affected venous vessel, further is able to cover more of the soft tissue down to cover the entire lower leg to the foot;
- the consistency of tissues – at first smooth, then stiff;
- for rigidity, the ability of swollen tissue to resist external pressure. Even with significant pressure with a finger on the cloth “dents” in them formed shallow and quickly disappears.
Oedema of different severity sooner or later develop to all patients with postthrombotic disease. Changes in tissue edema are not limited. A few months in the skin and subcutaneous tissue develops a fibrous tissue – there is induration (the so-called indurative changes of the soft tissues). While the skin is soldered to subcutaneous tissue and loses its mobility – it is impossible to pick a fold, in these attempts to develop pain.
Excessive skin pigmentation is also an essential feature of tromboliticescoy disease.
Its characteristics:
- color – dull brown hue;
- shape – circle, around the whole of the affected limb;
- localization begins above the ankles, then spreads to the lower part of the tibia. In advanced cases, may cover half of the skin of the lower leg.
With the progression of the disease in the site of occurrence of pigmentation developing:
- dermatitis – inflammation of the skin;
- eczema dry or moist, where the skin on the affected area becomes permanently wetted.
In the later stages tromboliticescoy of the disease is in areas of increased pigmentation appear poorly regenerative (healing) sores.
Characteristics of seizures:
- localization – include the calf muscles, the progression of postthrombotic disease can cover the entire foot;
- at the time of occurrence – may occur with physical stress on the feet (when walking, try running, and static standing in one position for a long time), but also often develop at night. Night cramps – a symptom characteristic of postthrombotic disease;
- for the duration – in the early stages of the pathology can occur for several tens of seconds, when it progression may last a few minutes;
- according to subjective feelings – painful, unbearable, bring physical suffering patients.
With the development of night cramps sleep of the patient is disturbed.
The inability to sleep properly and painful spasmodic sensation cause develop:
- feeling of General fatigue;
- reduction of General life activity, which is compounded by the functional worsening of the affected limb;
- the deterioration of health – both mental and physical, decline in productivity;
- irritability;
- at persons with the labile (sensitive and volatile) nervous system – sense of oppression, sometimes tearfulness.
Swollen-varicose form postthrombotic disease develops in 25% of all diagnosed cases of pathology. Patients complain that under the skin of the affected limb appear meandering, at first slightly, then more and more bulging veins. Due to the fact that they are involved in the pathological process along with the deep veins, clinical symptoms are even more pronounced.
The clinical picture in postthrombotic disease may develop in different ways- it depends on:
- the degree of recanalization of the thrombus;
- the regenerative abilities of tissues.
In some patients the symptoms develop slowly, for quite a long time they’re mild or moderately severe, progressing gradually. In other patients the clinical picture develops rapidly – trophic disorder can occur in the first month of onset. In the second case, there comes a strong disability.
Diagnosis
To identify postthrombophlebitis disease easy. In the diagnostic process, the doctor focuses on the characteristic complaints of the patient, and also takes into account the fact that he had thrombophlebitis. In some cases, patients with thrombophlebitis (particularly mild) do not go to the doctor about this nuance should remember to ask the patient, if he didn’t have long expressed edema of the lower limbs, not whether he suffered from distension. For accurate diagnosis it is necessary to resort to additional methods of examination – fyzikalni, instrumental, and laboratory.
If physical examination reveals the following:
- during the inspection, identified puffiness, pigmentation of the skin, in advanced cases – presence of trophic ulcerations. During the inspection it is noticeable that the patient can hardly stand;
- palpation (feeling) of the lower limb – soft tissue thickened, rigid, the pulse on the arteries may be impaired. Can be palpation tenderness of the affected lower limb in the lower leg area.
In the diagnosis of postthrombotic disease using such instrumental methods as:
- rheovasography of the lower extremities (or impedancia plethysmography) is the study of hemodynamics and the microcirculation (blood circulation at the capillary level) in the affected limb. At PTFs examination in dynamics – with replays to track the growing deterioration. The dynamics of the blood flow in this disease worsens;
- ultrasonic Doppler study of lower limb veins (Doppler ultrasound) – it is evaluated the state of the venous vessels in the affected limb (of their walls, valves), estimated blood flow;
- radionuclide venography in vein in the back of the foot of the affected limb contrast medium injected with radioisotopes, immediately after injection the patient is asked to perform flexion and extension movement in the ankle joint. How the radioactive material moves through the veins, see using the gamma camera;
- ultrasound angiography, the patient is intravenously injected contrast agent, and then make a series of x-ray images. Using this method, studies can reveal the exact location of the lesion.
Laboratory methods, which are used in the diagnosis tromboliticescoy disease is:
- common blood test helps track whether the inflammatory process in the affected veins. About its existence is evidenced by the increase in the number of leukocytes and erythrocyte sedimentation rate. Also appreciate the number of platelets is important for the early diagnosis of recurrent thrombosis;
- coagulation analysis of blood clotting. It should be performed in all patients undergoing thrombosis – for the timely detection of changes in the coagulation of blood, which increases the risk of thrombosis;
- prothrombin index – an indicator that displays the activity of the blood coagulation system. The purpose of this study is the same as the purpose of studying of coagulation.
Differential diagnosis of
Differential diagnostics of post-thrombotic syndrome is primarily carried out with such pathologies as:
Complications
The most common complication of postthrombotic disease is:
- venous insufficiency;
- infection of venous ulcers.
Treatment
Patients with tromboliticescoy disease treated by conservative and surgical methods.
Tactics of treatment depends on the form of postthrombotic disease and the stage of its development.
In the stage of compensation and subcompensation circulatory disorders purpose the following:
- avoiding heavy physical labour, work in workshops with high temperature and also at low temperatures, work, driving to constantly be in a standing position or walk often;
- the constant use of the means of elastic compression (bandages, stockings);
- physiotherapeutic methods of influence.
- When decompensation of blood circulation are these:
- antiplatelet agents – oppose re-thrombosis;
- fibrinolitiki – dissolve the blood clots;
- drugs that reduce the inflammation of a vein wall;
- medical treatment, improves tissue trophism including vitaminangels.
If developed and progresses of early decompensation of blood circulation in the affected limb, it is an indication for surgical treatment.
Operations which are in postthrombotic disease, the following:
- reconstructive;
- corrective.
For reconstructive operations include:
- resection (removal) of the affected veins;
- plastic veins, the wall of which can still be recovered.
- bypass – the formation of additional ways of outflow of venous blood.
- To corrective operations include:
- phlebectomy – while she removed the dilated saphenous vein;
- miniphlebectomy.
Prevention
Preventive measures aimed at the prevention of the postthrombotic disease is to:
- regular tests for assessment of blood coagulation;
- early detection and adequate treatment of thrombotic pathologies;
- during the adaptation period after suffering thrombophlebitis (first year) – conservative appointments to such patients;
- avoidance of inappropriate load on the lower limbs after suffering a thrombotic pathologies.
Forecast
Forecast in postthrombotic disease complex. During its slow development the patient can live without significant changes on the part of legs to old age. With the rapid development of decompensation can occur quite quickly.
To date, no single type of treatment (including operative) cannot interrupt the development of the disease if it is unfavorable. For 10 years since was diagnosed with postthrombotic disease, disability affected 38% of patients.



