Urine (Latin urina) is a form of excrement (products of the processes of human life), which is formed in the kidneys. This biological fluid has a complex composition, depending on the climatic conditions and lifestyle of the person, his sex and age, body mass and health status.
The basis of urine – water, in which there are more than 200 constituent elements: urea, creatine, histidine, ammonia and purine bases, nucleic acid, uric, bile, titanova acid and lactic acid. It contains all the vitamins and minerals present in the human body, cholesterol, hormones and enzymes, and also remnants of amino acids and proteins.
In the urine of the sick person contains harmful impurities – products of protein breakdown, toxic substances, herbicides, phthalates, heavy metals, dioxins. Practicing clinicians widely use the term “pathological urine components”.
This conventional concept considers those substances which in norm are not defined in urine and quantitative methods – glucose, ketones, bile pigments, proteins. In our article we want to talk in detail about the properties and chemical composition of urine, changes in urine and the causes of their appearance.

The structure of the system of urine formation
To the organs of the urinary tract includes the ureters, bladder, urethra (the urethra) and kidneys. A pair of bean-shaped organs located in the abdominal cavity on either side of the lumbar spine. The weight of each of them is about 150 grams, length – 10 cm
The kidneys are characterized by a complex microscopic structure – they contain over a million nephrons (functional units).
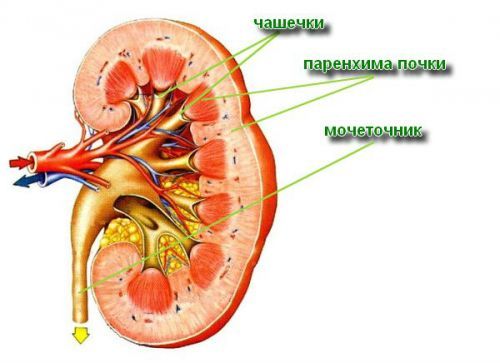
Each nephron consists of:
- two of the capsule (calyx) containing the capillary glomerulus;
- tubular system, the walls of which are formed by epithelial cells.
On the cut you can see the cortical layer (outer, darker) and medulla (inner, lighter)
In the cortical substance of the kidney are capsules, the brain layer, moving away from her convoluted tubules that form a loop. Straightening up and returning to the cortical layer, the loop forms a second tubule which empties into the collecting tube. Merging into one collective tube open into the renal pelvis cavity formed by the “pyramids” of the renal parenchyma.
On the concave edge of the kidney are the so-called “gate”, through which pass blood and lymphatic vessels, nerves, the ureter.
The functional activity of the kidneys
The kidney plays the role of the so-called “biological filter”, because of their work in the human body:
- Supported acid-alkaline balance.
- Displays the excess fluid and various substances, the end metabolites, toxins and foreign compounds.
- Regulate the level of blood pressure, the formation of red blood cells (erythrocytes), the synthesis of adrenocortical hormones.
- Ensured and maintained the constancy of the ionic composition of the internal environment.
- Maintained a constant circulating blood volume, tissue fluid and lymph.
One of the main kidney functions is the separation of substances that come from the blood flow into two different chemical components branches:
- needed by the body is reabsorbed (returned) in the blood;
- the final products enter into the urine.
Physico-chemical properties (colour, smell, transparency, relative density, reaction environment, connections are end-products of metabolic) urine of a healthy person is relatively stable. The concentrations of the main components of urine varies in relation to the flow in the body metabolism and the flow of some of them with food.
The changes in the body condition that occurs in physiological and pathological causes that lead to changes in normal parameters – this phenomenon is used for diagnostic purposes. Selection of chemical compounds with urine, increases with the development in the kidneys of various processes in which there is a violation of the selective reabsorption of substances and their appearance in the urine.
In that case, when the blood increases the concentration of a substance increases its urinary excretion
In some pathological conditions, which is accompanied by impairment of urinary function and changes in the composition of circulating blood, occur characteristic of the disease changes in urine. That is why the diagnosis of pathologies based on clinical examination of the urine.
Diagnostic importance of studying the physico-chemical properties of urine, establish the level of inorganic and organic (nitrogenous and nitrogen-free) compounds, the determination of the presence of various components in the urine of healthy humans. Let us consider the sequence of principal components, the presence of which in urine is observed during the development of the human organism various pathological processes.
Proteins
The products of protein metabolism are excreted in the urine in small quantities – not more than 30 mg per day. The presence of total protein in the sample of biological fluid is impossible to detect in a qualitative way.
Of human body with urine derived cells sladenkogo epithelial layer of the urinary tract, low molecular weight protein compounds and certain enzymes (special kind of active proteins that accelerate biochemical processes in the body):
- α-amylase;
- pepsin;
- leucinamide-peptidase;
- lipase;
- phosphatase;
- lactate dehydrogenase;
- ribonuclease;
- urokinase;
- aminotransferase.
With the development in the human body pathological processes, the level of protein increases dramatically. This phenomenon is defined by the medical term “proteinuria”.
Practitioners distinguish between the following types:
- Kidney – protein compounds of blood enters the urine as a result of damage of the nephron (the structural and functional unit of the kidneys), increased renal membrane filter, slowing the flow of blood through the glomeruli (the glomeruli).
- Extrarenal violation of the reabsorption of proteins due to lesions of the organs of the urinary tract (bladder, ureter, urinary canal, prostate gland in men).
- Functional (or temporary) which develops as a result of hypothermia, emotional stress, excessive physical load.

In pathological urine can be defined crystals of a specific protein of Bens-Jones, consisting of light chains of immunoglobulins
Detection in urine of this component indicates the formation in the human malignant disease:
- myeloma;
- Hodgkin’s disease;
- leukemia;
- osteosarcoma;
- macroglobulinemia;
- amyloidosis.
Glucose and monosaccharides
From the body glucose the urine is in such minimal quantities that it is impossible to determine the quality way. Level exceeded the “renal threshold”, which is from 8.1 to 9.9 mmol/l is indicated by the term “glycosuria”.
It is a pathological condition characterized hyperglycemia (an increase in the concentration of glucose in the blood), which observed:
- while increasing the functional activity of the thyroid gland – hyperthyroidism;
- diabetes;
- a secondary insulin-dependent(steroid) diabetes;
- long-term therapy with glucocorticoid drugs;
- renal (kidney) diabetes – a violation of the reverse suction of glucose in the renal tubules due to nephrotic syndrome, nephritis or nephrosis.
Natural glucosuria is observed in stressful situations, after the application of corticosteroids and caffeine, consuming excessive amounts of carbohydrates. Physiological causes of glycosuria can also be the presence in urine of large number of monosaccharides – fructose, galactose and pentose.

Fructosuria and pentosuria is caused by human consumption of significant quantities of fruit and berry juices, honey, fresh fruit
Galactosuria appears in congenital deficiency of enzymes that contribute to the transformation of galactose to glucose.
Acetone (ketone) bodies
In urine of the healthy person allocated during the day, contains not more than 10 mg of ketones.
Exceeding this level indicates ketonuria – positive test for acetone bodies.
This phenomenon is typical of such pathological States as:
- diabetes mellitus;
- education excessive amount of thyroid hormones – thyrotoxicosis;
- traumatic brain injury;
- prolonged fasting;
- exclusion from the diet of carbohydrates;
- infectious-inflammation – influenza, scarlet fever, tuberculosis, encephalitis, meningitis;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
Porphyrins
Natural organic compounds – breakdown products of hemoglobin that does not contain iron are called porphyrins. These substances are contained in urine in small amounts up to 0.3 mg/day.
Their separation increases:
- in pathological processes, accompanied by the defeat of hepatocytes (cells of the liver tissue);
- intestinal bleeding;
- General intoxication of the organism;
- In the12-scarce anemia – a disease in which the violation of the formation of red blood cells occurs as a result of deficiency of vitamin b12;
- congenital abnormalities of porphyrin.
Bile pigments
Normal biological products, formed during decomposition of hemoglobin of red blood cells, are present in the urine in small quantities. It bile pigments biological fluid in a yellowish tone. The allocation of direct bilirubin in the urine is possible with the increase in its blood concentration above 3.5 mmol/l, the allocation of indirect bilirubin is only possible due to severe kidney damage.
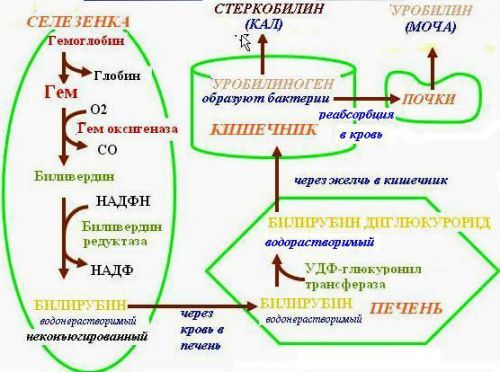
Of human body with urine, there are two kinds of bile pigments – bilirubin and urobilin
“Bilirubinuria” occurs when:
- the development of parenchymal and obstructive (mechanical) jaundice;
- stagnation of bile in the blockage of the bile ducts;
- viral hepatitis;
- Graves ‘ disease (hyperthyroidism).
Urobilin present in the urine only in low concentrations. Its increase is due to the reduced capacity of the liver to convert mitbringen coming from the intestines. It is a pathological condition observed in hepatic and hemolytic jaundice.
Blood
The appearance of this pathological element in the urine can be detected in the form of:
- hematuria – allocation in a biological fluid of red blood cells;
- gemoglobinurii – as a result of disintegration of red blood cells, when the content of the pigment in the blood increases more than 1 g/L.
There are two kinds of hematuria: macroscopic (blood visible to the naked eye) and microscopic (presence in the urine of erythrocytes can be determined only in the study of urinary sediment under the microscope)

Hematuria develops as a result of pathological processes in the organs of the urinary system, there are the following forms of this sign:
- kidney is the main symptom of acute inflammation of the vessels of the glomeruli, which struck the entire capillary system;
- extrarenal – its development is due to an inflammatory process or trauma of the genitourinary tract, the presence of kidney or bladder stones.
Very often blood in the urine can appear:
- in intense exercise, resulting in kidneys is excessive pressure, and they don’t manage to distinguish the products of metabolic processes;
- adenoma or malignant tumor of the prostate gland in men;
- cerebroretinal the angiomatosis genetic pathology in which a benign tumour-like formations are formed on the spinal column, kidneys and testes in men.
In conclusion, all of the above I want to stress again that the study of urine has important diagnostic value. The results of this analysis help to evaluate the functional activity of the kidneys and the General condition of the human body.




Such useful Post! You might also be interested in trying my online video
*An interesting discussion is worth comment. I think that you should write more on this topic, it might not be a taboo subject but generally people are not enough to speak on such topics. To the next. Cheers
*This web site is really a walk-through for all of the info you wanted about this and didn?t know who to ask. Glimpse here, and you?ll definitely discover it.
Such great Post!