Due to the fact that people are primarily social, any manifestation of disorders such intimate areas as the allocation system, will depress and reduce the quality of life.
Particularly stressful is the situation when a person has no power over the functions of your body and can not volitional effort to keep one process or another.
In medicine there is a special term – “urgent need” that describes the sudden, overwhelming, extremely strong desire to urinate or defecate. The urge is so strong, we can say – urgent (med. urgent) what is happening even independent urine. To cope with this condition, you must first “know your enemy”.
Distinctive features
You may have noticed that involuntary release of urine occurs when laughing, coughing, heavy lifting. That is, when greatly increased intra-abdominal pressure. In this case, talking about the stressful nature of incontinence.
The imperative urge to urinate and so different, that there is a strong need to immediately empty the bladder, even at low fullness. Characterized by the fact that by limiting fluid intake, the desire to urinate continues to haunt the average every 2 hours, regardless of time of day.

The first step of self diagnosis can be a simple questionnaire:
| Symptoms | The imperative urinary incontinence | Stress incontinence |
| Irresistible desire | There | No |
| Urinating more than eight times a day | There | No |
| Urine when coughing, laughing, physical load | No | There |
| The number of released urine | Rich | Minor |
| The urge at night | There | Rarely happens |
| The ability to postpone urination and to get to the toilet | No | There |
The reasons for the development
Briefly, the process of urination can be represented as follows:
- blood with dissolved substances filtered by the kidneys, as a consequence, urine is formed;
- urine (urine) flows through the ureters and collects in the bladder;
- the selection output occurs at the urethra – urethra.
Leakage of urine from the bladder to impede the sphincters (external and internal muscular constipation). When the muscle of the bladder wall are reduced, and the sphincter relaxes, urine flows freely through the urethra. The need to empty the bladder is caused by signal receptors speak to the brain about fullness (tension), and spinal nerves transmit the feedback signal to decrease. Since the command to contraction of the sphincter can be given arbitrarily, urination can be initiated or terminated at will. Normal urination occurs 5-6 times per day, rarely at night.

Thus, there are two main set of reasons for the development of disease – muscular and neurogenic (associated with the spinal cord and the brain). If the damage is in the brain urination to occur reflexively, without the participation of the human will. As young children, not accustomed yet to the controls.
Disorders in the nervous system can speed up the nerve impulses, and receptors in the smooth muscle of the bladder can react too strongly. There comes the perceived need to reset the ballast when the bladder is not yet full. Such a state of hyperexcitability in medicine called overactive detrusor.
Risk groups
The condition of overactive bladder is found somewhere in 10-15% of adults and has diverse origins.
- Degenerative diseases of the spine.
- Multiple sclerosis.
- A history of stroke, Parkinson’s disease.
- Neuropathy in diabetes.
- The spinal cord compression by the growing tumor or by metastases in lung cancer, breast cancer, prostate.
- Also cervical cancer in women may be accompanied by tumor invasion into the bladder.
- A group of infectious diseases – acute cystitis, urethritis, bacterial prostatitis, pyelonephritis, paranephritis.
- Urolithiasis – presence of stones in the ureter or bladder causing it irritation and imperative urges.
- Malformation of urinary system, traumatic or genetically determined.
- Some medications can increase urine output and to affect the bladder muscles.
Other types of incontinence
Once again I would like to emphasize that in urgent urinary incontinence in people of both sexes cause is primarily inadequate signal of fullness of the bladder, while its function of the sphincter is normal. They are not weakening and are able to hold urine inside, if only the nervous system does not give the command “reset”.

The mechanism of imperative urinary incontinence
Women are more susceptible to stress incontinence. First, men inner of the two sphincters of the urethra developed stronger than in women. Secondly, during pregnancy and childbirth the pelvic floor muscles women experience a strong tension, stretch and weaken. In menopause also contributes to this reduction of estrogen. Multiple or rapid childbirth, the weakening of the tone of the muscles and ligaments with age result in drooping of internal organs, which affects functions of the bladder. In addition, the urethra in women is wider and shorter, which contributes to its frequent infections and eventual defeat of the upper urinary tract.
Should have several types of urinary incontinence, as they all have different tactics of treatment.
Mixed incontinence is a combination, often is a combination of stressful and imperative incontinence.
The postoperative. In men, the result of surgery on the prostate gland and urethra. This could include removal of the prostate for cancer or benign tumors, surgery for urethral trauma. The effects of surgery in the form of incontinence can in the time pass on its own or will require medical treatment, physical therapy, fitting of artificial sphincter. In women removal of the uterus or ovaries, unnatural childbirth (caesarean section), which causes the weakening or injury of the bladder neck.
Incontinence from overflow. On the background of decreased sensitivity of the mechanoreceptors in the bladder wall there is no desire to visit the toilet, although detrusor is already full. When the fluid volume exceeds the cumulative capabilities of the organ, there is involuntary urination. The reason for the insensitivity can be diseases of the nervous system, spinal injury, nerve damage in diabetes. Men to the entire urinary tract can be squeezed enlarged prostate (in adenoma) or tumor in the urethra that impedes the flow of urine and the bladder remains constantly full.
Temporary incontinence – is when the effect of factors that caused its appearance – acute cystitis may constipation, strong alcoholic intoxication.
Diagnosis
Because the symptoms of incontinence are obvious enough, then pre-diagnose the majority of patients, conducting a survey, inspection, and on the basis of clinical analysis of urine.
External examination palpate the abdomen, determining its intensity, the location of the internal organs. For women necessarily gynecological examination for men digital rectal.
The ability of the bladder to empty determined by a transabdominal study. Is very informative and complex urodynamic studies, which has many points of application (see infographic). UDI consists of numeric data and graphical indicators.

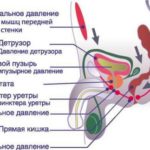
Urodynamic study in men (A) and women (B)
Also to confirm neurogenic cause of the disease, you may need to consult a neurologist, which evaluates the functioning of the nerves associated with the urinary tract. It nerves the lumbar and sacral segments. Verified by skin sensitivity, anal, Bulbo-cavernous and cough reflexes.
A survey of the patient, among other things, is aimed at clarifying the following points: the frequency of urination, the presence of imperative urgency, leakage of urine, its volume. To this end, the patient is “diary” not less than three days before the examination where marks each episode, especially the ratio of daytime and nighttime urination.
Treatment
The diversity of the causes of the syndrome of overactive bladder and imperative urge to urinate allows you to apply the following treatment methods:
- Conservative.
- Medication.
- Operational (surgical).
Among conservative treatment methods are often used:
- A change of diet – excludes products, irritating the bladder – sharp, sour, salty, coffee, alcohol.
- Restructuring of behavioral reflexes – for example, the patient always goes to the toilet before leaving the house, “on track”. In this case, it is recommended to gradually get rid of this, once again not to provoke the urge to “habit”.
- Training of the bladder – conscious increase the time between urination. This process is gradual and requires strong control of the will of the patient.
Medical treatment is directed at the neurogenic causes of disease. In the Central nervous system drugs are designed to strengthen the inhibitory effect on the contraction of the bladder. Mostly they affect the neurotransmitters – substances that transmit signals between nerve cells.
In the peripheral nervous system the doctor will “aim” on the receptors in smooth muscles of the urethra and detrusor. The main group of drugs – anticholinergics, blocking the muscarinic receptors of the bladder. And today these drugs occupy a leading position in the treatment.
| Drug | The degree of rekomendowane | ||
| I (the highest) | II | III | |
| Antimuscarinic drugs | |||
| Tolterodine | Yes | ||
| Trospium | Yes | ||
| Solifenacin | Yes | ||
| Darifenacin | Yes | ||
| Propantheline | Yes | ||
| Atropine, hyoscyamine, | Yes | ||
| Drugs acting on the channels of cell membranes | |||
| Calcium channel blockers | Yes | ||
| Agonists of potassium channels | Yes | ||
| Drugs with mixed mechanism of action | |||
| Oxybutynin | Yes | ||
| Propiverine | Yes | ||
| Dicyclomine | Yes | ||
| Flavoxate | Yes | ||
| Antidepressants | |||
| Imipramine | Yes | ||
| DULOXETINE | Yes | ||
| Blockers alpha-adrenergic receptors | |||
| Alfuzosin | Yes | ||
| Doxazosin | Yes | ||
| Prazosin | Yes | ||
| Terazosin | Yes | ||
| Tamsulosin | Yes | ||
| The beta-adrenoceptor | |||
| The terbutaline (beta-2) | Yes | ||
| Salbutamol (beta-2) | Yes | ||
| UM-178 (beta 3) | Yes | ||
| Toxins | |||
| Botulinum toxin (neurogenic pathology) injections into the bladder wall | Yes | ||
| Botulinum toxin (idiopathic pathology) injections into the bladder wall | Yes | ||
| Capsaicin (neurogenic pathology), the introduction into the bladder through a catheter | Yes | ||
| Resiniferatoxin (neurogenic pathology), the introduction into the bladder through a catheter | Yes | ||
| Other groups of drugs | |||
| Baclofen, subarachnoid | Yes | ||
Depending on the organ lesions such surgical intervention:
- On the spine when injury or a herniated disc of the lumbosacral spinal cord, removal of meningioma.
- Indirect impact – through the intersection of the nerves responsible for the disturbed act of urination, for example, the third pair of sacral nerves, the destruction of the pudendal nerve.
- Switching innervation of the bladder on the nerves of a segment of the small intestine.
- The implantation of a generator of radio-frequency stimulation of the bladder wall.
Correctly identified causes of the disease and an integrated approach to therapy – the key to successful treatment.



