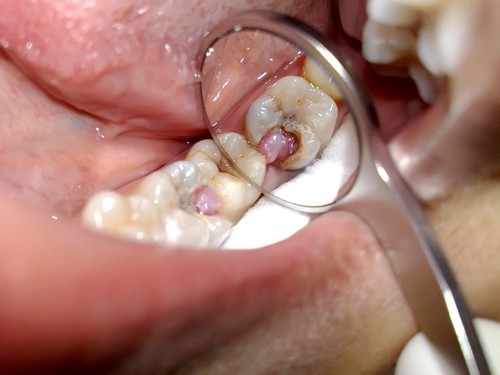
The most common cause of pulpitis is not treated early deep decay of the tooth. In this case, during the increase of carious cavity germs can penetrate into previously inaccessible pulp tissue.
The infection can get directly into the open area of the pulp (direct access) or through the dentinal tubules (indirect access).
The dental professionals are the following ways of development of pulpitis by infection in the pulp tissue:
- Using a dental crown in the case of complications of dental caries;
- Through the hole in the tip of the tooth root (retrograde form).
Pulpitis in retrograde form is quite rare, characterized by the specific pathogenesis.
According to experts, following are the reasons for this form of pulpitis:
- Inflammation of the dental pulp in the presence of the patient common infectious ailments by means of hematogenous spread of infection in the maxillofacial region;
- The spread of the infection from the foci located near the tooth roots. In many cases, the infectious focus is the maxillary sinus due to sinusitis;
- Spread through the space between the gum and tooth root – periodontal canal – in case of infection when periodontal attachment is broken, allowing the infection to get to the apex of the tooth root.
Often cause the development of pulpitis be wrong manipulation specialist and dental errors. This error is the overheating of the tooth during its preparation, accidental opening of the pulp chamber with the further imposition of seals, incorrect turning the tooth for a crown, held without complying with the technical features and do not complete installation of the cap to protect the treated tooth during the manufacturing of the dental crown.
Tooth affected by pulpitis, manifests itself immediately after the appearance or dental error that requires immediate expert intervention to resolve the problem.
IMPORTANT: Acute pulpitis usually appears with a closed pulp chamber and may be reversible if the cause of inflammation in the pulp tissues are damaged after the curettage of periodontal pockets, and irreversible if it is noted the impossibility of self-healing of the pulp.
German scientists have found that regular consumption of white wine may lead to severe tooth decay and subsequent development of pulpitis. The study, conducted by researchers from Germany, has allowed to prove the destructive force of white wine, which, unlike red wine, provokes a rapid and strong development of dental caries and pulpitis. According to scientific experts, the reason lies not in age, degree, or origin of white wine, and the duration of its effects on the enamel of the teeth and the level of acid-alkaline balance.
In the study, experts from Mainz University carried out experiments by immersing in a container with several types of wine, the teeth of adult subjects. It soon became apparent that white wine affects tooth decay is much stronger and faster than other varieties of the alcoholic beverage. During the day, the impact on the patient’s tooth white wine corroded calcium and phosphorus of tooth enamel to a depth of about 60 micrometers, which is a serious indicator. According to scientists, the most destructive effects on tooth enamel have white wines produced from the grape variety “Riesling”.
Symptoms symptoms of pulpitis varied and is represented by two main types:
- Acute diffuse and focal pulpitis;
- Chronic form gangrenous, hypertrophic and fibrotic pulpitis, exacerbation of pulpitis chronic form.
Clinical manifestations of chronic and acute pulpitis similar, but each manifestation has its own characteristics that allow the expert on the basis of subjective sensations of the patient and of objective data to correctly diagnose forms of pulpitis.
The clinical symptom of pulpitis is deep caries of the tooth, with dental caries in many cases the pulp becomes inflamed by cause of the thickness of the dentin.
Acute pulpitis usually appears with a closed pulp chamber and may be reversible if the cause of inflammation in the pulp tissues are damaged after carrying out curettage of periodontal pockets, and irreversible if it is noted the impossibility of self-healing of the pulp. Treatment of acute forms of pulpitis involves taking polyarnogo inflammation and may depend on the symptoms and stage of the disease.
Symptoms of acute pulpitis
- The pain occurs spontaneously, the frequency and intensity of which are associated with the severity of the occurrence of the inflammatory process;
- Chemical, mechanical and temperature stimuli cause prolonged painthat persist for some time even after the elimination of the stimulus. Dental caries, the pain disappears immediately after cessation of exposure to the stimulus. Acute pulpitis is accompanied by pain even in low irritation, liquid at room temperature causes the patient pain and a sensation of cold;
- The increased pain at night. It can also occur exacerbation of chronic pulpitis;
- Paroxysmal character of the pain with pain free intervals between attacks. Often on skin areas of the neck and face, corresponding to a disease of the teeth, there is increased sensitivity – hyperesthesia. The clinical manifestation is also characteristic for exacerbation of chronic pulpitis;
- The pain may resemble neuralgia because of the spread of its branches of the trigeminal nerve. In neuralgia, in contrast to acute pulpitis, pain is able to decrease at night, often disappearing entirely.
Experts distinguish several stages of acute pulpitis.
Acute focal pulpitis
Acute focal pulpitis – the initial stage of inflammation in the dental pulp, which lasts about 2 days. The hearth localized in pullparam the site, which is closest to the cavity decay. This form of acute pulpitis is characterized by intense, but intermittent and transient pain arising spontaneously, and any stimulus and lasting for 10-60 minutes. The intervals between the attacks lasted several hours. Because the scope of pain has a clear localization, the patient is easily able to determine exactly impressed with the pulpitis of the tooth.
IMPORTANT: the Most common cause of pulpitis is not treated early deep decay of the tooth. In this case, during the increase of carious cavity germs can penetrate into previously inaccessible pulp tissue.
Acute diffuse pulpitis
Acute focal pulpitis extends further on the crown and root Polyarnye part. This means the transition to the stage of acute diffuse pulpitis in which pain have a long duration, and intervals between attacks is reduced to 30-40 minutes.
At night there is severe painthat after the influence of stimuli of different duration. Tooth sensitive to hot and cold foods and drinks. Pain has no clear localization and distributed through branches of the trigeminal nerve, it can give to another jaw or in the opposite part of the jaw and in the area under the jaw, eyebrows, forehead, cheekbones, nape and ear. When we tap on the affected tooth, the patient feels the pain. Upon inspection, the dentist reveals a deep carious cavity.
Acute purulent pulpitis
The transition to the stage of acute purulent pulpitis is characterized by unbearable, pulsating and almost continuous pain. By day, she runs, but may slightly decrease. A touch hot to the tooth causes severe pain, cold can weaken it. Painful course of acute diffuse pulpitis with the flow in the purulent form lasts from 2 days to 2 weeks.
Chronic forms of pulpitis
If it wasn’t carried out timely treatment of acute pulpitis, then its inevitable transition to chronic pulpitis, forms that differ in long flowing inflammatory process a period of several weeks and months to several years.
The symptoms of chronic pulpitis
- An inflamed pulp with a bleeding region;
- The destruction of hard dental tissues;
- Not too severe toothache that occurs after exposure to the stimulus and a long time passing after its liquidation;
- Aching pain in contact of the affected tooth with a cold or in the process of eating;
- Difficulty chewing food on the side of the affected tooth.
In some cases, pain at a chronic pulpitis is absent, and the sluggish flow of inflammation are sometimes interrupted by periods of worsening of the disease.
IMPORTANT: the Conservative treatment of such dental diseases as pulpitis, can last for several days. During the treatment the specialist should hold a rational analgesia, completely remove the dentin affected by necrosis, the right to form a cavity, using only drugs that are fully compatible with the patient’s body.
Experts distinguish several stages of chronic pulpitis.
Chronic fibrous pulpitis
Chronic fibrous pulpitis occurs after the transition of acute inflammation in chronic inflammation and is characterized by long flowing, painful reaction of the tooth to any stimuli, and proliferation of fibrous connective tissue. After the liquidation of irritant the pain recedes. Sometimes there are spontaneous short-term pain.
Chronic gangrenous pulpitis
A chronic gangrenous pulpitis is the result of acute purulent and chronic pulpitis in case of death polyarnyh tissues. The process is accompanied by a bursting sensation and feeling of heaviness in the teeth, bad smell of the major cavities and pain caused by the influence of hot or transfer of the patient from cold to warmth. Painful reaction of the tooth to cold is not marked, the tooth crown has a dull grayish hue.
Chronic hypertrophic pulpitis
Chronic hypertrophic pulpitis is a rare form of chronic pulpitis, it occurs most often among young people arises in the case of strong destruction of the dental crown. This form of chronic pulpitis is characterized weak spontaneous pain, appears polarna hypertrophy, may form a polyp in the affected area of the tooth, preventing the patient in the process of clamping jaws with food. The reaction of the affected tooth to temperature changes is missing, there is often bleeding pulp.
Exacerbation of chronic pulpitis
Exacerbation of chronic pulpitis symptoms, characteristic of pulpitis in the acute form, e.g., spontaneous pain, sluggish, combined with the symptoms of pulpitis chronic form, for example, with extensive destruction of the hard dental tissues.
Diagnosis of pulpitis
Anatomical features of dental pulp pulpitis complicate diagnosis. Diagnosis of this disease involves a medical evaluation of such subjective data, as the duration and the nature of the pain. If any form of pulpitis, the dentist reveals a cavity having large dimensions. In acute pulpitis probing the bottom of carious cavity is painful, chronic pulpitis during the sensing of the bottom reveals the entrance to the tooth cavity. In the temperature caused by severe reaction, especially in the cold.
In addition, experts note a reduction in the threshold polyarnoi of elektrovozoremontnij to 20-80 mA. Changes in the mucous membrane in the area of transitional fold is not marked. In acute pulpitis on the radiograph is determined not damaged by the inflammation of the periapical tissue, which in the case of chronic pulpitis undergo adverse changes typically associated with granulomatous or fibrotic forms of periodontitis.
Differential diagnosis of pulpitis
Experts in diagnosis of pulpitis is carried out differential diagnosis with the following diseases:
- Alveolitis;
- Deep caries;
- Periodontal abscess;
- Sinusitis;
- Neuritis, trigeminal neuralgia;
- Chronic and acute apical periodontitis.
Complications of pulpitis
Complications of pulpitis occur in the absence of timely and adequate treatment. In addition, unscrupulous dental manipulation, for example, poor installation of the seal with the formation of voids or the introduction of material for the tip of the tooth can lead to complications, for example, the inflammation of the area near the root of the tooth – periodontitis.
Time has not carried out or incorrect treatment of pulpitis leads to the following complications:
- Inflammation in the area of the periosteum – periostitis, dental flux;
- Purulent inflammation of the bone marrow – osteomyelitis;
- Purulent inflammation of the tissues abscess;
- Blood poisoning – sepsis;
- The disease is caused by poisoning of the patient by the decay products of the affected tooth amyloidosis. Can cause cessation of operation of individual internal organs;
- A complication of pulpitis, caused by exudative outflow from the area of inflammation in the area of soft tissues – cellulitis. Is one of the most dangerous purulent inflammation, has no clear boundaries.
The treatment of this disease, experts recommend not to delay, because help dentist when pulpitis helps to relieve inflammation and strong pain, eliminate the source of infection, recovery polyarnoi functions, sometimes function of a tooth.
Conservative treatment of pulpitis
Conservative treatment of pulpitis, according to experts, has the following indications:
- Acute focal pulpitis;
- Cavities with low intensity;
- The age of 30;
- The absence of exacerbations of chronic fibrous pulpitis;
- The lack of respiratory viral diseases during the period of treatment;
- The inability of dental prosthetics;
- The absence of a burdened allergic anamnesis data;
- No visible changes on radiographs in the area of apical hole;
- Exposure of the pulp tissues the result of imprudence or after otloma of the crown, subject to the preservation of the nervous bundle in the area of apical openings.
Conservative treatment of such dental diseases as pulpitis, can last a few days. During the treatment the specialist should hold a rational analgesia, completely remove the dentin affected by necrosis, the right to form a cavity, using only drugs that are fully compatible with the patient’s body.
Stages conservative treatment of pulpitis
- Analgesia in the area of planned impacts;
- Treatment of cavities by using dental instruments;
- Treatment of carious cavity with the help of drugs in the form of heat;
- Degreasing and subsequent drying of carious cavity;
- The imposition of a special insulating strip;
- Staging seals.
The insulating spacer relieves inflammation in the pulp, reduces pain, stimulates the formation of dentin to replace Polarnye and normalizes metabolic processes.
Vital amputation of the pulp – a method of treatment involving the safe polyarnoy viability only in the channels of dental roots after removal of the coronal portion of the pulp. This method is used for the treatment of multi-root teeththat have a distinct boundary between the tooth crown and root dental pulp, but it is not relevant in the presence of diseases of the periodontium and periodontal. In addition, such treatment is conducted only for young patients.
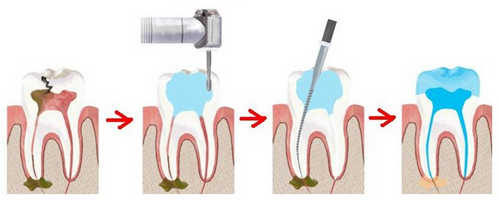
Surgical treatment of pulpitis
Surgical treatment of pulpitis, according to experts, is performed a few visits.
It implies a serious intervention and is conducted as follows:
- First comes the anesthesia area of the planned intervention;
- Next, the dentist uses the handpiece with the aim of drilling of the tissues affected by caries. This can be removed the healthy tooth areas;
- Then the root canals to block against the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms through cofferdam – a special protective shawl with holes for the teeth, and is composed of latex;
- The technician then carries out the removal of the pulp from the crown area and the root canals using pulpectomies – dental instrument with notches to extract the diseased pulp from the root canal of the tooth;
- Then, you must make careful measurements of the lengths of the root canals. If incorrect measurements are possible incomplete or excessive filling of the channels, causing the development of various complications and pain. To measure the length of the channels is applied to the apex locator and radiograph. In each of the channels specialist, introduces the K-files, joining the apex locator with the help of electrodes. Files advance in the depth of the root up until the apex locator will not give the signal reaching the anatomic end of a tooth root. The channels may have different length, so the measurements made for each of them individually;
- Next, the dentist performs mechanical processing of root canal using hand files to their enlargement for subsequent filling;
- The channels are washed with antiseptic, made a bookmark of drugs and the placement of a temporary filling. The patient goes home;
- In a new visit is made by the removal of the temporary filling and medication of the canals of the tooth root;
- Further, the channels are washed with warm antiseptics and dried;
- Dentist sealing root canals using the pasty, or sealer and gutta-percha pins,which the clerk enters into the channels and carefully tamp;
- Conducted x-rays to control the sealing quality of the channels. If on the radiograph significant bugs, you will need to re-install the pins and sealing;
- At the end of the treatment, the specialist makes the installation of permanent seal. This is possible only when radiography will show the absence of any errors or issues.
What to do if you have a toothache after treatment of pulpitis
Many people complain that after treatment of pulpitis they have strong enough pain.Users of online forums like regular people and dentists, I advise you strongly not to worry – in the first five days of such pain – totally normal – the reaction of the periodontium to the sealed channels. From the pain people are advised to take analgesics or making soda baths.
Often it also happens that the pain lasts a very long time. Many people have already gone through this, and suggest others in this case to go to the doctor and x-rays. Most likely x-rays show that the tooth is not fully cured, and it will have to perelechivat or remove. Forum users said that basically the removal is often because to perelechivat teeth very difficult.
What to do in case of pulpitis in children
Many mothers on Internet forums complaining that their children are very ill teeth. Often, as experience shows parents a pulpit. In children the caries pulpitis proceeds very quickly, however treatment methods are a little different.
Many parents prefer to just remove the problematic tooth. However, more experienced moms don’t agree with them – because after tooth extraction in a child can deteriorate the bite. Dental treatment some parents fear, but users of Internet forums, I assure you – now pulpitis treated absolutely painless and in one visit. And sometimes even give injections without pain, pre-treating the gums with anesthetic.



