During pregnancy, a woman is responsible for the health of the unborn baby and for her body. Any illness of the expectant mother can negatively affect the child.
The body of pregnant women changes dramatically : there are changes in the hormonal balance, the need for trace elements increases, vulnerability increases, which can affect the condition of the teeth.
Many pregnant women do not want to go to the dentist, believing that treatment will harm the baby. But filling does not harm the unborn baby, and untreated caries can lead to significant problems.
What is caries?
Caries is a complex, slow-moving process in which hard tooth tissues are destroyed. Initially, damage appears on the tooth, at which time the disease can still be stopped.
If caries are ignored, then the tooth is destroyed, the mineral substances that make up the tissues dissolve. In the future, a carious cavity forms, and the disease leads to tooth loss.
In countries where the preference is for soft, sweet foods (foods contain an overwhelming amount of carbohydrates), nearly 97% of people have tooth decay. In remote African and Pacific tribes, where people eat natural, often raw foods, caries was recorded in only 2-3%.
A common cause of caries is a violation of the acid-base balance, which occurs due to fermentation (glycolysis) of carbohydrates and the subsequent formation of organic acids. Glycolysis provokes bacteria that accumulate in the mouth.

The following factors affecting the development of caries are distinguished:
- poor oral hygiene – violation of the rules leads to the formation of plaque on the enamel. It is firmly bound to the tooth. This raid concentrates a large number of microorganisms.When carbohydrates enter the oral cavity, microorganisms convert them to organic acid. It first destroys the enamel, then the inside of the teeth;
- genetic predisposition;
- improper diet – a lack of proteins, vitamins and minerals, high consumption of sugar and fast carbohydrates worsen the condition of the teeth and lead to tooth decay;
- diet – the habit of eating at night, after brushing your teeth leads to the development of the disease;
- increased viscosity of saliva affects the development of caries;
- pregnancy, lactation;
- metabolic disorders and diseases associated with hormonal changes in the body;
- wearing dentures or braces;
- an increased number of streptococci in the microflora of the body, since they secrete a large amount of acid that destroys the hard tissues of the tooth.
Caries Stage :
- The first stage is the stage of the white spot – a condition in which the color of the tooth changes (a light or dark chalk stain appears). The enamel on the tooth is smooth, there are no unpleasant sensations. At this stage, you can easily stop the disease. This is a fairly quick and not expensive process.
- Superficial caries – this stage will begin if caries are not cured at the stage of occurrence. The chalky spot becomes rough, pain appears. The tooth begins to respond to hot or cold food. There is pain when eating acidic and sweet foods.
- The middle stage is the stage at which the enamel is already destroyed, and the inner layer of the tooth (dentin) is affected. Pain sensations become brighter and longer. At this stage, a carious cavity appears.
- Deep caries – this degree manifests itself if the teeth are not treated for a long time. Destruction approaches the near-pulp dentine. The cavity is enlarged, touching it causes severe pain. Destructive dentin affects the nerve of the tooth. A person is disturbed by frequent painful sensations.
- A complicated stage is the transition of caries into pulpitis or periodontitis. In this case, prolonged treatment by the dentist is required.
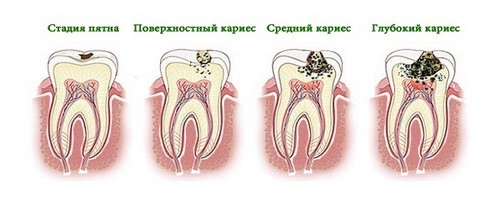
Caries is divided into types, based on the place of its localization:
- cervical caries – this type develops near the gums, where the enamel is most thin and vulnerable;
- contact type – caries that appears between the teeth, where the largest number of bacteria accumulates;
- fissure caries – it is also called caries of the chewing surface, this disease develops in the grooves of the chewing teeth;
- caries of cement – a disease characteristic of older people, in which the root of the tooth is affected.
Among dentists, a classification of caries has been adopted, based on the severity and prevalence of the process:
- compensated form – the intensity of caries in a patient is less than the intensity of the disease in his age group;
- subcompensated form – the prevalence of the carious process in a patient is equal to the average intensity indicators in his age group;
- decompensated form – the intensity of caries in the treated person is higher than the intensity in his age group.
Diagnosis of the disease
Doctors use x-rays to make an accurate diagnosis. The image will show a tooth damage, size and shape of the cavity.
X-ray studies even allow the establishment of latent caries. After diagnosis, the doctor prescribes treatment.
Symptoms
The following symptoms are the main symptoms of caries :
- the appearance of pain syndromes in the presence of external irritants – cold, hot food, sweet or sour food. The pain disappears immediately after the elimination of irritating factors;
- pain with mechanical pressure on the affected tooth – often it occurs when chewing food;
- the presence of damage (the color of the tooth may be slightly changed or a carious cavity will already be visible on the tooth), it can be detected independently by visual inspection;
- bad breath.
What is the danger (and is it dangerous?) Of caries during pregnancy?
Does caries (and how) affect the course of pregnancy, the health of a woman and the fetus?
During pregnancy and lactation, caries appears much more often, the process of tooth decay proceeds very quickly. Many pregnant women are afraid to go to the dentist, believing that treatment and anesthesia can harm the baby.
It was once believed that bacteria that cause tooth decay can enter the bloodstream. Through it, they will get to the baby and adversely affect its development. But the likelihood of them getting to the fetus is very low.
Bacteria cannot pass through the placental barrier (this is the ability of viruses). Even if they get to the embryo, they will not survive in its tissues.
But caries during pregnancy should still be treated. It can go into pulpitis or periodontitis.
With these diseases, toxic substances are formed, they enter the woman’s stomach, are absorbed into the bloodstream and disperse throughout the body, and can also reach the embryo.
Constant pain in the affected tooth worsens the general condition of the expectant mother. Painful sensations make eating difficult, increase nervousness. This can negatively affect the condition of the child.
Caries delivers a lot of unpleasant, painful sensations. It can lead not only to complications, but also to tooth loss. During pregnancy, the teeth are destroyed with great speed.
Untreated caries may mean that a woman will have to remove damaged teeth in the near future, since they will no longer be treated.
Caries is dangerous for the expectant mother (as well as for the fetus) with possible complications that cause severe pain. Pulpitis and periodontitis will have to be treated for a long time at the dentist.

Treatment features
Treatment of caries in the first trimester of pregnancy is undesirable. If a woman does not feel severe pain, then it is better to postpone the trip to the dentist until the second trimester.
If a pregnant woman is bothered by severe toothache associated with a complication of caries – periodontitis or pulpitis, then you should consult a dentist. But you need to warn the doctor about pregnancy.
In the first 12 weeks, all the vital organs of the unborn baby are laid. Treatment for tooth decay can trigger spontaneous abortion.
In the first trimester, two adverse periods for treatment are distinguished:
- mitotic period – at this time the mitotic activity of the embryo is increased, it is very sensitive to toxins, this period occurs on the 17th day after conception;
- organoleptic – the time when organs are laid in the embryo. Dental treatment during this period can lead to organ damage.
The second trimester – this period of pregnancy is called “fetal”. At this time, the child is growing rapidly. The likelihood of adverse effects of dental treatment on fetal development is significantly reduced.
Experienced doctors use medicines that are approved for pregnant women.
In the third trimester, the fetus becomes large enough, it presses on the aorta. Therefore, in the dental chair you need to lie, dodging to the left side, at a slight angle.
If a woman lies in a chair for a long time, in the usual position, then she may lose consciousness, as the fetus transfers to the aorta.
In the third trimester, the uterus becomes sensitive to any irritants. Any procedures can provoke a premature birth. To treat teeth in the third trimester is only in urgent cases.
During any trimester of pregnancy, you can not do an x-ray of teeth! This will negatively affect the fetus!

Prevention
The main measures for the prevention of caries:
- proper and regular oral care;
- nutrition correction: a decrease in sugar and carbohydrates in the diet;
- the use of fluoride-containing toothpastes;
- proper brushing and flossing;
- regular mouthwash;
- preventive visit to the dentist at least twice a year.
Women are advised to take care of their teeth in advance, even at the stage of pregnancy planning. This will help them avoid future problems associated with the treatment of caries, being in an interesting position.



