Experts identify the following types of luxation of the tooth:
Incomplete dislocation. Is a partial displacement of the tooth root of the alveoli, accompanied by rupture of the periodontal tissues to a lesser or greater extent;
Complete dislocation. Characterized by the loss of the tooth from the socket;
Impacted dislocation. Means full or partial displacement of the tooth from the socket in the direction of the jaw body, leading to severe destruction of bone tissue.
Luxation of tooth can be caused by the following reasons:
- Mechanical trauma caused by shock, drop, etc.
- Injury received as a result of biting too hard, solid food
- Injury received as a result of falling food foreign solids
- Some harmful habits (e.g., teeth opening bottles, etc.)
- Incorrect removal of teeth, resulting in dislocation of the adjacent teeth (usually indigenous)

IMPORTANT: IN most cases, dislocation of the tooth is in respect of temporary teeth.
Incomplete dislocation of the tooth
In case of incomplete dislocation of the tooth changes its position in the tooth row, there have been patient complaints of pain and mobility of tooth, manifest violation of chewing function. In the process of examination of the oral cavity is a partial dislocation of the tooth is characterized by the displacement of the crown of the damaged tooth in a different direction, for example, oral, distal, vestibular, in the direction of the occlusal plane and so on.
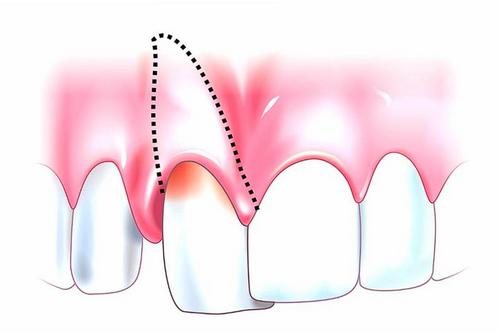
A damaged tooth may differ sharply painful, and the mobility of the percussion, but it is not shifted outside of the dentition. The gum is characterized by areas of redness and swelling, sometimes its possible gaps. The reason for the gap tooth circular ligament and periodontal tissues, as well as from damage to the alveolar walls can form pathological periodontal pockets, characterized by bleeding from them.
Luxation of the tooth and oral offset the crown of the tooth root, as a rule, is displaced in the vestibular direction, and Vice versa. When tooth displacement in the direction of the occlusal plane damaged tooth protrudes above the level of neighboring teeth, it is moving and interfere with occlusion. In many cases, the patient has a concomitant injury to the soft labial tissue in wounds, hemorrhage or injury.
Outcome and possible complication of incomplete luxation of the tooth is considered to be:
- Obliteration of the canal of the tooth root and the formation of granulomas within the pulp;
- Shortening of tooth root;
- The curvature of the tooth root;
- Stop the formation and further growth of the tooth root;
- Changes in the periapical tissues in the root of the cyst or chronic periodontitis.
Complete dislocation of the tooth
Complete dislocation of the tooth, or traumatic extraction, is due to complete rupture of the circular ligament of tooth and periodontal tissues of the tooth, which happened in the process of receiving a strong blow to the tooth crown. In most cases there is loss of the front teeth of the upper jaw, mainly the Central incisors, less often suffers lower jaw.
The clinical picture of complete dislocation of the tooth implies the absence of the tooth in the tooth row and the presence of a bleeding tooth, sometimes filled with fresh blood clot. Often there are associated injuries of the soft tissue labial. According to experts, in the preparation of treatment plan is necessary to assess the condition of the damaged tooth to determine the presence of cavities, the integrity of the root and the crown, the permanence or temporariness of the tooth.
IMPORTANT: If replantation of the tooth happens within half an hour after the injury, the tooth root is destroyed is minimal and the tooth can be preserved for years to come.
Intrusion luxation of the tooth
Impacted dislocation of the tooth, or tooth intrusion is the complete or partial immersion of the dental crown into the alveolus because of the receipt of the jaw injuries, tooth root while immersed in the spongy substance of bone tissue of the jaw.
In most cases there is damage to the front teeth of the upper jaw obtained by reason of the strong impact on the cutting edge of the tooth. With impacted dislocation of the damaged tooth is embedded deep into bone, thus there is a complete or partial rupture of the periodontal tissues and the fractured cortical plate of tooth holes, especially near the bottom.
Patients complain of shortening of the damaged tooth after injury compared to nearby teeth, they note that the tooth is practically invisible. Definition of reducing the height of the visible part of the dental crown is performed in a clinical setting, the tooth is usually located above or below the occlusal plane.
A damaged tooth is stable and mild percussion tenderness. Sometimes it happens that the crown of the damaged tooth is not visible because of her complete immersion into the tooth hole. In this case, detected by the cutting tooth edge in the process of medical examination of the tooth, there is rupture of the mucous membrane of the gums and bleeding from the hole.
Treatment of luxation of the tooth
First, you need to resolve the question of whether retention of such a tooth. The main criterion experts believe the condition of the bone around the tooth root. If its safety is not less than half the length of the tooth root – the tooth is recommended to keep.
The dentist sets a damaged tooth to its original place under anesthesia, further excludes any mobility with splinting rapid hardening plastic or wire. Next, the technician determines the condition of the tooth pulp and if there is a rupture of the neurovascular bundle, the pulp should be removed, and the channel – filling. If the pulp remains viable, it is recommended to keep. The condition of the pulp is determined by using its reaction to an electric current, but within 35 days after injury, the decrease in sensitivity of the pulp may be a response to trauma, so you need to check the state of excitability of the pulp in the dynamics.
If there is pulp necrosis due to rupture of the neurovascular bundle, it must be removed after the fixation of the tooth in the correct position. When necrosis of the pulp rapid removal is the prevention of disintegration of the tooth crown and its coloring in dark color.
When you receive an acute injury may occur complete dislocation of a tooth, involving the replantation of the tooth, which will lead to success in the constancy of periodontal tissues.
Holding the tooth replantation presented the following items:
- Trepanation of the tooth;
- Removal of the pulp
- The root canal of the tooth;
- Root treatment and tooth antiseptic solutions;
- Introduction and fixation of the tooth in the hole, and sometimes splinting;
- Further follow-up and radiological control in the absence of patient’s complaints on pain.
If replantation of the tooth happens within half an hour after the injury, the tooth root is destroyed is minimal and the tooth can be preserved for years to come. If replantation is carried out some time after the injury, within one month after replantation marked resorption of the tooth root, through the year leading to its complete destruction.
Statistics of child injuries tooth
According to experts, obtaining an acute injury, approximately 32% of all cases, is the cause of the destruction and loss of front teeth in children.
In most cases, dislocation of the tooth is in respect of temporary teeth, a little less common broke off the crown. In respect of permanent teeth is most often the case broke off of the crown, a little less – dislocation or injury of the tooth, and a broken dental crown.
Dental injuries happen in children at different ages, in most cases, temporary teeth trauma happen in 1-3 years, and injuries of the permanent teeth – in 8-9 years.
Dislocation of the tooth of the child
Dislocation of the tooth is one of the most common injuries in children. Children are very active, often running and falling, and temporary teeth are much less durable, which makes them very vulnerable.
Many parents believe that the dislocated tooth need to return to the place immediately, however, the more experienced say – it is not always necessary. Only a dentist can determine whether to shift the tooth, especially if the appearance of the baby is not particularly harmful. And certainly in any case can not “fix” the tooth on their own – this will lead to a more serious injury.
In addition, damage to a baby tooth is dangerous because it can affect the permanent tooth, so that even the slightest injury should visit a pediatric dentist.