The human brain is well protected by the skull. To identify the pathology, it is necessary to resort to various methods of hardware diagnostics.
The basis of the action of CT is X-rays. MRI – electromagnetic rays. The first is faster. This does not bother the patient in a stationary state.
CT allows you to examine hard tissue, skull bones and their pathology. MRI – soft tissue. MRI is used to diagnose pregnant women in the 2nd and 3rd trimesters, which can not be said about CT.
A tomograph is used there and there . They are fairly safe procedures. They help to make a more accurate diagnosis than other examination methods.
Study results are provided in 3D. Subjects receive a small dose of radiation.
It weighs only 400 grams, but controls the entire human body. If any problems start with it, it affects the whole body.
Ultrasound and X-ray examination do not always allow an accurate diagnosis. Effective research methods are becoming increasingly popular: CT (computed tomography) and MRI (magnetic resonance imaging).
What is the peculiarity of each diagnosis, are there any negative aspects of the impact? In what situation and what should be preferred?
CT: diagnostic features
Like x-rays, CT is carried out thanks to x-ray radiation. In the first case, a two-dimensional image is achieved by passing the rays through the body and focusing on the film or plate.
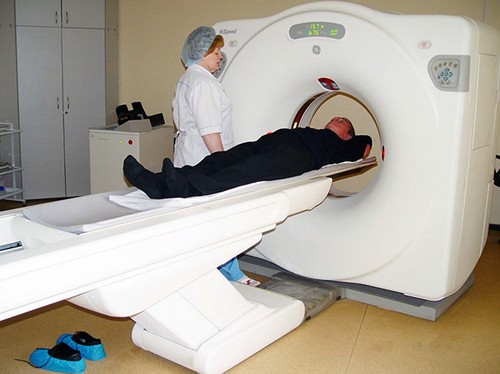
In the second, the image is more voluminous. The tomograph is designed so that the table for the patient is inside an annular contour emitting x-rays through movable sensors.
As a result of this, with a different slope, a group of pictures is taken from different points. After that, the computer processes the information and simulates a 3D image of the brain. From the monitor it can be transferred to disk.

If the settings of the device allow, the attending physician opens various sections or sections of the brain 1 mm thick. In this case, it is easier to determine the cause and make an accurate diagnosis.
CT does not provide for special preliminary training. Except if the procedure will be performed with a contrast medium. Then you will need to refrain from eating for several hours before diagnosis.
When carrying out the procedure, it is necessary to observe some rules:
- Eliminate metal objects, dentures, earrings, hearing aids, glasses.
- Consult a physician regarding the drugs used and the possible allergic reaction to the contrast medium.
- Accompanying the patient, such as parents, must be provided with a protective apron.
After the procedure with contrast, a heavy drink is recommended. Diagnosis is carried out for 15 minutes.
MRI: diagnostic features
The principle of the method is similar to CT: modeling a three-dimensional image of the brain based on the obtained data array. MRI is characterized by the effect of magnetic resonance. Using electromagnetic waves, softer tissues are examined.
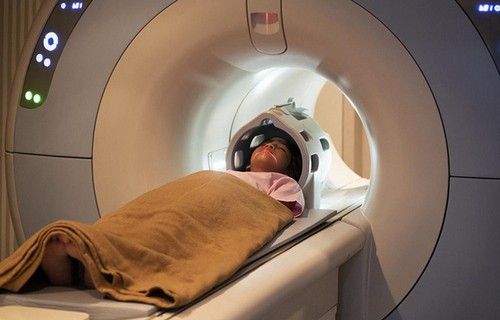
A closed-type tomograph is used. The cylindrical apparatus accommodates a retractable table on which the subject is laid.
Under the influence of electromagnetic waves, different parts of the tissues react in their own way. The device device accepts this “response” and focuses. Then it processes the received signals, converting it into an image.
The volumetric image allows you to see slices in layers, in the desired projection (horizontal or axial, direct or frontal, lateral or sagittal), in the desired area.

The device provides a clear picture of the problem of soft tissues: tumor shape, size, location, volume of edema.
To make the patient feel more comfortable and not worry because of the sounds and noises inside the tunnel, they put on headphones.
The device is equipped with a button, which allows you to keep in touch with the doctor. Diagnosis takes about 40 minutes. It does not require special preparation. Eliminates the presence of metal implants.
In which case and for whom are modern diagnostic methods suitable
Common indicators for CT scans are:
- Displacement of brain structures.
- The need for confirmation of hemorrhage.
- Determination of the location of a foreign body.
- Concussion.
- Violations in the bone tissue of the head.
- The presence of a headache after an injury.
- Traumatic brain injuries.
CT scan is not suitable during pregnancy. The procedure is not indicated for patients with a large body weight (≥130 kg).
Contrast analysis is contraindicated in patients with:
- Renal, liver failure.
- Endocrine disruption.
- Diabetes mellitus.
- Allergy to iodine.
The procedure is carefully prescribed lactating. If this took place, then breastfeeding is canceled for a day.
Common indicators for MRI scans are:
- Stroke.
- Memory impairment, ability to concentrate.
- Partial loss of hearing, vision.
- Suspicion of neoplasm.
- Headaches, fainting, dizziness at regular intervals.
- Injuries with hematomas and edema.
- The inability to conduct a CT scan.
MRI is used for control diagnostics after the treatment of malignant tumors and in the postoperative period.
This diagnosis is suitable for the children’s category of patients in the case of: intrauterine pathologies. developmental lag. cramps, fainting, dizziness, speech problems. The procedure is allowed from 3 years.
Hardware diagnostics will not work for patients who have:
- Dentures made of metal.
- Artificial heart valves.
- Devices for hearing.
- Dental crowns made of metal (gold, iron).
The first trimester of pregnancy, claustrophobia – indicators of careful use of MRI.
Severe back pain can be a contraindication to the procedure, as it requires a long fixed position.