HIV infection is a disease caused by human immunodeficiency virus, characterized by acquired immunodeficiency syndrome, contribute to the occurrence of secondary infections and malignancies in Association with the deep depression of the protective property of the body.
HIV infection has many variants of course.
The disease may only last a few months or stretch out to 20 years. The main method of diagnosis of HIV infection is the detection of specific antiviral antibodies and viral RNA. Currently, the treatment of patients with HIV is with antiretroviral drugs can reduce the replication of the virus.
HIV infection
HIV infection is a disease caused by human immunodeficiency virus, characterized by acquired immunodeficiency syndrome, contribute to the occurrence of secondary infections and malignancies in Association with the deep depression of the protective property of the body. Today the world celebrates the HIV pandemic, the incidence of the world population, particularly countries in Eastern Europe is growing steadily.
Characterization of the pathogen
The human immunodeficiency virus DNA belong to the genus Lentivirus of the family Retroviridae. There are two types: HIV-1 is the major causative agent of HIV, the cause of the pandemic, the development of AIDS. HIV-2 is rare type found mostly in West Africa. HIV is an unstable virus dies Quickly outside the body of the carrier, sensitive to the effects of temperature (reduces infectious properties at a temperature of 56 °C killed in 10 minutes when heated up to 70-80 °C). Well preserved in blood and blood products prepared for transfusion. Antigenic structure of the virus is very variable.
Reservoir and source of HIV infection is the people suffering from AIDS and the media. Natural reservoirs of HIV-1 not detected, it is believed that the natural host in nature are wild chimpanzees. HIV-2 is transferred to the African apes. Susceptibility to HIV infection in other animal species is not observed. The virus is found in high concentrations in the blood, semen, vaginal secret glands and menstrual secretions. Can come from breast milk, saliva, lacrimal secretions and cerebrospinal fluid, but these biological fluids represent a lower epidemiological risk.
The probability of HIV transmission increases when there is damage to the skin and mucous membranes (trauma, abrasion, cervical erosion, stomatitis, periodontal disease, etc.). HIV is transmitted via blood-contact and bioconductor mechanism in a natural way (through sexual contact and vertically from mother to child) and artificial (mainly implemented with hemoperitoneum the transmission mechanism: when the transfusions, parenteral administration of substances, traumatic medical procedures).
The risk of HIV during a single contact with a carrier is low, regular sexual intercourse with an infected it greatly increase. Vertical transmission of infection from sick mother to child is possible during pregnancy (through placental barrier defects), and in childbirth, after contact of the child with the mother’s blood. In rare cases, fixed postnatal transmission through breast milk. The incidence among children of infected mothers up to 25-30%.
Parenteral infection occurs through injection with needles contaminated with blood of HIV-infected persons, transfusion of contaminated blood, unsterile medical manipulation (piercing, tattoos, medical and dental procedures, producing tools without proper treatment). Contact-household path HIV is not transmitted. Sensitivity to HIV infection is high. The development of AIDS in individuals older than 35 years, usually in a shorter time since infection. In some cases there is immunity to HIV, which is associated with specific immunoglobulins A, present in the mucous membranes of the genitals.
Pathogenesis of HIV infection
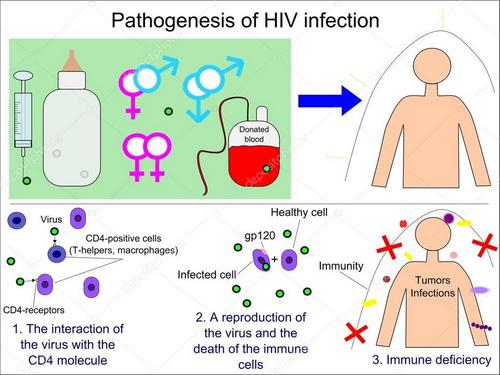
The human immunodeficiency virus if it enters the blood introduced into the macrophages, microglia and lymphocytes which are important in the formation of the immune responses of the body. The virus destroys the ability of the immune Taurus to the recognition of its antigens as foreign, occupies a cell and begins to reproduce. After the release of the virus multiply in the blood, a host cell dies and the viruses infect the healthy macrophages. The syndrome develops slowly (years), waves.
The first time the body compensates for the mass death of immune cells, producing a new, over time the compensation becomes insufficient, the number of lymphocytes and macrophages in the blood is greatly reduced, the immune system is destroyed, the body becomes vulnerable both in relation to exogenous infection, and the bacteria that live in the organs and tissues in norm (leading to development of opportunistic infections). Moreover, it undermined the protection mechanism of the reproduction of defective blastocito – malignant cells.
The population of the virus of immune cells often causes a variety of autoimmune conditions, in particular typical neurological disorder in the result of autoimmune destruction of narocito, which can develop even before manifest clinic of immunodeficiency.
The classification of HIV
The clinical course of HIV infection distinguish 5 stages: incubation, primary symptoms, latent, stage of secondary diseases and terminal. Initial manifestations may be asymptomatic, in the form of primary HIV infection and may also be combined with secondary diseases. The fourth stage depending on the severity is divided into periods: 4A, 4B, 4C. Periods are phases of progression and remission vary from occurring antiretroviral therapy or lack thereof.
The symptoms of HIV infection
1. Stage incubation can range from 3 weeks to 3 months, in rare cases extended to years. At this time there is active replication of the virus, but the immune response to it yet. HIV incubation period ends or a clinical picture of acute HIV infection, or appearance in the blood of HIV antibodies. At this stage the basis for the diagnosis of HIV infection is detection of virus (antigens or particles, DNA) in serum.
2. Stage of primary manifestations characterized by the manifestation of the body’s response to active replication of the virus in the form of clinical acute infection and immune response (production of specific antibodies). The second stage may be asymptomatic, the only sign of growing HIV infection will be positive on the serological diagnosis of antibodies to the virus.
The clinical manifestations of the second stage occur type acute HIV infection. Start of acute, observed in 50-90% of patients three months after infection, often preceding the formation of HIV antibodies. Acute infection without secondary pathology is quite varied current: may include fever, a variety of polymorphic rash on the skin and visible mucous membranes, polylithionite, pharyngitis, lierally syndrome, diarrhea.
In 10-15% of patients with acute HIV infection occurs with the accession of secondary diseases due to decreased immunity. It could be tonsillitis, pneumonia of various origins, fungal infections, herpes etc.
Acute HIV infection usually lasts from several days to several months, averaging 2-3 weeks, after which the vast majority of cases, enters a latent stage.
3. Latent stage is characterized by gradual increase of immunodeficiency. The death of immune cells at this stage kompensiruet their increased production. At this time, to diagnose HIV using serological tests (the blood contains antibodies to HIV). Clinical sign may be an increase in multiple lymph nodes from different, unrelated groups, excluding the inguinal lymph nodes. Thus other pathological changes in the enlarged lymph nodes (painful, changes in the surrounding tissue) were observed. Latent stage can last from 2-3 years, up to 20 or more. On average, it last for 6-7 years.
4. Stage of secondary diseases is characterized by the occurrence of associated (opportunistic) infections viral, bacterial, fungal, protozoal origin, malignant tumors on the background of pronounced immunodeficiency.
Depending on the severity of the secondary diseases distinguish 3 periods of flow.
- 4A – loss of body weight exceeds 10%, there are infectious (bacterial, viral and fungal) destruction of epithelial tissues (skin and mucous membranes). Reduced performance.
- 4B – the loss in weight of more than 10% of the total body mass, prolonged thermal response, the possible prolonged diarrhea without organic cause, can join pulmonary tuberculosis, infectious diseases recur and progress, revealed a localized Kaposi’s sarcoma, hairy leukoplakia.
- 4B – there is a General cachexia, secondary infection becoming generalized form, the candidiasis of the esophagus, respiratory tract, Pneumocystis pneumonia, extrapulmonary forms of tuberculosis, disseminated Kaposi’s sarcoma, neurological disorders.
Podstudio secondary diseases go through phases of progression and remission vary from occurring antiretroviral therapy or lack thereof. In the terminal stage of HIV infection are secondary diseases that have developed in a patient irreversible, interventions lose their effectiveness, the lethal outcome occurs after a few months.
The course of HIV infection is quite diverse, not always all stage, certain clinical signs may be absent. Depending on the individual clinical course of the disease duration can be a few months, and 15-20 years.
Peculiarities of a clinical course of HIV infection in children
HIV in early childhood contributes to the delay of physical and psychomotor development. Recurrence of bacterial infections in children mark more often than adults, there are lymphoid pnevmonity increase the pulmonary lymph nodes, various encephalopathy, anemia. Frequent cause of child mortality in HIV infection is a hemorrhagic syndrome resulting from severe thrombocytopenia.
The most frequent clinical manifestation of HIV infection in children is the delayed rate of psychomotor and physical development. HIV infection acquired by children from their mothers ante – and perinatal leaking noticeably heavier and faster progresses, unlike that of the children infected after a year.
Diagnosis of HIV infection
Currently, the main diagnostic method in HIV infection is detection of antibodies to the virus, produced primarily using the method of ELISA. In the case of a positive result examined the blood serum using the method of immune blotting. This allows you to identify antibodies to specific HIV antigens that is a sufficient criterion for final diagnosis. Failure to identify with the help of blotting antibodies characteristic molecular weight, however, does not exclude HIV. In the incubation period of the immune response to the introduction of the virus has not yet been formed, and in the terminal stage as the result of pronounced immunodeficiency antibodies cease to be produced.
If you suspect HIV and lack of positive results of immune blotting effective way to detect particles of RNA viruses is PCR. Diagnosed by serological and virological methods HIV infection is an indication for dynamic monitoring of the immune status.
Treatment of HIV infection
Therapy of HIV-infected persons involves constant monitoring of the immune status of the organism, prevention and treatment of secondary infections occurs, control over the development of tumors. Often HIV-infected persons need psychological help and social adaptation. At the present time in connection with a high prevalence and high social importance of the disease in the state and worldwide support and rehabilitation of patients, expanding access to social programs that provide medical assistance to the sick, facilitating for, and improve the quality of life of patients.
To date, the predominant causal treatment is the appointment of drugs that reduce reproductive capacity of the virus.
Antiretroviral drugs include:
- NRTI (nucleoside transcriptase inhibitors) different groups: zidovudine, stavudine, zalcitabine, didanosine, abacavir, combination of drugs;
- Ntot (nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitors): nevirapine, efavirenz;
- protease inhibitors: ritonavir, saquinavir, darunavir, nelfinavir, and others;
- inhibitors of the merge.
When making the decision to start antiviral therapy, patients should remember that the use of drugs is carried out for many years, almost for life. The success of the therapy depends on strict adherence to recommendations: timely, regular medication in the correct dosage, adherence to the prescribed diet and strict regime.
Emerging opportunistic infections are treated in accordance with the rules effective against that pathogen therapy (antibacterial, antifungal, antiviral agents). Immunostimulating therapy in HIV infection does not apply because it contributes to its progression, cytotoxic agents appointed by malignant tumors, inhibit the immune system.
HIV treatment includes bracing and supporting the human body (vitamins and biologically active substances) and methods of physiotherapy for the prevention of secondary diseases. Patients suffering from drug addiction, recommended treatment in the respective clinics. Due to the significant psychological discomfort, many patients undergo prolonged psychological adaptation.
The prognosis of HIV infection
HIV infection is not fully reversible, in many cases, antiviral therapy with very little results. Today, on average, HIV-infected people live 11-12 years, but careful therapy and modern medicines will significantly lengthen the life of patients. A major role in containing the emerging AIDS is the psychological condition of the patient and his efforts to comply with the prescribed regime.
Prevention of HIV infection
Currently, the world health organization holds a General prophylactic measures to reduce the incidence of HIV infection in four main areas:
- education in matters of safe sex, distribution of condoms, treatment of sexually transmitted diseases, the promotion of a culture of sexual relationships;
- control of manufacture of preparations from donor blood;
- management of pregnancy in HIV-positive women, providing them with medical care and the provision of drugs for chemoprophylaxis (in the last trimester of pregnancy and delivery women receive antiretroviral drugs that also for the first three months of life are assigned to babies);
- organization of psychological and social care and support for HIV-infected citizens, business.
At the present time in world practice, special attention is paid to epidemiologically important in disease HIV infection factors, including drug abuse, promiscuous. As a preventive measure in many countries, there is a free distribution of disposable syringes, methadone maintenance therapy. As measures that reduce the sexual illiteracy, educational program, educational sex hygiene courses.