To describe changes associated with the act of urination, use special terms. Strangury – difficulty in urination – accompanied by a number of diseases in persons of any age and gender.
It hard to urinate may lead to congenital or acquired pathology.
Sometimes the condition develops gradually, but there are diseases which are complicated by acute urinary retention. Treatment depends on the cause, the therapy is always the recovery of the outflow of urine with bladder catheterization or operative intervention – epicystostomy.
If difficult urination the bladder is emptied completely, it is a conservative therapy, for example, when urethritis, cystitis, BPH, infections, sexually transmitted.
In what diseases is found difficult urination
The most common cause is prostatic hyperplasia in men older than 60 years, although the pathology is diagnosed at a younger age.
Experts believe that for the complaints is more important than the volume of the prostate as the direction of the growth of adenomatous nodes/tumors and the degree of compression of the urethra.
Women have it hard to urinate may cause cancer or uterine fibroid of large size, as well as the weakening of muscle tone of the pelvic floor with prolapse of organs or overlap of the meatus tissue of the vagina.
Incomplete emptying of the bladder initially there is no pain. Muscle layer of organ hypertrophies, the volume can reach 800 ml or more (at a rate of 300-350 ml).In the future, this condition will lead to the formation of diverticula, and chronic cystitis. More serious complications include hydronephrosis, recurrent urinary tract infection and chronic renal failure.
Shortness of urination occurs in any obstruction of the lower urinary tract:
- the tumor of the prostate, bladder, uterus and urethra;
- congenital valves and diverticula;
- matasanos (narrowing of the external opening of the urethra);
- pronounced phimosis;
- stricture of the urethra;
- blockage of urine outflow by calculi, protein or salt plug, blood clot;
- acute inflammatory process in the lower urinary tract: urethritis, cystitis;
- neurological diseases in which impaired conduction of nerve impulses;
- complications of diabetes (polyneuropathy);
- trauma, tumors, secondary metallicheskie the spinal cord;
- complications after surgery on the organs of the urogenital related to the damage of the detrusor and the development of fibrous tissue.
Sometimes difficulty urinating concerned about pregnant women because the growing uterus puts pressure on the bladder, is a temporary phenomenon, and if changes in the urine, not, worry much not worth it.
According to observations, young people cause “squeezing” of urine – migratory calculus lodged in the urethra or inflammation on the background of the venereal disease; in elderly adenoma or neoplastic process. Malformations that impede flow of urine, diagnosed in childhood.
What are the symptoms besides the shortness of urination, indicate pathology
As a rule, urinary disorders (with the exception of the stuck stone, clot, foreign body) develops gradually appear: difficulty urinating, weak urine flow, feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder, frequent urge to the toilet. An increased amount of residual urine promotes the accession of infection. Urine volume after micturition of more than 200 ml can lead to hydronephrosis of the kidneys and chronic renal failure, so at the first sign of trouble it is important to consult a doctor.
Acute cystitis and urethritis:
Blood often appears at the end of urine and indicates involvement of the cervix in the inflammatory process.
Urolithiasis and stuck the calculus, in addition to the above complaints, you may be laying the stream of urine, which is associated with the movement of the stone. Temperature indicates inflammation of the member.
Tumor of any localization at an early stage any demonstration has not, and only periodic preventive examination can help in early diagnosis.
Difficulty urinating in cancer of the body of the pelvis evidence in favor of the prevalence of cancer process.
In addition, pay attention to the following signs and symptoms:
- reduction of body weight;
- causeless temperature, mainly in the evening hours;
- poor appetite;
- weakness, fatigue, sweating;
- cameo appearance of blood in the urine (cancer of the bladder, urethra, prostate);
- dull pain in the abdomen;
- pale skin against the background of anemia.
When uterine tumors or fibroids typical dysfunctional uterine bleeding.
Phimosis and matasanos diagnostic difficulties can not imagine, as the pathology is visible for external inspection at the urologist.
What diagnosis is necessary and difficult urination
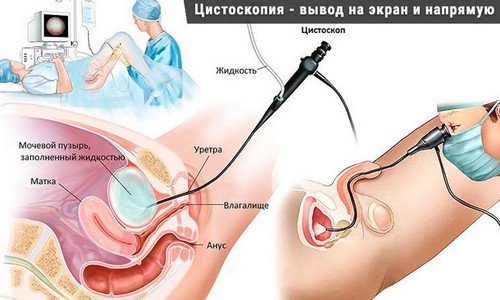
In disorders of urination and inflammation is indicative of the General analysis of urine:
- leukocyturia;
- bacteriuria;
- protein;
- hematuria.
Be aware that in some diseases, changes in the urine may not be or the inflammatory process will be secondary.
Upon discharge from the urethra shows the microscopic examination of biological material on STIs for correct diagnosis it is possible to conduct PCR-based diagnostics.
The abundance of salts and difficult urination and red blood cells indicates a dysmetabolic nephropathy or calculus.
Increase level of urea and creatinine confirmed the impairment of renal function. Biochemical parameters are taken into account, if the introduction of contrast; in severe chronic renal failure intravenous urography is contraindicated.
In men over 45 years of age, if there is suspicion on the tumor of the prostate, before doing the blood test for the tumor marker PSA. In severe inflammation the result can be above normal (4 ng/ml), which requires additional instrumentation of the study: TRUS, MRI of pelvic organs. Verify their purchases prostate cancer through transrectal biopsy.
For women there is a special tumor markers, but they are not widely used as blood for prostate specific antigen in men, therefore, according to the testimony perform MRI as the initial diagnostic – ultrasound examination of organs of small pelvis, uterus and appendages. The final diagnosis is established by salpingostomy and biopsy.
The gold standard in establishing the causes of obstruction of the lower urinary tract is urethrocystoscopy: with this imaging technique can reveal a tumor of the bladder or urethra, strictures, diverticula, valves, growths, warts, etc.
The functional ability of the kidney can be clarified by means of intravenous urography down zistografii; method is suitable for confirmation of urolithiasis, prostate adenoma, chronic pyelonephritis, hydronephrosis of the kidneys, etc.

The treatment of difficult urination
For the treatment of BPH with a weak stream of urine or dripping urination there are enough medications. Before choosing the tactics of the doctor is required to assess prostate volume, residual urine and the dynamics of conservative therapy. If the effect of drug treatment is insufficient, it is possible to perform the operation. Less invasive is the TUR – transurethral resection of the prostate. If comorbidity or the severity of the condition does not allow you to perform transurethral resection or open prostatectomy, the bladder is removed the drainage tube – epicystostomy. The measure may be temporary – until the normalization of condition or constant, if there is a high probability that the patient will not survive large operations or anesthesia.
Tumors involve various combinations of surgical intervention, chemotherapy and radiation.
When stricture of the urethra, depending on its localization, the extension of the urethra can be achieved by begerovaya, run a TOUR or plastics.
Calculus in the urethra can be removed during ureteroscopy, in the urinary bladder with the help of cystolithotripsy.
Phimosis, valves, diverticula, cysts, warts, violates the outflow of urine, mean surgery.
If the cause of difficult urination – inflammatory process, antibiotic therapy is carried out with sensitivity to the antibiotics prescribed uroseptic, aseptic instillation of drugs into the urethra or bladder.
Neurological disordersassociated with retention of urine, difficult to treat. For many spinal patients, the only way is to install a permanent catheter or catheterization, as needed every 4-6 hours, or operating epicystostomy. The method of sacral nerve stimulation, in which implanted electrodes, is used less frequently.
The weakening of the pelvic floor muscles, prolapse of the anterior wall of the vagina, prolapse of the uterus treated by gynecologists. In severe pathology performs the surgery, some women helps wearing the special tools – necessary to discontinue entered vnutrivlagalischnye and restore normal anatomy.




What are the symptoms besides the shortness of urination, indicate pathology
Regards for this post, I am a big fan of this internet site would like to continue updated.