Sometimes, before an acute attack of glaucoma, a person may notice precursors, such as blurred gaze, bright circles when looking at a light source.
But an attack can develop without preliminary symptoms.
Symptoms occur sharply, suddenly, have a pronounced intensity. When presenting such a spectrum of complaints, the diagnosis of an acute attack of glaucoma is established at the prehospital stage even without any examinations.
The acute attack of glaucoma itself is manifested by the symptoms:
- sudden unbearable pain in the eyeball;
- headache, mainly in the area of the superciliary arches;
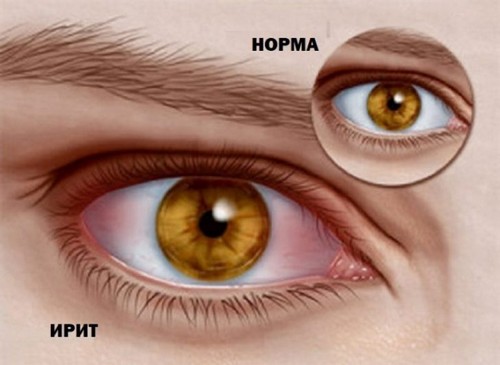
- there is a sharp compaction of the eye, it becomes hard to the touch, “stone”, reddens, tears;
- there is swelling of the mucous membrane of the cornea;
- pupil dilation;
- irregular reaction of the pupils to the light;
- the eyelids tend to close;
- suddenly and sharply deteriorates the clarity of vision;
- general symptoms: nausea, vomiting, a feeling of weakness, dizziness, a moderate increase in body temperature, sometimes there are pains in other organs (in the abdomen, heart).
But these clinical signs can also occur with other eye pathologies, so examinations will still be needed for a more detailed diagnosis.

The mechanism of occurrence of an attack of glaucoma
To understand the mechanism of development of an acute attack with angle-closure glaucoma, it is necessary to present the basics of the anatomy of the organ of vision.

The eye has a ciliary body – the structure responsible for the production of aqueous humor, which continuously circulates inside the eye and carries out metabolic processes. Excretion of this fluid occurs through the angle of the anterior chamber of the eye.
When for one reason or another, a block occurs in the path of intraocular fluid, i.e., the angle closes, an increase in pressure inside the eye (IOP) occurs. If this happens abruptly, quickly, with a rapid increase in IOP to 50–80 mm Hg. Art. and an increase in vivid symptoms, then this is an acute attack of glaucoma.
Some anatomical features predispose to an acute attack of glaucoma:
- thinned cornea;
- enlarged lens due to pathological swelling;
- large ciliary body;
- shallow front camera;
- small eyeball.
The listed features are often found in farsighted people.
Possible causes of glaucoma
Acute glaucoma is also called an acute attack of glaucoma. It is characteristic of a closed-angle form of the disease.

It can be asymptomatic for a long time, and a person first learns about it precisely by the onset of a sudden acute attack. And it can occur with symptoms, a person knows about the disease, but nevertheless, under the influence of a number of provocateurs, an acute attack occurs.
Can provoke an acute attack of glaucoma:
- psycho-emotional overstrain, stressful situations, exhaustion;
- long stay in the dark with subsequent exit to the light;
- long sitting with a bowed head;
- heavy drinking;
- exposure to high or low temperatures;
- intense workouts;
- instillation of drops dilating the pupil.
Glaucoma Diagnosis
Examinations are carried out on the basis of an ophthalmic clinic.
The diagnosis can be established based on the minimum spectrum of examinations:
- IOP measurement (tonometry);
- examination of the anterior chamber (gonioscopy).
To clarify the features of the morphology of the eye, the preservation of visual functions, other changes in the structures of the eye – conduct the following examinations:
- biomicroscopy and ophthalmoscopy (for examining the entire eye in an enlarged form);
- perimetry, refractometry and visometry (for evaluating vision functions);
- Ultrasound biometry;
- Force test;
- electronic tonography.
From laboratory examinations, a blood test (OAC, glucose, syphilis) and urine (OAM) are performed. In the presence of concomitant human pathologies, they are sent for consultation to a therapist, endocrinologist or other specialists of an appropriate profile.
In an acute attack of glaucoma, emergency care is required. The preservation of vision depends on the speed and correctness of actions.
Emergency care in the prehospital phase
First aid at home is to reassure a person, put him to bed and call an ambulance. At this time, you need to make a hot foot bath in order to reduce the flow of blood to the head. The arrived team introduces intravenously and gives a pill of the drug “Diacarb” inside.
In-patient drug therapy
The treatment of an acute attack of glaucoma is performed by an ophthalmologist in a hospital.
From drug therapy, drops are prescribed:
- “Pilocarpine.” In the first hour, bury every 10-15 minutes. Then 1 time in 30 minutes – 2 hours. Then 3 times every hour. After stabilization of IOP drops use 6 r / d.
- “Diacarb.” Tablets take 2 p / d.
- Timolol. Instillations do 2 r / d.
- “Azopt.” Instillations spend 3 r / d.
Additionally, to relieve an attack of glaucoma, appoint:
- Glucocorticosteroid: Dexamethasone;
- diuretics: “Torasemide”, “Furosemide”, “Mannitol”;
- injections of painkillers: “Ketorol”, “Analgin”;
- osmotic preparation: “Urea”;
- antiemetic agent: Metoclopramide.
All this time, medical workers monitor the dynamics of changes in the level of IOP. If within 3-4 hours the intraocular pressure does not decrease less than 35 mm RT. Art., the person is injected with a lytic mixture: “Chlorpromazine”, “Diphenhydramine”, “Trimeperidine.”
After the introduction of drugs, a person should lie 3 hours or more.
Glaucoma Surgical Treatment
If the attack persists throughout the day, intraocular pressure does not decrease, then surgical treatment is performed. The date and methodology of surgical benefits is determined by the attending physician.
Operations:
- Laser iridectomy. The bottom line is to remove part of the iris, thereby opening the outflow paths for aqueous humor.
- Laser iridotomy. An opening is created in the iris through which intraocular fluid flows.
- Laser trabeculoplasty. Microburns are formed using a laser beam, which stimulates the outflow of fluid.
- Trabeculectomy. Partial removal of the trabecular pathways and the creation of new ones are carried out.
- Shunting the front camera. New outflow pathways are being created.
To see how the operation on a glaucoma laser goes:
Complications and prognosis of glaucoma
An acute attack of glaucoma is a dangerous condition, so it is important to start medication or surgical treatment as quickly as possible to normalize IOP.
With the right tactics, the forecast is favorable: it is possible to maintain vision. If treatment is started late or in insufficient volume, then a significant deterioration in visual function is possible up to complete blindness.
The occurrence of an acute attack of glaucoma is possible at any age, but the risk is higher in people after 60 years. Symptoms are very specific, diagnosis is not difficult. Emergency care is required, because there is a threat of partial loss of vision or complete blindness.
The goal of preventive measures is to stabilize IOP. For this, a person with a diagnosis of “glaucoma” must follow the doctor’s recommendations, use drugs to reduce IOP, and avoid situations that can cause an acute attack.