Haemorrhagic fever – a viral infection with a natural focal distribution, occurring with acute febrile and hemorrhagic syndrome. Symptoms of hemorrhagic fever include severe intoxication, high fever, hemorrhagic rash, bleeding of different localization, multi-organ disorders.
Form of hemorrhagic fever is determined based on clinical, epidemiological and laboratory data (PCR, ELISA, RIF).
In hemorrhagic fevers is detoxifying, antiviral, haemostatic therapy, the introduction of specific immunoglobulins, the fight against complications.
Hemorrhagic fever
Haemorrhagic fever – a group of infectious diseases of viral nature, causing toxic damage of the vascular walls, contributing to the development of hemorrhagic syndrome. Occur on the background of General intoxication, provoke multiple organ pathology. Hemorrhagic fevers are common in certain regions of the planet, the habitats of vectors of diseases. Cause of hemorrhagic fever viruses of the following families: Togaviridae, Bunyaviridae, Arenaviridae and Filoviridae. The characteristic feature uniting these viruses, is an affinity for endothelial cells of blood vessels of a person.
Reservoir and source of these viruses is man and animals (various species of rodents, monkeys, squirrels, bats, etc.), vector – mosquitoes and ticks. Some hemorrhagic fevers can be transmitted contact-household, food, water and other ways. According to the method of infection these infections are divided into groups: tick-borne infections (Omsk, Crimean-Congo fever casinorama forest), mosquito (yellow, dengue, Cucamonga, rift valley) and contagious (fever Laos, Argentine, Bolivian, Ebola, Marburg, etc.).
Susceptibility to haemorrhagic fevers in humans is quite high, mainly sick persons, whose professional activity is connected with wildlife. The incidence in cities is often marked by citizens who do not have permanent residency and employees of home services that come into contact with rodents.
Symptoms of hemorrhagic fever
Hemorrhagic fever in most cases combines a characteristic for a sequential change of periods: incubation (usually 1-3 weeks), elementary (2-7 days), middle (1-2 weeks), and convalescence (several weeks). The initial period obscheintoksikatsionnogo manifested by symptoms are usually very intense. Fever in severe may reach critical numbers, intoxication is to contribute to the disorder of consciousness, delusions, hallucinations.
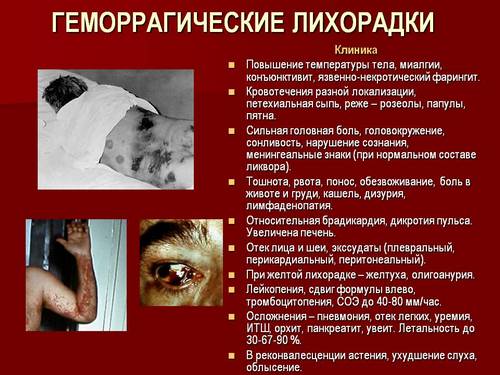
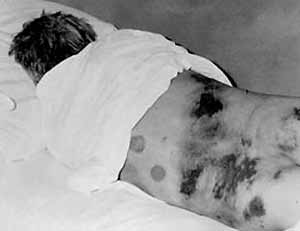
On the background of General intoxication during the initial period noted toxic haemorrhage (capillariasis): face and neck, conjunctiva patients usually hyperemic, injected sclera, can be detected elements hemorrhagic rash on the mucous membrane of the soft palate, the endothelial symptoms (“harness” and “pinch”) is positive. Observed toxic heart rhythm disorders (tachycardia, turning into bradycardia), decrease in blood pressure. During this period, a General analysis of the blood shows a leukopenia (persists for 3-4 days) and increasing thrombocytopenia. In the formula of blood neutrophilia with a left shift.
Before the peak there is often a short-term normalization of body temperature and improvement in General condition, after which the toxicity increases, the intensity of the General clinic increases, develop multi-organ pathology, hemodynamic instability. In the period of convalescence is the gradual regression of the clinical manifestations and recovery of the functional state of organs and systems.
Far Eastern hemorrhagic nephrosonephritis is often called hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome, since this disease is characterized by preferential loss of renal vessels. Incubation of hemorrhagic nephrosonephritis of the far East is 2 weeks, but could be reduced to 11 and to be extended to 23 days. The first days of the disease may be prodromal symptoms (fatigue, malaise). Then develops severe intoxication, the body temperature rises to 39.5 degrees or more and lasts 2-6 days. After 2-4 days from the onset of fever appears hemorrhagic symptoms on a background of progressive intoxication. Sometimes may include meningeal symptoms (Kernig, Brudzinskogo, stiff neck). Due to toxic lesions of the brain, the mind often confused, appear hallucinations, delusions.
General haemorrhagic syndrome accompanied by symptoms in the kidneys: low back pain, positive symptom pasternatskogo in the General analysis of urine reveals red blood cells, cylinders, and protein. With disease progression renal syndrome is aggravated, as well as hemorrhagic. In the midst of the disease observed bleeding from the nose, gums, hemorrhagic rash on the torso (mainly in the region of the shoulder girdle and lateral surfaces of the chest). During the inspection of the oral mucosa and oropharynx reveal petechial hemorrhages on the palate and the lower lip develops oliguria (in severe cases up to complete anuria). It is noted gross hematuria (the urine has colour of “meat slops”).
The fever usually lasts 8-9 days, and then within 2-3 days, the lower body temperature, however, after normalization of the patients ‘ condition not improving, you may experience vomiting, progressing nephritic syndrome. Improvement and regression of clinical symptoms occurs 4-5 days after the remitting fever. The disease enters into a phase of convalescence. At this time, characterized by polyuria.
Crimean hemorrhagic fever is characterized by acute onset, marked vomiting, abdominal pain on an empty stomach, chills. The body temperature rises dramatically. Appearance characteristic of patients with haemorrhagic fevers: hyperemic edematous face and injected conjunctiva, eyelids, sclera. Hemorrhagic symptoms are expressed: petechial rashes, bleeding gums, nosebleeds, blood in the stool and vomit, uterine bleeding in women. The spleen often remains normal size, some patients may experience an increase. Severe disease manifested by intense pain in the abdomen, frequent vomiting, melinoe. Labile pulse, blood pressure reduced, heart tones are deaf.
Omsk hemorrhagic fever occurs more easily, and benign hemorrhagic syndrome is less pronounced (although lethality occurs in this infection). In the first days the fever reaches 39 with a small degree, in half of the cases the febrile period occurs in waves, with periods of increase and normalize body temperature. The duration of fever is 3-10 days.
Dengue haemorrhagic fever is characterized by an incubation period of 5 to 15 days, benign course, with symptoms of General intoxication, increasing to 3-4 day, and maculopapular rash hemorrhagic origin, passing through 2-3 days after the onset (usually occurs in the midst of the disease) and not leaving behind pigmentation or flaking. The temperature curve may be two-wave fever is interrupted 2-3-day period of normal temperature, after which there is a second wave. This form is characteristic of Europeans, the inhabitants of South-East Asia, Dengue fever is developing hemorrhagic variant and has a more severe course.
Hemorrhagic fever can contribute to the development of severe, life-threatening disease: infectious-toxic shock, acute renal failure, coma.
Diagnosis of hemorrhagic fevers
Diagnosis of hemorrhagic fevers are produced on the basis of clinical and epidemiological history data, confirming the preliminary diagnosis laboratory. Specific diagnosis is made using serology (DGC, IF, etc.), enzyme immunoassay (ELISA), detection of viral antigens (PCR), virological method.
Hemorrhagic fevers usually are characterized by thrombocytopenia in the General analysis of blood detection of red blood cells in the urine and feces. In severe hemorrhages symptoms of anemia. Positive stool for occult blood says bleeding in the course of the gastrointestinal tract.
Fever with renal syndrome also manifests itself in laboratory diagnosis of leukopenia, aneosinophilia, increased number of band neutrophils. Significant pathological changes in the General analysis of urine – specific gravity is reduced, it is noted protein (often the increase is 20-40%), the cylinders. In the blood increased residual nitrogen. Crimean fever is characterized by a lymphocytosis with the overall normocytosis, shift leucoformula left and a normal erythrocyte sedimentation rate.
Treatment of hemorrhagic fever
Patients with any haemorrhagic fever be hospitalized. Prescribed bed rest, semi-high-calorie digestible diet, maximum rich in vitamins (particularly C and b) and vegetable broths, fruit and berry juices, dogrose infusion, fruit drinks). In addition, prescribed vitamin therapy: vitamins C, R. Daily for four days was adopted by menadione (vitamin K).
Intravenous drip administered glucose solution, during the fever can be blood transfusion in small portions and the introduction of preparations of iron, preparations based on aqueous extract of the liver of cattle. In the complex therapy include antihistamines. Discharge from hospital is after full clinical recovery. At discharge patients for some time been on an outpatient basis.
Prognosis and prevention of hemorrhagic fever
The prognosis depends on the severity of the disease. Hemorrhagic fever can vary the flow within very wide limits, in some cases causing the development of terminal States, and ending in death, but in most cases with timely medical care, the prognosis is favorable – infection ends in recovery.
Prevention of hemorrhagic fevers primarily involves measures aimed at the destruction of vectors and the prevention of bites. In the area of infection produce thorough cleaning of places compiled under a settlement, from blood-sucking insects (mosquitoes, ticks), epidemically dangerous regions recommended in the forests to wear thick clothes, boots, gloves, protivostoyanie jumpsuits and masks, to use repellents. For Omsk hemorrhagic fever, there is a method of specific prevention, routine vaccination of the population with the killed virus vaccine.