Cortisol, which in excess produces Cushing’s syndrome, in this case can be called the hormone of death. In large quantities cortisol reduces the production of glucose, so necessary for most cells in our body, so due to lack of glucose, some cell functions fade away or even stop working.
Cushing’s syndrome (hyperadrenocorticism) is a long – term and chronic effects on the patient’s body excessive amounts of adrenocortical hormones, mainly cortisol. The syndrome may be caused by some internal disease, and taking certain medications.
According to statistics, women suffer from this disease more often than men (10 times more), and the main risk group is women aged 25 to 40 years. Due to the strong imbalance of hormones in a patient occur the pathological changes in appearance and biochemical processes in the body.
The causes of Cushing’s syndrome.
There are a lot of reasons that cause excessive formation of hormones of the adrenal cortex. There are three types of Cushing: exogenous, endogenous and pseudo-Cushing’s syndrome. Let us examine each of them separately and the reasons that most often cause them.
Exogenous hypercortisolism.
One of the most frequent causes of Cushing’s syndrome is an overdose or prolonged treatment with steroids (glucocorticoids) other any disease. Often steroids are used to treat asthma, rheumatoid arthritis or for immunosuppression in organ transplants.
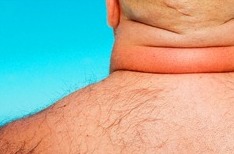
Endogenous hypercortisolism.
In this case, the cause of the disease is already internal disorders in the body. The most common cause, approximately 70% of cases, the development of the syndrome is a disease Itsenko-Kushinga (not to be confused with Cushing’s syndrome). Disease Itsenko-Kushinga is increased production of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), which in turn stimulates the release of cortisol from the adrenal glands.

This hormone can be produced by the pituitary microadenomas or actophilornis corticotropinomas. Ectobiology malignant kortikotropinom can be located in the bronchi, testes, ovaries. More rarely, Cushing’s syndrome occurs in the primary lesion of the adrenal cortex, for example, adrenal hyperplasia or malignant, benign tumors of the adrenal cortex.
Pseudo-Cushing’s syndrome.
Sometimes the symptoms can be caused by quite different factors, but this is only a temporary phenomenon and does not mean that the person is an hyperadrenocorticism. Frequent causes of pseudo – Cushing’s syndrome is obesity, chronic alcoholic intoxication, pregnancy, stress and depression, and sometimes even oral contraceptives which contain a combination of estrogen and progesterone. Increase the level of cortisol in the blood can occur even in infants, when their body together with breast milk comes alcohol.
Signs and symptoms of Cushing’s syndrome.
Rapid weight gain and obesity is found in 90% of patients, with than fat deposited on the face (Crescent-shaped, rounded face with rosy cheeks), stomach, chest and neck, and the arms and legs look thin.
Muscle atrophy is very noticeable on the shoulder girdle and feet. A quick reduction in muscle mass of the patient is accompanied by General weakness and fatigue. Together with obesity, this symptom creates great difficulties for patients when you perform any physical activity. Sometimes there is pain during squats and lifting.
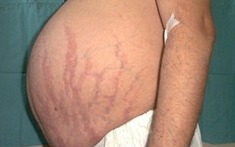
Very often, when hypercortisolism in a patient can observe the thinning of the skin. The skin is marble in color, dry and with areas of local hyperhidrosis. The patient not infrequently observed on the body of purple-bluish band stretching (striae), as well as any violation of the integrity of skin wounds and cuts heal slowly.
In women Cushing’s syndrome is often develop hirsutism (excessive pilosis on man’s type). The hair begins to grow on the upper lip, chin and chest. All this is caused by the adrenal cortex starts an enhanced production of male hormones – androgens. In women in addition to hirsutism occur menstrual disorders (amenorrhea), and men may experience erectile dysfunction (impotence), and reduced libido.
Osteoporosis – the most common symptom (90%), which is found in patients with hypercortisolism. Osteoporosis first manifests as pain in bones and joints, and then can occur spontaneous fractures of ribs and limbs. If the disease manifests in childhood, it becomes noticeable lag child development growth.
Cushing’s syndrome often develop cardiomyopathy with a mixed flow. This state occurs on the background of arterial hypertension, electrolyte shifts or catabolic effects of steroids on the myocardium. These violations manifest in the form of heart rhythm disturbances, high blood pressure, congestive heart failure, which in most cases leads to death of the patient.
Often about 10 – 20% of cases in patients with hypercortisolism is found steroid diabetes, which can be easily controlled with medication (glucose-lowering drugs).
From the nervous system are observed such signs as lethargy, depression, euphoria, various sleep disorders and steroid psychosis.
Treatment for Cushing’s syndrome (hyperadrenocorticism).
Treatment of Cushing’s syndrome are primarily aimed to remove the cause of the hypercortisolism and to balance the hormones in the body.
There are three methods of treatment: medication, radiation therapy and surgery.
The main thing – time to start the treatment, because according to statistics, if not to start treatment in the first five years from the onset of the disease, then death happens in 30 – 50% of cases.
The medical method of treatment.
If drug therapy the patient is assigned drugs that reduce the production of hormones in the adrenal cortex. Often pharmaceutical drugs are prescribed to the patient in the combined therapy or in that case not helped by other treatments. For the treatment of hyperadrenocorticism, your doctor may prescribe mitotane, metyrapone, or aminoglutethimide trilostane. Mostly these drugs are prescribed, if surgery is ineffective or it is impossible.
Radiation therapy.
This method is especially effective if the disease is caused by a pituitary adenoma. Radiation therapy, the effects on the pituitary gland causes it to decrease the production of adrenocorticotropic hormone. Usually, radiation therapy along with medical or surgical treatment. Most often, in combination with drugs, can this method be used since it enhances the effect of medical treatment of Cushing’s syndrome.
Surgery.
When hypophyseal Cushing’s syndrome is often used revision transsphenoidal pituitary and adenoma excision using microsurgical techniques. Improvements come very quickly, but the effectiveness of this method is 70 – 80%. If hypercortisolism caused by a tumor of the adrenal cortex, that is performed surgery to remove this tumor. In a single case, especially in severely ill people, and remove both adrenal glands, due to which the patient is prescribed lifetime use of glucocorticoids as replacement therapy.




I understand what you mean, but I have questions. Could I PM you?
It’s not dull when you discuss it.. out of every blog about this, yours is worth reading.
Your attitude should be taken as the standard when it comes to this topic.
Very good.
I quite like looking through a post that will make men and women think. Also, many thanks for permitting me to comment.
I want to to thank you for this excellent read!! I absolutely loved every bit of it.
I’ve got you book-marked to check out new stuff you post…