Hemorrhagic Marburg fever – an acute infectious disease caused by RNA-containing filoviruses (Marburg virus), occurring with severe kapilliarotoxicos and high mortality.
Symptoms of hemorrhagic Marburg fever include high fever, severe intoxication, severe diarrhoea and vomiting, skin hemorrhages, internal bleeding, liver, heart, kidneys, CNS.
When diagnosing accounted epidemiological and clinical data, laboratory (virological, serological, electron microscopic) studies. Patients with hemorrhagic Marburg fever be hospitalized and isolation; treatment is mostly symptomatic; sometimes effective interferon, the introduction of convalescent plasma.
Hemorrhagic fever Marburg
Hemorrhagic fever Marburg – natural-focal infection, characterized by severe intoxication and hemorrhagic syndrome, liver, gastrointestinal tract, Central nervous system and other internal organs. Hemorrhagic fever Marburg belongs to the group of especially dangerous (quarantine) infections, characterized by high transmissibility and lethality.
The first outbreak was in 1967 in Marburg and Frankfurt, why the infection received the name “Marburg hemorrhagic fever”, “Marburg disease”; also synonyms for this disease are “hemorrhagic fever Maridi”, “green monkey disease”, etc. in addition to Germany, cases of hemorrhagic fever Marburg was observed in Serbia, Sudan, South Africa, Kenya.
Causes hemorrhagic fever Marburg
The causative agent of hemorrhagic fever Marburg (Marburgvirus) belongs to the family filovirus. The virions have a spiral, vermiform or rounded; the length 665-1200 nm and a diameter of 70-80 nm; contain RNA and lipoprotein. The stability of the virus in the environment is average. In their morphology and properties of Marburg virus similar to the viruses that cause Ebola, but between them there are some differences in the antigenic structure.
The source of the European outbreak of hemorrhagic fever Marburg in 1967, was brought from Africa green monkey, most of which died from an unknown disease. Hemorrhagic fever then developed in contact with primates, as well as the medical staff, caregivers. Out of 25 cases of hemorrhagic fever Marburg died 7 people. Later, similar cases were recorded in the natural habitats of African green monkeys, which gave grounds to consider them as the main source of infection and reservoir of Marburg virus.
Human infection is possible by contact, in contact with blood and other secretions of the patient; airborne droplets in contact with the virus on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity and the conjunctiva; by injection in the injections. Known case of infection with hemorrhagic fever Marburg through sexual intercourse. After infection formed long-lasting immunity; the cases of recurrence are not known.
After entry and initial replication of the virus in cells of the monocyte-macrophage system develops massive viremia, the overwhelming immune response. This leads to a generalized microcirculatory disorders and the development of DIC, kapilliarotoxicos and multiple organ failures. Foci of hemorrhage and necrosis in hemorrhagic fever Marburg are formed in the myocardium, lung, liver, kidney, adrenal, spleen and other organs.
Symptoms of hemorrhagic fever Marburg
From the moment of infection until the first symptoms is from 2 days to 3 weeks. Manifestation of acute without prodromal phenomena. The characteristics of hemorrhagic fever Marburg serve long-term (within 2 weeks) and high fever (up to 39-40°C), chills, severe intoxication, accompanied by headache, fatigue, myalgia and arthralgia. From the first day the patient found enanthema, conjunctivitis, erosion of the mucous membrane of the oral cavity. In 3-4 days for hemorrhagic fever Marburg is compounded by cramping abdominal pain, vomiting, watery diarrhea, resulting in the development of rapid dehydration.
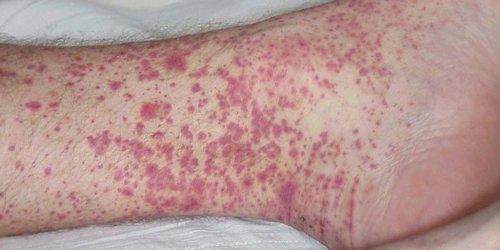
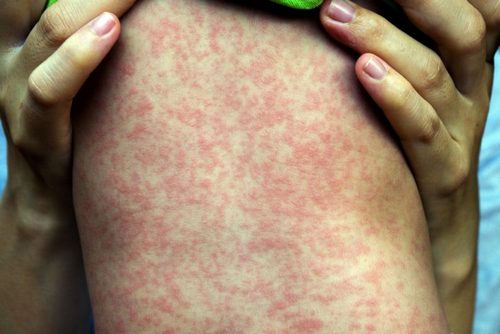
On the 5-6 day of disease on the trunk, upper extremities, neck and face appears maculopapular rash often associated with pruritus and scaling of the skin. To further develop hemorrhagic syndrome, bleeding in the skin and conjunctiva; gingival, nasal, uterine, gastrointestinal bleeding. By the end of the first week in patients with hemorrhagic fever Marburg are determined by the signs of hepatitis, myocarditis, renal damage. Changes in the Central nervous system characterized by weakness, lethargy, convulsions, loss of consciousness.
Maximum severity of signs of toxicity, dehydration, hemorrhagic manifestations and multiple organ disorders reach the second week of illness. The death of patients with hemorrhagic fever Marburg may occur from pulmonary edema or brain, hypovolemic shock, DIC, acute renal failure. In survived patients the period of convalescence is protracted how long remains asthenia, headache and muscle pain, periodic abdominalgia; often develop alopecia. Among the complications and sequelae of hemorrhagic fever Marburg include uveitis, encephalitis, myelitis, orchitis, testicular atrophy, pneumonia, mental and intellectual disorders.
Diagnosis of hemorrhagic fever Marburg
Diagnosis of hemorrhagic fever Marburg is based on clinical, epidemiological and laboratory data. When collecting history revealed the fact of stay of the patient in endemic areas, contact with vectors of diseases and of sick people. Nonspecific changes in the blood include leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, elevated liver enzymes. To confirm the diagnosis of hemorrhagic fever Marburg used molecular biological and serological (RT-PCR, REEF, IFA, RSK, PH), electron-microscopic study. Testing of the biomaterial is carried out in special laboratories in compliance with maximum security.
For assessment of internal organ is performed EKG, renal ultrasound and ultrasound of the liver, coagulation study, urinalysis, KOS. In connection with the development of multiple organ disorders patients need consultation of the nephrologist, neurologist, gastroenterologist, cardiologist, a hematologist, an ophthalmologist.
Differential diagnosis is from other haemorrhagic fevers (yellow, hemorrhagic with renal syndrome, Crimean, Omsk, Bolivian, Argentine hemorrhagic fever, lasa fever, Ebola, etc.). Also eliminated malaria, cholera, shigellosis, typhoid and relapsing fever, leptospirosis, hepatitis, meningitis, etc.
Treatment of hemorrhagic fever Marburg
Patients with suspected hemorrhagic fever Marburg should be immediately hospitalized in the infectious hospital and isolated in individual boxes. At the organization of patient care measures increased sanitary-epidemiological control: intensified disinfection measures, protection of medical personnel, organized safe conduct diagnostic and treatment procedures.
Etiotropic therapy of hemorrhagic fever Marburg is not developed, therefore, focuses on the pathogenetic and symptomatic events. Is parenteral disintoxication therapy and oral rehydration, intravenous platelet mass. There is information about the effectiveness of the introduction of plasma convalescents, the conduct of interferon, plasmapheresis. With the development of bacterial complications is assigned antibiotic therapy.
Prognosis and prevention of hemorrhagic fever Marburg
The disease has a serious prognosis and is an increased risk in terms of occurrence of epidemic outbreaks. Mortality among patients with hemorrhagic fever Marburg is 25-70%. In identifying cases of Marburg haemorrhagic fever must be strict adherence to precautions recommended for work with especially dangerous infections. Transportation and treatment of patients is carried out in special detention facilities. Patient care should be conducted by trained personnel using personal protective equipment. Specific prophylaxis of hemorrhagic fever Marburg is not developed. It is advisable to organize the epidemiological control of persons coming from endemic regions.

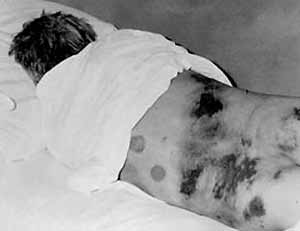

Human infection is possible by contact, in contact with blood and other secretions of the patient; airborne droplets in contact with the virus on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity and the conjunctiva; by injection in the injections. Known case of infection with hemorrhagic fever Marburg through sexual intercourse