Hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome – Hantavirus zoonotic infection characterized by thrombohemorrhagic syndrome and primary renal disease. Clinical manifestations include acute fever, hemorrhagic rash, bleeding, interstitial nephritis, in severe cases, acute renal failure.
The specific laboratory methods for diagnosis of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome belong to the REEF, ELISA, RIA, PCR.
Treatment consists in the introduction of specific immunoglobulin, interferon preparations, conducting detoxification and symptomatic therapy, hemodialysis.
Hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome
Hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS) is a natural focal viral disease, the characteristic symptoms of which are fever, intoxication, increased bleeding, and kidney damage (nephrosonephritis).
On the territory of our country, endemic areas are the far East, Eastern Siberia, Transbaikalia, Kazakhstan, the European territory, therefore HFRS is known under different names: Korean, far Eastern, Ural, Yaroslavl, Tula, Transcarpathian hemorrhagic fever, etc. in Russia Annually is registered from 5 to 20 thousand cases of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome. The peak incidence of HFRS occurs in June-October; the majority of cases (70-90%) are males aged 16-50 years.

Causes HFRS
The causative agents are RNA-containing viral agents of the genus Hantavirus (Hantaviruses), belonging to the family Bunyaviridae. To 4 human pathogenic serotypes of Hantaviruses: Hantaan, Dubrava, Levi, Seoul. In the environment viruses a relatively long time to maintain stability at subzero temperatures and are unstable at 37°C. the Viruses have a spherical or spiral shape, 80-120 nm in diameter; contains single-stranded RNA. Hantaviruses possess a tropism for monocytes, kidney cells, lung, liver, salivary glands and multiply in the cytoplasm of infected cells.
Carriers of pathogens of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome are the rodents of field and forest mice, voles, house rats that are infected from each other by the bites of ticks and fleas. Rodents carry the infection in the form of latent virusological, releasing pathogens into the environment with saliva, faeces and urine. Getting infected excreta of rodents of the material in the human body can occur aspiration (inhalation), contact (with the skin) or alimentary (while eating) by.
High-risk on the incidence of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome include agricultural and industrial workers, tractor drivers, drivers, active contact with objects in the external environment. The incidence depends on the number of infected rodents in the area. HFRS is registered mainly in the form of sporadic cases; rarely in the form of local outbreaks. After the infection remains persistent lifelong immunity; the cases of re-incidence single.
Pathogenetic essence of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome are necrotizing penascola, DIC and acute renal failure. After infection, initial viral replication occurs in vascular endothelium and the epithelial cells of internal organs.
After the accumulation of the virus occurs viremia and generalization of infection, which clinically manifest toxic symptoms. In the pathogenesis of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome is a big role playing formed autoantibodies, autoantigens, CEC, providing kapilliarotoxicos the action causing the damage to the walls of blood vessels, impaired blood clotting, the development of thrombohemorrhagic syndrome with damage of kidneys and other parenchymatous organs (liver, pancreas, adrenal glands, myocardium), the Central nervous system. Nephritic syndrome is characterized by massive proteinuria, oligoanuria, azotemia, violation of KOS.
The symptoms of HFRS
Hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome is characterized by cyclic course with succession of several periods:
- incubation (2-5 days up to 50 days – an average of 2-3 weeks)
- prodromal (2-3 days)
- feverish (3-6 days)
- oligonicella (3-6, on the 8-14 day HFRS)
- politicheskogo (9-13 days HFRS)
- reconvaleszentov (early – from 3 weeks to 2 months late up to 2-3 years).
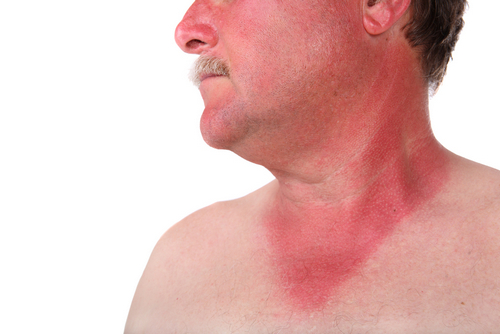
Depending on the severity of symptoms, severity infectious-toxic, hemorrhagic and renal syndromes distinguish typical, erased and subclinical variants; light, moderate and severe forms of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome.
After the incubation period is short prodromal period, during which marked fatigue, malaise, headaches, myalgia, low-grade fever. The febrile period develops acutely, with the increase in body temperature to 39-41°C, chills, and General toxic symptoms (weakness, headache, nausea, vomiting, sleep disorders, arthralgia, aches in the body). Characterized by pain in the eyeballs, blurred vision, flashing “flies”, the vision of objects in red color. In the midst of a hectic period, appear hemorrhagic rash on the mucous membranes of the mouth, the skin of the chest, axillary regions, neck. At objective examination revealed hyperemia and puffiness of face, injection of vessels of conjunctiva and sclera, bradycardia and hypotension up to the collapse.
In alegorically period of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome, the body temperature reduces to normal or subfebrile, but it does not improve the patient’s condition. This is even more amplified symptoms of intoxication and symptoms of kidney damage: increasing back pain, sharply decreased urine output, developing hypertension. In the urine reveals hematuria, proteinuria, cylindruria. With an increase of azotemia ARF develops; in severe cases, uremic coma. Most patients have uncontrollable vomiting and diarrhea. Hemorrhagic syndrome can be expressed in varying degrees and include gross hematuria, bleeding from the injection site, nasal, uterine, gastrointestinal bleeding. In alegorically period can develop serious complications (bleeding in the brain, pituitary, adrenal) which are the cause of death.
The transition of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome in politicheskuju stage is marked by subjective and objective improvement: normalization of sleep and appetite, cessation of vomiting, disappearance of pain in the lower back, etc. the Characteristic features of this period is the increase in daily diuresis of 3-5 l isoheptane. In the period of polyuria persists dry mouth and thirst.
The period of convalescence in hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome may take several months or even years. In patients with persistent post-infectious asthenia characterized by General weakness, decreased performance, fatigue, emotional lability. The syndrome of vegetative dystonia is expressed hypotonia, insomnia, shortness of breath with minimal exertion, increased sweating.
Specific complications of severe clinical variants of HFRS can appear toxic shock, bleeding in parenchymal organs, pulmonary edema and brain, hemorrhage, myocarditis, meningoencephalitis, uremia, etc. When joining a bacterial infection may develop pneumonia, pyelonephritis, suppurative ear infections, abscesses, phlegmon, sepsis.
Diagnosis of HFRS
Clinical diagnosis of HFRS is based on the cycles of the current infection and characterized the change of periods. When collecting epidemiological history draws attention to the patient’s stay in endemic area, possible direct or indirect contact with rodents. When conducting a nonspecific survey takes into account the dynamics of changes of indicators of General and biochemical analysis of urine, electrolytes, biochemical blood samples, KOS, coagulation, etc. With the purpose of evaluating the severity and prognosis of the disease is performed renal ultrasound, EGD, x-rays of the chest, Akhi.
Specific laboratory diagnosis of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome is carried out using serological methods (ELISA, IF, RIA) in the dynamics. Antibodies in serum appear at the end of the 1st week of the disease, by the end of the 2nd week, reach a maximum concentration and persist in the blood for 5-7 years. Virus RNA may be isolated using polymerase chain reaction analysis. HFRS differencebut with leptospirosis, acute glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis and enterovirus infection and other haemorrhagic fevers.
Treatment HFRS
Patients with hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome hospitalized in the infectious hospital. Assigned strict bed rest and diet №4; held control of fluid balance, hemodynamics, indices of functioning of cardiovascular system and kidneys. Etiotropic therapy of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome the most effective in the first 3-5 days of onset and includes the introduction of donor-specific immunoglobulin against HFRS, the appointment of the interferon, antiviral chemotherapy (ribavirin).
In the febrile period is infusion detoxification therapy (intravenous Levanevsky and saline solutions); prevention of disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome (introduction of drugs-and of antiplatelet agents angioprotectors); in severe cases, corticosteroids are used. In the oliguric period is the stimulation of diuresis (administration of shock doses of furosemide), correction of acidosis and hyperkalemia, prevention of bleeding. With the increasing of the arrester shows the transfer of the patient to extracorporeal hemodialysis. In the presence of bacterial complications is assigned antibiotic therapy. In politicheskuju stage the main task is an oral and parenteral rehydration. In the period of convalescence is tonic and metabolic therapy; recommended nutrition, physical therapy (diathermy, electrophoresis), massage and physical therapy.
Prognosis and prevention of HFRS
Light and moderate forms of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome in the majority of cases end in recovery. Residual effects (post-infectious asthenia, back pain, cardiomyopathy, mono – and polyneuritis), long observed in half of the survivors. Convalescents require quarterly follow-up of infectious disease specialists, nephrologist and ophthalmologist throughout the year. A severe course associated with high risk of complications; the mortality of HFRS varies in the range of 7-10%.
Prevention of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome is the destruction of rodents in natural foci of infection, prevention of contamination of dwellings, water sources and food by excreta of rodents, deratization residential and industrial premises. Specific vaccination against HFRS have not been developed.



50 OFF for all private proxies – buy proxies today
I’m going to look into this
Super informative!