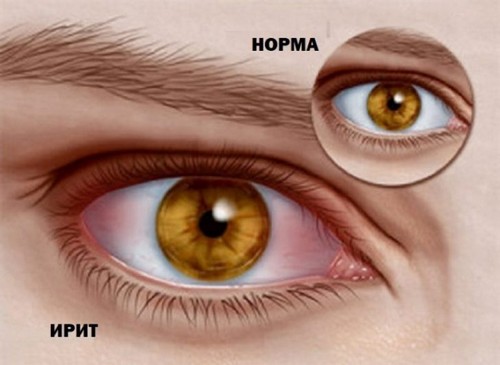
Iritis is a medical condition in which the inflamed iris of the eye. Iris, tapering and expanding, changing the diameter of the pupil. In addition, its color depends on the color of the eyes.
Suffer from iritis people of active working age, in 70% of cases the disease becomes chronic.
Isolated inflammation of the iris is rare. This part of the eye is anatomically and functionally very closely connected with the ciliary body (together they are the anterior division of the vascular shell of the eyeball), so patients almost always occur simultaneously and iritis, and cycles (inflammation of ciliary body). This disease is called iridocyclitis.
The causes of pathology
Irit in most cases is not only eye disease, its development usually occurs on the background of General infectious and non-infectious diseases.
This inflammatory process is provoked, or bacteria and viruses, or the immune aggression of the organism, or the metabolic and microcirculatory disorders (since the iris is part of the choroid, any problems in the vascular system affect its state).
Thus, the most common causes of iritis include:
In addition, inflammation of the iris may occur due to eye injury and botched surgery on the organ of vision. Iritis may also be a complication of other eye diseases. In some cases, to determine the exact cause of iritis and iridocyclitis doctors and fails. The role of a provoking factor in such situations can play a strong fatigue, hypothermia, hormonal imbalance, chronic stress.
Types of iritis
The nature of the flow under consideration, the disease is acute or chronic. However, this is not the only classification. Irity divided into various options, and based on the nature of the disease, and especially inflammatory process in the eye.
So, depending on the causes of inflammation of the iris can be of four types:
- Toxic-allergic. It occurs in infectious diseases, and autoimmune processes. The iris can be affected by toxins of bacteria. It can develop an allergic response, but allergens can be antigens of bacteria, an autoimmune complexes and other substances.
- Metastatic. Metastases in this case are the microorganisms, which penetrate into the iris through the vessels of foci of infection in the oral cavity or other organs.
- Traumatic. Especially dangerous in terms of developing iritis penetrating wounds of the eyeball.
The nature of the inflammatory process iritis can be:
- Serous.
- Purulent.
- Hemorrhagic.
- And fibrous.
- Mixed.
- Granulomatous.
The most unfavorable are purulent, fibrotic and granulomatous inflammation, as they often lead to complications.
The symptoms of iritis
Inflammation of the iris usually develops on one side only, with the exception of diabetic iridocyclitis. The severity of symptoms highly depends on the causes of pathology.
The main features of acute iritis include:
- Eye pain that increases with pressure on the eyeball and increases if the patient does not receive medical care.
- Blurred vision. There is a “blurring of vision”, “fog”, and “fly”.
- A strong contraction of the pupil.
- Photophobia.
- Change the color of the iris (it’s like she’s covered with rust).
- Redness of the eyes (but not always)
In the chronic form of iritis these symptoms are less pronounced.
However, the pathological process progresses, and rarely leads to serious complications:
- The formation of adhesions between the iris and beyond, the lens that affects the quality of accommodation of the organ of vision.
- Deformation or complete imperforate pupil.
- Progressive deterioration of vision.
- Of secondary glaucoma. It arises from the fact that the structures of the eye are soldered among themselves, thus disrupting the circulation of intraocular moisture.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of “Irit” is usually made on the basis of the results of biomicroscopy of the eye. In this study, doctors identify patient’s clouding of moisture in the anterior chamber, the accumulation there of an inflammatory exudate in the form of a Crescent, purulent and fibrous deposits on the posterior surface of the cornea.
After diagnosis be sure the survey is conducted, allowing to establish the cause of iritis. It is necessary for more effective treatment of disease. Patients undergo clinical tests (check blood, urine, sugar levels) and specific investigations, if there is a suspicion for a particular disease.
In chronic iritis the patient must also see an ophthalmologist and other specialists – a physician, a tuberculosis specialist, an endocrinologist, a rheumatologist, dentist, ENT.
Treatment of iritis
The main component of the treatment of iritis is the impact on the disease that caused the inflammation of the iris. So, diseases of the connective tissue is necessarily systemic therapy with hormones. If there is a severe purulent iritis, the patient shows antibiotics internally and externally. When inflammation of the iris tuberculous, syphilitic, or any other specific infectious nature to stop the pathologic process will not succeed without specific treatment.

In parallel with treatment of the underlying disease the patient is prescribed a course of ophthalmic drugs to reduce the severity of inflammatory changes, accelerate the absorption of exudate and eliminate the unpleasant symptoms of iritis. The sooner you get started this comprehensive treatment, the smaller will be the risk of complications.
Ophthalmic drugs used in iritis:
- Hormone drops and ointments.
- Funds for pupil dilation.
- Antibacterial or antiviral drops (depending on species).
Good efficiency with iritis also have a physiotherapy (UHF, electrophoresis, heating of the eye). In addition, patients indicated drugs immunostimulating action and vitamins.
Surgical treatment of iritis
Surgery is an extreme measure in the studied disease. It is usually resorted to in following cases:
- If the anterior chamber quickly and in a large number of accumulated inflammatory fluid.
- If adhesions have formed.
- If the pupil had fully healed.
- In secondary glaucoma.
- With the spread of purulent process outside of the iris.

Ophthalmologists use various options transactions – draining the anterior chamber of the eye, cut through the fibrous bands that form the hole in the iris, and remove rotting tissue, etc. to Avoid surgical treatment is possible if the time to go to the doctor and to pass a comprehensive anti-inflammatory therapy.
In General, the prognosis for iritis favourable. But only if the patient receives all the necessary range of medical care. Without treatment, acute iritis very quickly transformered chronic, persistent marked reduction of vision.