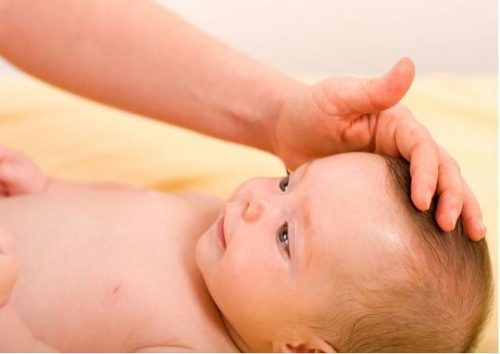
Each newborn child has at least one fontanel on its skull, which is represented by a non-ossified area of membranous tissue. Performing a huge number of functions, these structures through the increase or decrease can reflect some congenital and acquired pathologies in the baby.
Therefore, the large fontanel of the newborn requires dynamic monitoring both from the side of the parents and from the pediatrician.
During each monthly examination, the local pediatrician should evaluate the size and condition of the existing fontanels, which will allow him to suspect a developing disease in time. However, do not forget that an increase in the anterior fontanel in some cases falls within the normal range.
Causes
The anterior fontanel itself is large in comparison with the others and is characterized by a gradual closure. Only after measuring it with a ruler and comparing the child’s age with the standard can we judge the increase or decrease of the fontanel.
Some physiological reasons that affect the size of the cartilage of the child’s skull :
- Transient conditions that occurred in the mother during pregnancy. Hypovitaminosis and calcium deficiency due to malnutrition, mild anemia – all this can contribute to an increase in the anterior fontanel;
- Genetic predisposition. In the event that the child is calm, eats well, is gaining weight, but, like many of his relatives, has a large fontanel, this is included in the concept of the norm and is considered a family feature;
- The diet of the baby and the nature of feeding. As you know, breast milk is an ideal balanced product that allows a baby to fully develop and grow. Even the most adapted and expensive artificial mix can never be compared with breast milk. Therefore, children who are on mixed or exclusively artificial nutrition often reveal large fontanel sizes;
- Immaturity and prematurity also serve as the causes of the large front tempech, which is large in size. After a longer adaptation, such children eventually reach normal, age-appropriate growth rates, body weight and psychosomatic development.
Age features
The skull of any newborn child consists of 5 supple bones: two frontal, occipital and two parietal. They are interconnected by means of sutures made of dense fibrous tissue, which facilitates their movement during childbirth and as the brain grows.
The largest and most visualized fontanel in a newborn is the anterior, or large. It is localized at the junction of the connection of the parietal bones with the frontal and normally closes by 12-18 months of the baby’s life. Lateral fontanelles can be found on the left and right side of the skull, one of which is located somewhat closer to the front, and the second is behind the mastoid process. Their natural closure occurs by a year and a half.
The posterior, or small fontanel, is located in the area of the junction of the occipital bone with a pair of parietal. During the first two months of the baby’s life, he undergoes significant changes (fibrous tissue is replaced by bone) and eventually closes.

Age stages and dynamic monitoring of changes in the large fontanel :
- during the first month after birth, as a rule, no changes are detected;
- at the 7-8th week of life, a slight increase in the anterior tempera is possible;
- at 4 months, the processes of ossification start and the fontanel size tends to decrease;
- by 6 months, visible pulsation still persists despite overgrowing of the edges;
- at 7-8 months, signs of ossification progresses, as a result of which the size of the structure decreases significantly, the pulsation becomes poorly noticeable, and the shape from the diamond-shaped changes to oval;
- by 12-18 months in a healthy child, all fontanelles should be closed.
Due to the presence of pliable cartilaginous structures, the bones of the skull are easily found on top of each other, which facilitates the child’s passage through the birth canal and reduces the possibility of injury, including maternal. The fontanelles also provide heat transfer and cooling of brain tissue. In a way, they perform a cushioning function, protecting the baby from severe traumatic brain injury in the event of a fall.
What pathologies can a large fontanel talk about?
Pathological causes of a large fontanel:
- Rickets. The disease is characterized by a violation in calcium metabolism due to a deficiency of vitamin D and its metabolites. It is possible to suspect not only by the front temper, but also by flattening the nape, rolling the hair and softening the bones of the skull. Therapy is the oral administration of a vitamin. Read more about rickets →
- Congenital hypothyroidism. At the heart of pathogenesis is a lack of thyroid hormones. Such children are most often born later than expected, with a large body weight. Typical manifestations are a large hypertrophied tongue, a swollen abdomen, a child’s lethargy and a tendency to swelling. The treatment is carried out with hormone replacement therapy and, with a timely start, leads to good results, otherwise, there is a high probability of mental retardation.
- Down Syndrome. It is a consequence of chromosomal aberration and is usually diagnosed by ultrasound and genetic screening during pregnancy. Such a child will have a specific phenotype (deep-set eyes of a Mongoloid shape, an epicant – a fold of skin that covers the inner corner of the palpebral fissure, a short neck, a skin fold in the area of the little finger), an enlarged abdomen, and very often combined heart defects.
- Apert Syndrome. This pathology is a congenital malformation, mainly of the bones of the skull with a combined lesion of the hands of both hands. As a result of severe deformity, intracranial hypertension syndrome develops.
- Hydrocephalus. The etiological factor is the overproduction of cerebrospinal fluid, which accumulates in large volumes in the subshell spaces of the brain. As a result, intracranial pressure rises, and the size of the head reaches large numbers.
- Clavicular-cranial dysplasia syndrome. It is a genetic defect, manifested by underdevelopment of the bones of the skull and the complete absence of both clavicles.
- Intrauterine growth retardation. Most often it is a consequence of the perinatal infection that the child received from the mother.
- Achondroplasia. An inherited disease manifested by dwarfism, damage to the spinal column and multiple bone defects.
When it’s dangerous
All the above reasons are quite serious and have their grave consequences, as a result of which the general condition of the child can be disturbed and the pace of his development can slow down. If the size of the large fontanel in the newborn exceeds the permissible 3.5 cm, parents and the attending physician must carefully monitor its condition and take measurements daily, including the head circumference.
A prognostically bad sign is the constant bulging of a previously enlarged little crown. Such a symptom most often indicates intracranial hypertension, which requires the mandatory consultation of a neurologist and adequate therapy. In some cases, a short-term swelling of the fontanel is possible due to loud crying or crying of the child, which does not require any diagnosis.
Quite often, with a prolonged course of intestinal infection in a nursing infant, an anterior fontanel retraction can be detected. The appearance of such a sign indicates dehydration, which should be immediately stopped by the introduction of fluid through the mouth and infusion.

How is the closure of a large fontanel
A large fontanel in newborns should grow to one and a half years of life. This process is affected by the level of calcium ions and active vitamin D metabolites in the blood, the nature of the baby’s feeding, and the genetic predisposition. According to statistics, ossification of the skull occurs faster in boys (at about 8-9 months).
Rules for the care of a large fontanel
The large size of the little head requires proper care of it. Parents are advised to avoid excessive pressure on this area, try to shift the child in different poses so that he is not in the same position for a long time.
The possibility of injury, abrasions or scratches on it should be excluded. When peeling and yellow crusts appear in the fontanel fontanel area, they must be combed out carefully and the skin treated with a moisturizing baby lotion. It is also advisable to avoid prolonged exposure to direct sunlight.
Thus, the fontanelles in a baby perform a number of necessary functions, and any pathological change in their size can indicate the presence of a disease. Therefore, both the mother and the pediatrician should monitor them, up to closing.