Adhesions of the pelvis called the strands of connective tissue that covers the surface of organs located in the pelvis and forming adhesions between them and the pelvic walls.
Other name of disease is a plastic pelvioperitonit. The disease appears pelvic pain, disturbing the patient continuously or periodically, signs of disorder of bowel function (flatulence, constipation, alternating diarrhea) and in women miscarriage and/or infertility.
More than 50% of patients with chronic pelvic pain and disorders of the menstrual cycle, diagnosed plastic pelvioperitonit. In women, this pathology is found about 2.5 times more often than men, the development of acute intestinal obstruction, the cause of which appeared peritoneal adhesions was observed 1.6 times more often than male patients.
Plastic pelvioperitonit diagnosed patients, the burdened history of abdominal surgery or inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs. The likelihood of the formation of adhesions increases with the number of deferred laparotomy. Connective tissue bands are seen in 16% of patients after the first laparotomy and in 96% of cases after the third.
Reasons
The formation of adhesions refers to the protective mechanisms of the body and aims at the delimitation of the damaged area (inflammation or trauma) in the pelvic or abdominal cavity from healthy tissue. The tendency to formation of adhesions, the intensity of their formation and spread of the process is determined by several factors: the increased reactivity of the connective tissue, weakened immunity and individual susceptibility of the peritoneum to the formation of adhesions.

Risk factors for the formation of connective tissue adhesions are divided into 3 groups:
- endogenous, due to genetic predisposition of the organism to the formation of adhesions (reduced or increased production of the enzyme N-acetyltransferase);
- exogenous – influence from outside the body (trauma, surgery, infection);
- combined, when the formation of adhesions involved the internal and external factors.
Direct causes of adhesion formation in the pelvis are:
- Surgery. The intensity of adhesion is directly related to produced by the surgery in the abdomen. The factors that increase the likelihood of formation of adhesions include: operating access (laparoscopic or laparoscopiceski), volume and traumatic surgery, its duration, temperature (excessive cooling or heating loops of the intestine), the installation of drains in the pelvis, removing the blood and peritoneal fluid used suture material and chemical substances (iodine, alcohol, various powders).
- Inflammatory disease. Acute endometritis, oophoritis, vaginitis, parameters, and other diseases of the pelvis contribute to the formation of adhesions. Hidden sexual infections occurring with the erased clinical picture (chlamydia, ureaplasmosis) cause chronic inflammation in the pelvis that serve as the impetus for the formation of adhesions.
- External endometriosis. Regular flow of blood from endometriotic lesions in the pelvic cavity leads to aseptic inflammation and formation of adhesions.
- Bleeding in the pelvic cavity. Rupture of ovary, interrupted ectopic pregnancy by type of tubal abortion or rupture of the tube occurs with the outpouring of blood into the peritoneal cavity, subsequent aseptic inflammation and formation of adhesions.
- Injury to the lower part of the abdomen. Bruising, bleeding, open wounds of the pelvis resulting from a fall, blow, accident.
- Systemic connective tissue disease. Scleroderma, dermatomyositis, arthritis and others.

In 50 percent of cases the formation of adhesions due to the combined action of several factors. Predispose to the education of their promiscuity, abortion, invasive gynecological procedures, failure to intimate hygiene, and later access to a doctor.
The mechanism of formation
The abdominal cavity is lined with peritoneum – the serous membrane that forms a closed space where the organs of the abdomen. The peritoneum presented with 2 sheets: the parietal, lining the cavity of the abdomen, and visceral, enveloping the internal organs. Both sheets of peritoneum are connected and pass one another. The main functions of peritoneum are the creation of mobility agencies, prevent their friction against each other, protection against microbial agents and delimitation of the infectious process when the penetration of microorganisms into the abdominal cavity or pelvis.
Damaging factor (trauma or inflammation of the peritoneum) causes the release of mediators that stimulate regeneration. In the initial stage of the process aktiviziruyutsya fibroblasts that produce fibrin. The formed fibrin fibers cause adhesion of surrounding organs and tissues. The result is an inflammatory lesion is delineated from healthy tissue. If there is extensive traumatic injury or chronic inflammation, dissolution of the connective tissue is disturbed in the spikes formed blood vessels and nerve endings, and the density of the collagen fibers increases.
The spikes are loose and the sheets of the peritoneum become more dense, the mobility of the pelvic organs is limited. Any displacement of the organs (pan, tilt, physical exercise) leads to the tension of adhesions, irritation of the nerve plexus and pain in the abdomen.
Classification
Depending on the characteristics of the disease are the following clinical forms of plastic pelvioperitonit:
- Sharp. The disease is characterized by severe clinical picture. The patient was worried about intense pain, fever, reduced blood pressure, nausea, loss of appetite, vomiting. Increasing intoxication evidence of the development of intestinal obstruction and requires immediate surgical intervention.
- Intermittent. Characterized by a power phase current. Bouts of severe pain followed by periods of rest. On the background of the emergence of pain join the intestinal disorders. In the phase of remission of the symptoms are absent or expressed only slightly.
- Chronic. This form of the disease occurs with mild symptoms or asymptomatic. The most common patient complaints: periodic constipation, dull or aching pain in the abdomen. The main reason for the treatment of women to the gynecologist serves as the complaint in the absence of pregnancy.
Because pelvic adhesions are often the cause of female infertility, gynaecologists in the classification of the pathology of the allocate stage of the disease, which was determined by laparoscopy:
- First. There are single thin strands, arranged around the ovaries, the fallopian tubes or the uterus. The presence of adhesions does not violate the process of movement of an egg from the sex gland into the pipe, and then into the uterine cavity.
- Second. Between the ovary and the oviduct or other bodies have tight bands, but more than half of the area of the reproductive glands free. Adhesions interfere with the capture of the egg fimbriae pipe.
- Third. Most of the area of the ovary covered in dense adhesions, which violates the process of release of ovum from the follicle and its connection with the surface of the gland. There is also a deformation and partial or complete occlusion of the fallopian tubes, making fertilization impossible.
Symptoms of adhesions of the pelvic organs
The leading clinical symptom of plastic pelvioperitonit acts pain syndrome. Women with adhesions in the small pelvis have persistent pain in the abdomen, which is amplified, weakens. Pain can be dull or aching, localized in the suprapubic, lumbar, sacral areas, or take it to the rectum. Pain increases during physical exertion or stress (weight lifting, physical exercises, sharp turns, bending or jumping), straining during bowel movements, intercourse and afterwards, a full bladder or after urination. The increased pain can cause the nervous stress, hypothermia, menstruation or ovulation.
If adhesions pull the bladder, the patient complains on frequent urination, inability to tolerate a full bladder, a possible intermittent or painful urination. When compression of the spikes of the large intestine observed disorders of its functions. Intermittent constipation replaced palpitations stool or diarrhea, marked flatulence and bloating. May cause nausea and rarely vomiting. Intestinal disorders increase after the consumption of foods that stimulate flatulence (peas, beans, garlic, grapes, muffin, beet). Hauling the adhesions of the ovaries and fallopian tubes is accompanied by a disorder of the reproductive function, infertility.
Complications
The disease is dangerous to the development of the following complications and implications:
- Acute intestinal obstruction.Compression of the connective tissue strand of the intestinal tube leads to a complete or partial stricture and disturbance of microcirculation in the wall of the colon that requires urgent surgery.
- Infertility. Diagnosed in 25% of patients with a plastic pelvioperitonitis. Caused by impaired patency of the fallopian tubes, disorder of the processes of ovulation and fertilization.
- Ectopic pregnancy. Impaired transport of ova through the oviduct as a result of its constriction hinders the penetration of the ovum into the uterine cavity and leads to its forced implantation in the fallopian tube.
- Miscarriage. The limitation of prodovolstvia spikes when growth in the period of gestation causes hypertonicity of the uterus, which could result in the termination of pregnancy (miscarriage or premature birth).
Diagnosis
Pathology diagnosis begins with medical history and complaints of the patient. The gynecological examination allows to establish a limited mobility of the uterus, shortening of the vaginal vault to palpation in the region of the appendages, is determined by tenderness, palpable tyazhistosti.
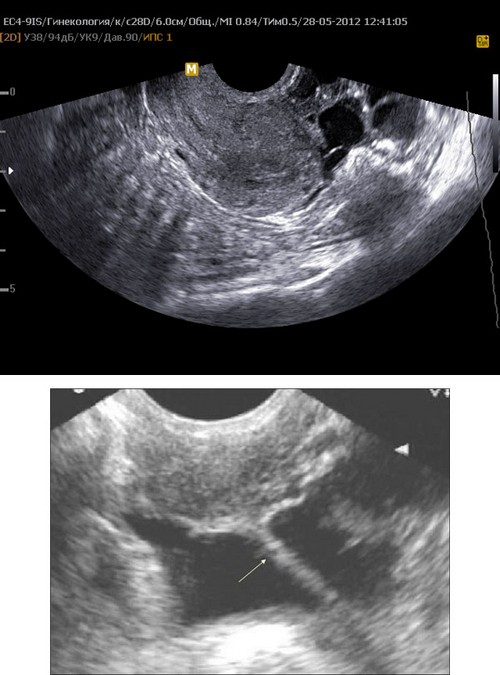
Additional screening includes:
- Diagnostic laparoscopy. The method allows to determine the adhesions of the pelvis in 100% of cases. If necessary, diagnostic laparoscopy was transferred to the medical – dissection of adhesions.
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs. The accuracy of the method reaches 90 – 100%. Adhesions are visualized as heterogeneous echo signals that connect to the pelvic wall and organs.
- The metrosalpingography. Radiological research method allows to determine the patency of the fallopian tubes.
- MRI of organs of small pelvis. The shots are visualized anechoic white seam.
With the aim of establishing a microbial agent, triggering chronic inflammation, produce taking swabs for vaginal flora, bacterial seeding of the vaginal content and definition of sensitivity to antibiotics of the detected microorganisms, PCR for the hidden sexual infections.
Treatment of adhesive disease of the pelvic organs
The treatment is conservative and surgical. Conservative therapy is carried out for stage 1 of the plastic pelvioperitonit and includes:
- Antibiotics. Identification of an infectious agent requires the holding of antibiotic therapy, selection of drugs is carried out according to the results of tank. planting and taking into account rezistentnosti bacteria to them.
- NSAIDs. Of NSAIDs use indomethacin, diclofenac, which cropped pain, eliminate swelling of the inflamed tissues and resolves friable adhesions (early stage disease).
- Hormonal agents. Hormone treatment is carried out at discovered endometriosis.
- Fibrinolytic enzymes. Longidasa, lidaza, terrilitin help dissolve adhesions due to the breakdown of glycopeptide ties. Enzymes are assigned in rectal suppositories, intramuscular injection and physical therapy.
- Physiotherapy, pelvic massage, exercise therapy. From physiotherapy is effective electrophoresis with enzymes, paraffin, SMT.
- Vitamins, immunomodulators. Improve the General condition, normalize blood flow and metabolism in tissues, stimulates the immune system.
Surgical treatment is indicated in failure of conservative therapy, and in the case of acute and interkurrentny forms of the disease.
With the development of severe complications (ectopic pregnancy, intestinal obstruction), is performed emergency surgery.
Dissection of adhesions performed endoscopy (laparoscopy):
- laser therapy (the spikes are cut with a laser beam);
- electrosurgery (adhesions dissect electronicam);
- equidistance (dissection of adhesions produced by high pressure water).



Diagnostic laparoscopy. The method allows to determine the adhesions of the pelvis in 100% of cases. If necessary, diagnostic laparoscopy was transferred to the medical – dissection of adhesions.
Injury to the lower part of the abdomen. Bruising, bleeding, open wounds of the pelvis resulting from a fall, blow, accident.
Inflammatory disease. Acute endometritis, oophoritis, vaginitis, parameters, and other diseases of the pelvis contribute to the formation of adhesions. Hidden sexual infections occurring with the erased clinical picture (chlamydia, ureaplasmosis) cause chronic inflammation in the pelvis that serve as the impetus for the formation of adhesions.
Loramumnbomsmomounax , Santamedical PM-510 Tens Unit Electronic Pulse Massager
Aw, this was a really nice post. In idea I want to put in writing like this additionally – taking time and actual effort to make an excellent article… but what can I say… I procrastinate alot and not at all appear to get one thing done.
Your website has outstanding content. I bookmarked the website
So this post honestly made me think! Thanks-I wouldn’t have considered things from your p.o.v otherwise.
There are certainly quite a lot of details like that to take into consideration. That could be a nice point to bring up. I provide the thoughts above as common inspiration however clearly there are questions just like the one you convey up where a very powerful factor will be working in honest good faith. I don?t know if best practices have emerged round things like that, but I’m positive that your job is clearly recognized as a good game. Each girls and boys feel the affect of only a second’s pleasure, for the remainder of their lives.
I definitely wanted to write down a simple message to thank you for the marvelous ideas you are giving at this website. My extensive internet lookup has now been paid with awesome facts and strategies to write about with my best friends. I ‘d state that that many of us readers are rather fortunate to exist in a magnificent website with so many wonderful professionals with very helpful techniques. I feel truly happy to have come across your entire web pages and look forward to plenty of more fabulous moments reading here. Thank you again for a lot of things.
I know that you’re trying to avoid upsetting anyone with this content, but please know that the jucier opinions usually promote awesome debate when approached with respect..and it is your page after all, let your “take” rule here!
Nice post. I was checking constantly this blog and I’m impressed! Very helpful information particularly the last part 🙂 I care for such info much. I was seeking this particular information for a very long time. Thank you and good luck.