Most of the patients faced with this disease in childhood. This contributes to stay in organized groups (kindergartens, schools, boarding schools). In adults, the infectious disease is most difficult. In such a situation, the treatment must be in hospital. Hepatitis a in children and adults can develop when visiting tropical countries.
Features of viral hepatitis A
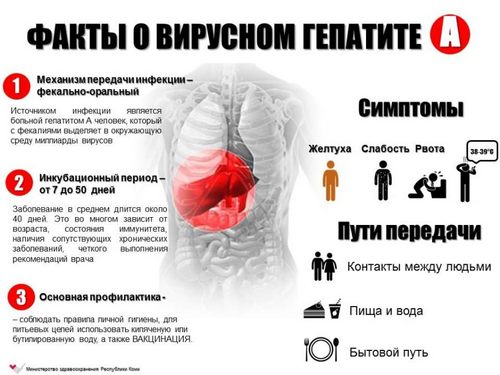
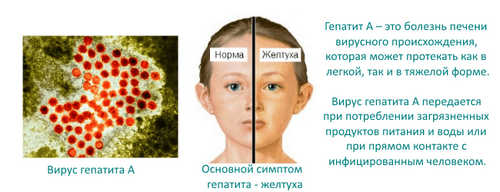
Hepatitis a in children and adults is an infectious disease of viral etiology that occurs in an acute form and is characterized by intoxication and jaundice. This disease is called the disease of dirty hands due to the fact that the disease is transmitted by the fecal-oral mechanism.
Annually in the world there are millions of new cases of hepatitis A. This form of inflammation of the liver occurs is benign. Viruses do not have a direct damaging effects on the body. In most cases, the infectious disease ends in recovery.
It is there recorded the highest incidence.
The percentage of deaths in this pathology is about 0.4%. The symptoms of hepatitis A in children and adults disappear within two weeks.
The ways of human infection
The causative agent is a virus of hepatitis A. It has the following features:
- small size;
- contains RNA;
- does not have a shell;
- capable of long time to persist in the environment (in water and on household items);
- withstands freezing;
- sensitive to disinfectants and boiling;
- replicates within hepatocytes.
A sick person is the main source of infection. The virus with feces gets into soil and water. Human infection occurs by the fecal-oral mechanism, in the use of unboiled water, vegetables, fruit, seafood. Contamination of vegetables and fruits may occur during their cultivation under irrigation with contaminated water or when washing just before use.
The main route of infection – nutritional. Less common symptoms appear after transfusion of blood from an infected person. Possible gender and contact-household transmission. It is characteristic of homosexuals. Infection can occur when swimming in contaminated with the virus reservoirs in the process of accidental water ingestion.
At risk for hepatitis A include the following categories of persons:
- rural drinking unboiled water from wells and captaia;
- children in organized groups;
- the staff of children’s institutions;
- persons working in sewage services and water supply;
- homosexuals;
- users of drugs;
- living together with the sick person;
- staying in the field.
People living in large cities, suffer from this disease less often. This is due to the disinfection of water before supply to the distribution network. By the predisposing factors include poor living conditions, crowding groups, poor personal hygiene, inability to drink boiled water.
The main symptoms of the disease
Symptoms of hepatitis A do not appear immediately after infection. The incubation period is from 14 to 28 days. Early symptoms of the disease Botkin applies General malaise, nausea, weakness, lack of appetite, myalgia, vomiting, mild fever, chills. These symptoms are associated with intoxication. This period lasts up to a week. After him begins the icteric period.
The following symptoms of hepatitis A in children and adults in icteric period:
- discoloration of stool;
- change the color of urine;
- yellowness of skin and sclera;
- pain in upper quadrant right;
- splenomegaly;
- pain in the joints;
- muscle pain;
- itching.
During this period the General condition of patients improved. Symptoms of intoxication are reduced. Jaundice occurs in 5-10 day. The specific sign of the disease jaundice is dark urine. It becomes brown. This is due to the excessive renal excretion of bilirubin and urobilin. Often, patients complain of discoloration of feces. This happens due to the violation of patency of the bile ducts. Hepatitis A may experience bloating, violation of the chair-type constipation, belching.
The infectious disease can result in complications such as:
- biliary dyskinesia;
- inflammation of the gallbladder;
- pancreatitis;
- diabetes mellitus;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- stagnation of bile;
- liver failure.
Diagnostic and therapeutic measures
Diagnosis of hepatitis A includes the detection in blood of specific antibodies, ultrasound of the liver and spleen, General and biochemical blood analysis, urine analysis, visual inspection, survey, palpation of the abdomen. In the presence of hepatitis A treatment can be performed on an outpatient basis or in hospital. Hospitalization is carried out in the presence of complications or the combination of Botkin’s disease with other viral hepatitis. Children under one year and older are also recommended to be hospitalized.

Treatment of hepatitis A involves a diet and bed rest during the period of jaundice, infusion therapy, drink plenty of liquids. To ensure a normal digestion preparations based on lactulose. To prevent stagnation of bile apply spazmolitiki (but-shpa, papaverine). Patients assigned to the diet №5.
Treatment of hepatitis A antiviral drugs is not carried out. Before to treat hepatitis, you should consult with your doctor. To prevent possible complications is very important screening. It aims to identify patients. Screening should be conducted among risk categories. Prevention of hepatitis A is to eat only boiled water, washing fruits and vegetables with clean water, sanitary protection of water sources, hand washing, refuse from swimming in contaminated waters.
To prevent the spread of infection in the outbreak disinfection. Thus, hepatitis a rarely leads to complications. The negative effects of hepatitis A can be attributed to the self and failure to comply with the recommendations of the doctor.



