Gingivitis – periodontal disease, accompanied by inflammation of the outer part of the gingiva (tissue swelling, pronounced hyperemia). In children, the occurrence and development of disease is associated with the active flow of biological processes in periodontal tissues: the eruption of the teeth, development of occlusion, formation of roots.
In puberty in most cases gingivitis is the result of hormonal changes in the body.
If you notice that your kid is naughty during meals or when brushing your teeth causes blood, make an appointment with a pediatric dentist. It is possible that you will be diagnosed as “gingivitis”.
Important. The disease is common, occurs in approximately 2% of children aged 2-4 years, children older, the rate of diagnosis is much higher.
The causes of gingivitis in children
80-90% of cases of the disease in children is associated with accumulation of plaque, which is an ideal environment for the growth of pathogenic microflora. The more dental plaque and the higher the prescription, the greater the number of bacteria in them develops. Quite some days without oral hygiene, to the first signs of the disease. Gingivitis treatment in this case is an occupational hygiene – the removal of stones and plaque.
By the predisposing factors also apply an uneven load to the periodontal complex child. It may be associated with malocclusion, crowding, presence of tooth decay or poorly fitted seals. The appearance of gingivitis in children can be caused by injury to the gums (e.g. while brushing teeth), the result of burns from hot food.
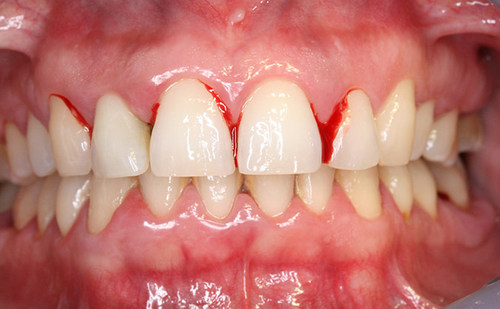
In some patients acute gingivitis occurs in the background of the eruption, or change of teeth. The gums at this time inflamed appearance and distinctive bright red color. Puberty also relates to risk factors.
In some cases, gingivitis may develop on the background of infections or systemic diseases that weaken the immune system. Diabetes, heart disease and thyroid gland predispose to the emergence of the disease.
The symptoms of gingivitis in children
Common symptoms of gingivitis in children are swelling of the gums, hyperemia (overfilling of blood vessels with blood), pain in the mouth. In the running form itself with fever and General malaise. Also the unifying feature of all varieties is poor oral hygiene.
Quite often, the gingivitis with stomatitis (gingivostomatit). In this case, affects not only the gums, but the entire mucosa of the oral cavity. The child is in constant pain, itching, burning, becomes capricious and unruly.
Especially dangerous viral gingivitis on the background of herpes quickly turns into ulcerative form. The most susceptible small children. Year-old child because of their age pulls all objects in the mouth, thus creating a favorable environment for the development of pathogenic bacteria.
The types of gingivitis
The disease can occur in different ways, depending on the type of gingivitis. The treatment is prescribed by a doctor individually in each case.
Important. Children have a much more common acute form of the disease. The chronic form occurs in the absence of treatment.
Classification
The disease is classified according to several characteristics:
- area of distribution – local (one maisonny inflamed papilla) or generalized (most inflamed part of the gums) gingivitis;
- the character of the course – acute or chronic stage;
- the rate of change of the mucous membrane of the gums – catarrhal, ulcerative, hypertrophic, atrophic, marginal, desquamative.
According to the severity of the disease there are three forms – mild (loss of one or two interdental papillae), medium (inflammation of the gum margins), severe (defeat most of the gums).
Catarrhal
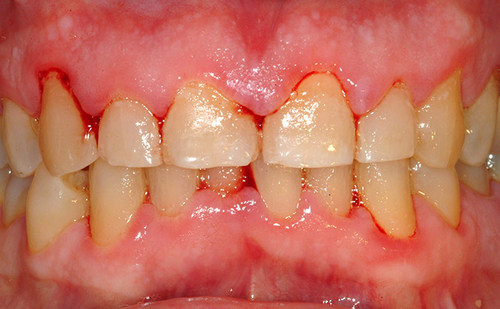
Acute catarrhal gingivitis is diagnosed most often in the leg or change of teeth, as well as on the background of infectious diseases.
Characteristic features:
- severe redness and swelling of the affected areas;
- unpleasant sensations in the gums, pain, itching, bleeding gums when brushing your teeth or eating;
- bad breath;
- low-grade fever.
Discomfort occurs, but the General condition is not worrisome.
Marginal
Occurs usually in children, evidence of poor oral hygiene. Passes immediately into the chronic form, another name of the disease – dirty gingivitis. Manifested in bleeding gums, usually when brushing your teeth. Regional tissue is edematous, hyperemic with cyanotic shade. Treatment consists in removing dental plaque and adherence to the rules for the care of the oral cavity.
Desquamative
The main feature of the desquamative gingivitis is the rejection of the epithelium. The affected areas are also enhanced redness in the form of separate spots. In the initial stage of the disease does not cause concern, but in the future, in the absence of treatment, the mucosa becomes friable, appear pain and a burning sensation in the gums, erythema spots expand. In poor condition at the place of spots popping bubbles with yellowish contents, then place the bubbles formed ulcers. In parallel, disturbed sleep, a headache, irritability.
Important. Desquamative gingivitis occurs in cycles with a sudden exacerbation without precipitating factors. Remission – long lasting, up to two years.
Hypertrophic
The second title of hyperplastic. The disease is characteristic of prepubertal and pubertal age, due to the influence of sex hormones on gingival tissue at this age. When fibrous form is observed the growth of papillae, gums greatly enlarged and partially closed teeth. Edematous form is more severe – the gums are enlarged and hyperemic. When brushing your teeth and chewing food pain and bleeding markedly increase.

A dental exam reveals the strong growth of the gums, looseness and swelling of the gingival papillae, the presence of false gingival pockets. Also a distinctive feature of hypertrophic gingivitis is a significant amount of plaque on the teeth.
Ulcerative
Ulcerative form is the next stage of catarrhal gingivitis on the background of low immunity after influenza, acute respiratory viral infections, infectious diseases, herpetic stomatitis. Another reason for hypothermia.
Characteristic symptoms:
- redness, swelling, bleeding gums;
- the appearance of ulcers;
- General weakness, subfebrile temperature;
- cyanotic hue of the gums.
In the absence of adequate therapy, the disease becomes ulcerative and necrotic stage of ulceration, covered with bloom gray-green, there is a putrid smell from the mouth, the saliva becomes viscous. Disturbances of sleep and appetite, the child becomes capricious.
Atrophic
In most cases, the disease occurs in a chronic form, and is discovered during examination a dentist. Observed improper fillings, the presence of congenital defects of the frenulum of the tongue or abnormal occlusion.
Symptoms were not clearly expressed:
- weak bleeding gums;
- exposure of roots of teeth;
- the decrease in the volume of the gums.
In the initial stage of the inflammatory symptoms and pain are absent, the gums are not bloodshot. Then, with the gradual exposure of roots of teeth when taking hot or cold foods a discomfort and pain. In the absence of treatment observed progressive degenerative changes in the gingival margin.
How to treat gingivitis in children
Gingivitis – a disease with a favorable prognosis. The exact implementation of the recommendations the doctor gives you to fully recover and avoid further relapses.
Treatment always begins with rehabilitation of the oral cavity. Removal of Tartar and soft plaque is required, because the deposits represent a source of infection. For small children the purification is carried out using special brushes, older (after 10 years) using ultrasound. After cleaning, the doctor prescribes twice a day rinsing anti-inflammatory drugs (in pharmaceutical form or decoctions of chamomile, sage, peppermint, eucalyptus).
Important. Dear parents. Some folk remedies the disease cure is not possible. Ignoring this rule, you risk to aggravate the condition of their child.
In the treatment of gingivitis, the doctor uses a holistic approach tailored to the individual characteristics of the child. Removed cavities, hold the replacement of fillings with overhanging edges or poor polishing. In the presence of congenital malocclusions or frenulum of the tongue performed the necessary manipulations. At a certain stage may require consultation with narrow specialists, dental surgeon, dentist-orthopedist, internist, endocrinologist, cardiologist.
If necessary, the doctor appoints vnutrizonovye electrophoresis, laser therapy, massage, UFO. At an advanced stage of the disease requires antibiotics. In severe cases, when conservative treatment does not bring results, may require surgical intervention.
The most important role in the treatment of gingivitis in children plays vitamin therapy and proper nutrition. You need to make a diet so that cooking using products with a high content of vitamins.
Important. During treatment, you need to ensure that the food has been pureed or soft. Parents are required to make the process of eating has taken a minimum of discomfort.
Cure for gingivitis
Your child needs medications appoint a doctor, based on the clinical picture of the disease and individual condition of your child. Self-medication in this case is unacceptable, as it can lead to significant complications down to osteoporosis bone tissue.
Than to smear
Gels and ointments applied after rinsing the mouth. The surface of pre-dried with a cotton swab or gauze.
Holisal. The gel has a good anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties. Applied three times daily to the affected areas of the gums.
Evident asset. Ointment based on natural components, quickly relieves pain and inflammation. The composition is applied to inflamed areas and rubbed with gentle circular movements.
Solcoseryl. Used for the healing of bleeding sites, the gel was applied on both sides of the gums. Use on prescription.
Asepta gel. Mostly prescribed for the treatment of chronic gingivitis. the drug is well relieves inflammation, pain, itching. Apply 2-3 times a day depending on the severity of the condition.
Than rinse
Important. For rinsing not to use alcohol tinctures, because their use will lead to even greater irritating effect.
Rinses are required when conducting anti-inflammatory therapy. Hold after each meal and during the day. For small children the parents spend of an application with a swab impregnated with solutions. In severe cases, the treatment of the mouth and gums is carried out in the dental office.
For rinsing prescribe:
- Chlorhexidine 0,05 %. Apply after each meal. Intense mouthwash for 30 seconds.
- Furatsilin. Use ready-a 0.02 % rinse or dissolve one tablet in a glass of boiled water. The drug is well disinfects the mouth.
- Formistin of 0.01 %. Has powerful antibacterial effect, use after a meal.
- Herbal infusions. Prepared in the home in accordance with doctor’s recommendations.
Important. Before using the solutions, rinse the mouth with clean water to remove food residue.
Antibiotics
In the chronic stage, and in severe forms of the disease (peptic ulcer, ulcerative-necrotic), and at high risk of complications prescribed antibiotics. Medication and dosage is selected by the doctor individually.
Folk remedies
Traditional methods based on the specific properties of plants, the decoctions of which have a good anti-inflammatory action.
Sage. Two tablespoons herb pour 0.5 liters of boiling water, boil for 10-15 minutes, infuse for an hour. Rinse your mouth 2-3 times a day. A decoction of the well reduces inflammation, reduces bleeding gums.
A pine needle. 1-2 tablespoons of needles, pour a glass of hot water, bring to the boil, infuse for 40 minutes. Use 3-4 times a day. The infusion has a strong antimicrobial activity.
Aloe. Cleaned and well-washed leaves to chew on several times a day.
The camomile. Take in equal proportions chamomile flowers and Linden flowers. Tablespoons of the mixture pour boiling water, boil for 20 mins, allow to stand for half an hour. Infusion has a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect. Apply three times a day.
Herbal (oregano, St. John’s wort, peppermint mixed in a ratio of 1:1:2). Three tablespoons collection pour 1.5 cups of boiling water, boil for another 30 minutes. Infuse for two hours, rinsing three times a day. The broth helps reduce inflammation and pain, eliminates bleeding, bad breath.
How long does the treatment of gingivitis in children
Non-running form of the disease in children can be cured in 10-20 days. In more complex cases, the physician is tasked to prevent the aggravation of illness and translate it into a long remission.
Diagnosis how to know that the child has gingivitis
The doctor makes a diagnosis based on examination of the oral cavity, the patient (or his parents), and conducted functional tests for determination of the bacterial plaque index and bleeding.

To avoid errors in diagnosis, the doctor prescribes an x-ray examination of the teeth. The main difference between gingivitis from other diseases is that the inflammatory process affects only the gum. Bone tissue and muscle tissue remain unchanged.
Complications of gingivitis
One of the features of gingivitis, the disease can be cured completely. Under the advice of a doctor and personal hygiene, the disease is not refundable.
In case of prolonged non-professional treatment as well as the long failure to seek to the doctor’s gingivitis can gradually turn into periodontitis. There is a softening of the bone, the teeth start to become loose, gum pockets are formed, there is a putrid smell from the mouth.
Prevention of child gingivitis
Of great importance in the prevention of child gingivitis is the correct selection of toothbrush. The bristles should be soft and age appropriate to avoid damage to the gums while brushing. Special attention is waged daily personal hygiene to avoid the accumulation of plaque.
You also need:
- visit the dentist regularly for early detection of dental problems;
- carefully inspect the child’s mouth during the eruption and change of teeth;
- to teach children to self rinse your mouth after every meal, especially after sweet (sugar contributes to the rapid destruction of the enamel and the bacterial accumulation of precipitation;
- to organize the food children;
- be careful after the transfer of child infectious or other serious diseases, leading to decreased immunity.
Important. To prevent the occurrence of gingivitis easily. Simply adhere to these simple rules, which should become the norm.

With thanks! Valuable information!
What i do not realize is in truth how you are no longer actually a lot more smartly-liked than you may be now. You are so intelligent. You understand therefore significantly on the subject of this topic, made me in my view believe it from so many varied angles. Its like men and women don’t seem to be interested except it¡¦s one thing to do with Girl gaga! Your own stuffs great. Always maintain it up!
Thanks for your personal marvelous posting! I definitely enjoyed reading it,you might be a great author. I will be sure to bookmark yourblog and will eventually come back at some point.I want to encourage you continue your great job, have a nice morning!
Just commenting to register my support. Your opinion is well thought out Good job!
You sound a little out of touch-you should be clearer?
Hello, I enjoy your blog and I resonated with this article a whole lot. . How can I learn more?
I and my friends were reading the great advice located on your website and then immediately developed a horrible suspicion I never thanked you for those techniques. Most of the young boys had been excited to learn all of them and already have actually been tapping into those things. Appreciation for actually being considerably thoughtful and for getting these kinds of ideal subject matter most people are really wanting to be informed on. Our sincere regret for not expressing appreciation to sooner.
Excellent Blog, Nice Work Keep it up!
Good info. Lucky me I recently found your site by accident (stumbleupon). I’ve book-marked it for later.