The development of radiology and the development of methods of diagnosis of renal pathology has, since the forties of the twentieth century to introduce into medical practice the ways to study the structure and functional capacity of the urinary organs.
Almost every major city there are private clinics and laboratories of the type “Invitro” who offer their services on the survey.We will try to understand the possibilities of this method of diagnosis, as urography, find its shortcomings.
Urography call any x-ray examination of the urinary organs, with mandatory confirmation of visual changes in images (x-rays), including the structures of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, urethra.
Some authors believe a more appropriate term “pyeloureterostomy”. It actually includes x-ray inspection of all mochevyvodyashih tract, clarifies the scope of the procedure. Others stop at “urography of the kidneys”, if we are talking only about the isolated study of renal structures.
In the appointment of “imaging” the doctor expects the layered images of the body to Refine the localization and size of lesions of organs with a different penetration depth of x-rays. The series of images allows you to select the optimal image.
Patients would not pay attention to it, but when you pay for a diagnosis at a private clinic, the cost will vary, this should be ready to clarify in advance. Moreover, you should pay attention to what kind urography want to use.
Currently used:
- review;
- excretory urography (intravenous).
Each method has its indications and negative sides.
The value of the review urography
Review the kidney actually involves bony structures of the spine, part of the abdominal organs, soft tissue.
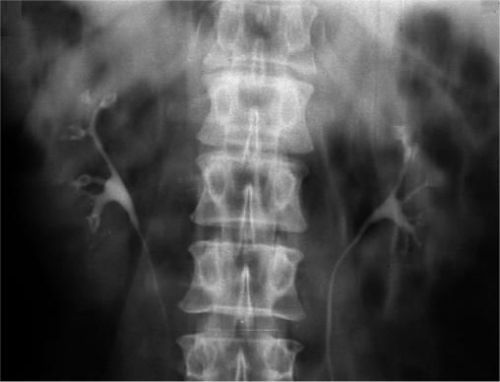
This is a standard examination method, which allows to obtain a minimum of information about:
- the location of both kidneys;
- large concretions (stones);
- gross change in the structure, contours, sizes.
Cup-pelvis-plating apparatus of the kidneys in the review urography not visible
This type of survey is usually used in primary diagnostics. It does not require injection of contrast.
Excretory urography
The method is carried out with obligatory use of radiopaque substances. The essence of the method: intravenous (bolus or infusion), introduced the medication clearly visible under x-rays. He quickly accumulates in the urinary system. As the processing and allocation of kidneys are completely filled cups and pelvis, then the substance passes into the ureters, the bladder and the urethra.
Controlling the process time selection can make the best pictures of these structures, which get much more information than a review urography. Using established standards the first day of the contrast, it is possible to register the delay in one of the kidneys and, consequently, to estimate its functional capacity.
Requirements contrast
From a choice of contrasting substances depends on the quality of the resulting image, the accuracy of the information about the pathological changes.
The right drug must not:
- “leave” and accumulate in the tissues;
- to participate in the General metabolism;
- to have toxic properties.
Used finished products with maximum radiographic visibility with minimal allergenic properties.
Often apply products that contain iodine. A day or two before the examination the patient is supposed to do a test to detect individual sensitivity. If rash, itching, swelling of the drug is strictly contraindicated.
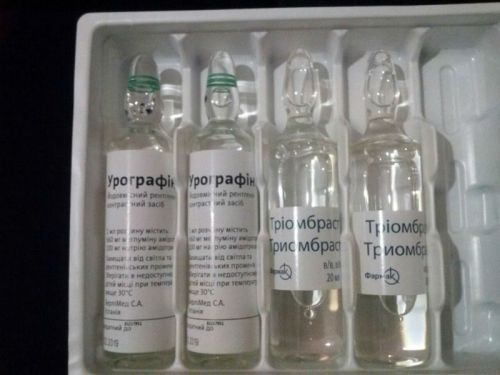
In practice are used:
- Kardiotrast,
- Triombrast,
- Visipak,
- Urografin.
The drug is administered slowly into a vein bolus or a drip
How is the preparation for urography?
A prerequisite for the readiness of the patient for urography is thorough cleansing of the intestines from gas and feces.
For this preparation for urography includes tips:
- 3 days to stop taking carbohydrate food, foods causing flatulence and fermentation in the gut (black bread, sparkling water, eat vegetables and fruits, yogurt, cottage cheese);
- make the day before laxative;
- to do an enema in the evening and 3 hours before the test;
- make the Carbol or activated charcoal, chamomile.
The difficulty lies in the fact that the possibility of complete clearance depends not only on the nature of power, but also from individual characteristics of the intestine, the liver, the patient’s age.
- For young people important diet for elderly with intestinal – enema.
- Debilitated bedridden patients swallow air in large volume, so they are encouraged more to walk around the house in the ward.
- Generally out-patients are better prepared because they are not deprived of the opportunity to move a lot.
- We have to consider that the use of iodine-containing substances impairs the ability of the liver to absorb intestinal gas.
Specifically, how to prepare for the exam will tell the doctor. There is no common opinion can I eat on the morning of the procedure.
Some prefer to carry it on an empty stomach, others do not exclude light Breakfast. This is especially true for children and patients with diabetes. It is proved that the hunger only intensifies the formation of gas.
If you cannot eliminate gases, there is a method of filling the intestine with water for displacement of the gas bubble. The image of the renal structures is improved. In medical institutions asked to sign their consent to the study. Before entering the x-ray room need to remove all metal objects. Often offer to change into a gown.
Patients expressed fear and anxiety give sedatives. After the procedure for accelerated elimination of contrast substances it is recommended to drink plenty of liquids.
Who is a intravenous urography?
Excretory urography of the kidneys and lower urinary organs assigned patients to identify and eliminate:
- congenital anomalies of the urinary system;
- chronic inflammatory diseases;
- neoplastic processes;
- vesical functional changes in children;
- kidney stone disease with bouts of renal colic;
- prolapse of the kidney;
- hydronephrosis;
- of traumatic injury.
The study is carried out upon detection of the patient such vague symptoms, such as:
- hematuria;
- partial or complete blockage of the ureter;
- unusual mobility of the kidneys.
Contrast urography necessary in the preparation for surgery and monitoring after surgery.
When and how to make pictures determined by the radiologist. They are usually held from the first minute you first intervals of 5-7 minutes, then 12-25 minutes in an hour.
If the drug is injected slowly drip, radiographs are performed after 45 minutes, an hour. With the introduction of the contrast agent, patients may feel fever, moderate pain in Vienna, at least there is nausea or dizziness. The unpleasant symptoms disappear within a few minutes.
What are the contraindications?
Contraindications are related to a possible reaction to contrast, worsening of certain diseases.
Such conditions are possible when:
- identified prior to application of contrast allergic reaction to the drug;
- pregnancy in any trimester;
- unclear internal bleeding;
- the identification of reduced blood coagulability;
- •renal failure with impaired renal excretory function;
- the acute phase of glomerulonephritis;
- thyrotoxicosis;
- pheochromocytoma (adrenal tumors).
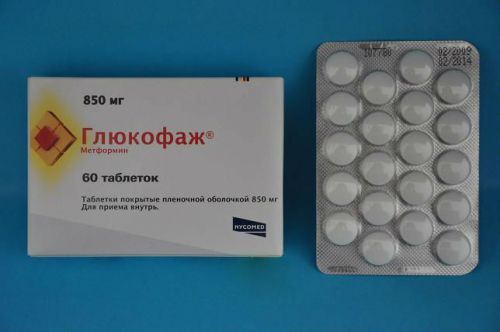
Particular attention is drawn to the examination of patients with diabetes taking the drug Glucophage from the group of biguanides. It contains a substance Metformin, capable of connecting to iodine contrast to cause a sharp increase in the patient’s blood level of lactic acid and cause acidosis.
Glucophage should, in consultation with an endocrinologist to cancel two days before x-ray examination
For patients with diabetes it is especially important to ensure enough preserved renal function, the contrast was promptly removed from the body.
What if urography is contraindicated?
If the contraindications, the doctor takes the decision to replace the research method on the other. Perhaps they will be less informative, but safe for the patient.
In such cases it is recommended to do ultrasound examination of the kidneys, conduct computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance examination (Mr).
The most expedient way is MRI urography or magnetic resonance layer-by-layer study of the kidneys.
Competitive examination methods of
When magnetic resonance study on magnetic field and radio frequency waves. Computer allows to obtain the required image at different depths.
MRI urography help diagnose:
- the size of the kidneys, thickness of cortex and medulla;
- the anatomical structure of the vascular bundle, cups and pelvis;
- the density of the fabric structure;
- cystic changes;
- tumor;
- dynamics of growth of cysts or tumors;
- the functional capacity of the kidneys;
- lesions of the urinary ways.
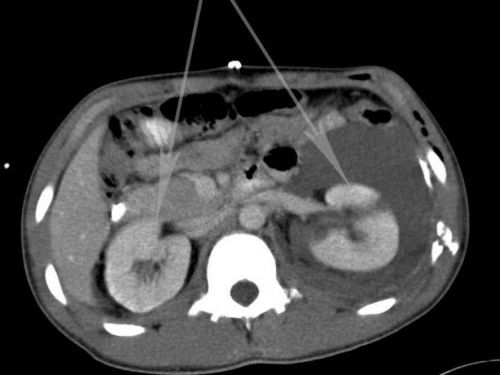
Diagnostics can be performed without contrast, and with the introduction of a contrasting substance. It is believed that the second option improves diagnosis by 15%.
For CT typical top view of the optimum “cut” at the level of the kidneys
For contrast in MRI use products containing salt of gadolinium. It is a soft metal with soluble salts. Is considered to be little toxic. Has the ability to penetrate into cells and amplify the magnetic signal.
Possible application:
- Primavista,
- Of Magnevist,
- Dotarem,
- OmniScan.
Cross-reactions to iodine was observed. Also, as with excretory urography beforehand put skin test to detect allergies.
Methodology in recent years is widely used in the early diagnosis of tumors. But if there are contraindications for urography can trust its results.

Meccinna cystography is chosen by the physician with the necessary careful examination of the bladder. Method is to install a catheter through the urethra into the ureter and injection into the bladder of radiopaque substance.
Modern devices allow you to monitor picture by mictional cystoscopy to monitor
The first picture is performed on the background-filled bladder. Then the patient is instructed to urinate and in the process performs the second radiograph.
The method is designed to detect vesicoureteral reflux. In the process of urination straining muscle, the detrusor, increased intravesical pressure. If the sphincters of the urinary tract is weak and cannot cope with deterrence, the contrast up into the ureters. They are visible in the second picture.
Select if required, replacement method excretory urography can only specialist. MRI does not expose the patient to radioactive operation, therefore can with great indication to be used for examination of the child.
Varieties urography
To study the patency of the urinary tract, including the ureters are applied antegrade (descending) and retrograde (upward) pyeloureterostomy.
Retrograde urography is performed on only one side. With the help of a cystoscope into the ureter a catheter is inserted a desired size (taking into account the degree of narrowing). Through it cautiously filled with contrast pelvis and ureter. Typically, you enter an adult about 5 ml.
Experience has shown that bilateral catheterization is poorly tolerated by patients due to spasm of the pelvis and cups. To prevent pain solution pre-warmed to body temperature, the introduction is very slow.
Images are held in a horizontal position the patient on the abdomen and back, as well as in the vertical. It is necessary to completely fill the cups in all parts of the kidneys.
In an hour from the time of introduction of contrast it is recommended to repeat the to assess the evacuation capacity of the pelvis and ureters.
Features antegrade pyelography
Antegrade pielografia allows you to explore upper urinary tract.
There are 2 option depending on the method of administration of contrast:
- percutaneous;
- using pyelo-(nephrotoxicity)stoma.
Percutaneous method is indicated when other methods did not help to identify the disease of the kidney and upper urinary tract. For example, if excretory urography is not the selection of a contrast agent due to disturbed kidney function or if you can’t perform retrograde urography in connection with:
- the reduced size of the bladder;
- stone in the ureter;
- a sharp narrowing;
- the compression of the outflow pathways by the tumor.
Percutaneous antegrade pyelography is mostly for suspected hydronephrosis, where other diagnostic methods do not cause confidence in the identified pathology. This method allows not only to identify hydronephrosis, but also to detect its cause (stone, scarry stricture, tumor).
Usually before antegrade urography produce review images of the venous and excretory urography. They need to select the site of puncture of the pelvis.
How is the procedure antegrade urography?
The patient is placed on stomach, on the x-ray table. Locally injected anesthetic substance into the skin and muscles. The puncture needle is a puncture in the projection point of the pelvis of the kidney. To control the position of the needle in difficult cases the necessary x-ray.
Another reference point is the receipt from the syringe colored urine when administered intravenously 10 minutes before you puncture the blue of the Indigo Carmine solution.
Of pelvis completely remove urine (send it to a testing lab), and a syringe in the kidney injected contrast agent in a volume of 10 to 20 ml.
Then produced images of the patient on the abdomen, on the side vertically.
After that, the syringe and remove all the contents of the pelvis and the withdrawal of the needle from the body.
After surgery leave on the early days of artificial nephrostomy for rinsing the kidney, introduction to pelvis of antimicrobials and the control urography
The introduction of contrast pyelo– nefrotoksicheskoe drainage is used mainly in the postoperative period, especially when drainage is left in the pelvis for this purpose. The end of the tube is treated with alcohol and secured with a clamp.
To introduce contrast it is possible not earlier than 14 days after the operation. Usually it is enough 6-8 ml. A greater number can cause hyperextension of the pelvis.
If the tone of the ureters saved, then a minute later observed the promotion of contrasting substance in the lower parts. Latency indicates reduced motor function.
Medical reviews operating of urology says about the experience of conducting percutaneous antegrade urography in the diagnosis of polycystic kidney disease, hydronephrosis in children.
The authors describe interesting diagnostic phenomenon: on the background of antegrade pyelography doctors observe after 15-20 minutes, the excretion of contrast medium in the opposite kidney. This is due to hit parts of the drug in the General circulation, and confirms quite a good excretory function of the other kidney.
What are the advantages of intravenous urography and what weaknesses?
To excretory urography of the kidneys must be approached with the understanding of its positive and negative properties.
When compared with the retrograde method can be considered an advantage:
- obtaining information about the functional and morphological state of the kidneys on both sides;
- the same applies to the bladder;
- no need for pre-cystoscopy;
- virtually painless examination form;
- the opportunity to examine patients with injuries in serious condition.
A method of excretory urography is preferable to use for children
After retrograde method possible:
- fever,
- chills,
- increased symptoms of intoxication.
The disadvantages include:
- fuzzy image contrast of the shadows;
- the reduced amount of urinary tract;
- non-simultaneous and unequal filling of the cups;
- picture of the ureters cut sections;
- the inability to detect early small changes in the structure of the kidneys.
Depending on the completeness and quality of the obtained examination information, the diagnosis and the chosen method of treatment. All of the methods of examination of the kidneys for its own good. Patients should remember that it is better to entrust the execution of urography experienced experts and also clinical institutions that are involved with the diagnosis and treatment of urological pathology.



