Ureters constitute the tube connecting the organs that produce urine (kidney), unpaired education – bladder, accumulating and releasing it from the body.
The ureter in women has distinctive features only in the pelvic part. The rest of the building equally with the male.
The output from buds formed betrothed hole pelvis. The mouth of the ureter within the bladder. It passes through the wall and forms on the mucosa of the bladder two-way slit-like openings. At the confluence of the upper part formed a fold, is lined with mucous membrane.
Anatomy of the ureter include:
-
- the structure;
- basic dimensions;
- location in relation to surrounding organs;
- features of blood supply and innervation.
Location in relation to organs and the peritoneum
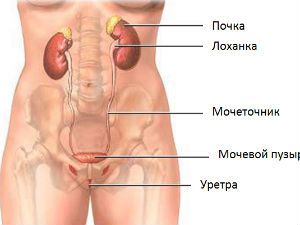
To distinguish between 3 of the ureter.
Abdominal – passes through the retroperitoneal fat in the back wall of the abdomen, then directed on a lateral surface to a small pelvis, adjacent to the front of the psoas major muscle. The initial part of the right ureter lies behind the duodenum, and closer to the pelvic Department of the mesentery of the sigmoid colon.
A guide for the left – serves as the rear wall of the bend between the duodenum and the jejunum. In the transition zone in the pelvic part of right ureter lies behind the base of the mesentery.
Pelvic women is located behind the ovary, around the neck of the uterus at the side, passes along the broad ligament, placed between the bladder wall and the vagina. In men, the urethral tube passes laterally and anteriorly from the VAS deferens, passing through it, enters the bladder almost at the top edge of the seminal vesicle.
Distal (most distant from the kidneys) – is in the thickness of the bladder wall. It is up to 1.5 cm in length. Called intramural.
In clinical practice it is more convenient to divide the ureter along the length into three equal parts:
- top;
- medium;
- lower.
Dimensions
The adult length of the ureter is 28 to 34 inches depending on the height determined by the height of the kidneys when they are laying in the embryo. In women the length of body 2-2. 5 cm shorter than men. Right ureter one centimeter shorter than the left, because the localization of the right kidney a little lower.
The lumen of the tube is not the same: narrowing alternating with areas of expansion.
The narrowest parts are:
- near the pelvis;
- on the border of the abdominal and pelvic divisions;
- at the confluence into the bladder.
Here, the diameter of the ureter, respectively, equal to 2-4 mm and 4-6 mm.
In the diagnosis of pathological changes shape pomegrantate
Between the tapering sections of isolated segments:
- top – pyeloureteral segment;
- the site of crossing with the iliac vessels;
- lower – vesicoureteral segment.
Abdominal and pelvic divisions of the ureter differ in clearance:
- in the area of the abdominal wall he is 8-15 mm;
- in the pelvis – extension of the uniform of not more than 6 mm.
However, it should be noted that because of the good elasticity of the wall, the ureter can dilate to 8 cm in diameter. This possibility helps to maintain the delay of urine, congestion.
In cross section the lumen of the body like a star shape
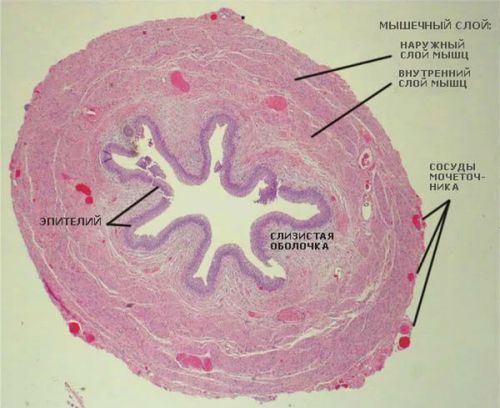
Histological structure
The structure of the ureter is supported by:
- from the inside – mucosa;
- the middle layer – muscle tissue;
- outside, the adventitia layer and fascia.
The mucosa consists of:
- transitional epithelium, are located in several rows;
- plate containing elastic and collagen fibers.
Inner shell throughout forms longitudinal folds, which protect the integrity of the tensile. In the mucous layer grow muscle fibers. They allow you to close the gap against reverse flow of urine from the bladder.

Figure 1 shows a multilayered transitional epithelium, the detection of cells in urine sediment indicates pathology
The muscle layer is formed by bundles of cells running in the longitudinal, oblique and transverse direction. The thickness of the muscle cells are different.
The upper part consists of two muscle layers:
- longitudinal;
- circular.
The lower part is reinforced by three layers:
- 2 longitudinal (internal and external);
- the average between them is circular.
Cells myocytes are connected by many bridges (nexus). Between the beams there are connective tissue fibers that pass from the lamina of the mucosa and adventitia.
Blood supply
Tissue of the ureter are powered from arterial blood. Vessels lie in the adventitia (outer) shell and accompany him along the whole length, penetrate deep into the walls of small capillaries. Arterial branches are in the upper part of the ovarian artery in women and testicular in men, and also from the renal artery.
The middle third receives blood from the abdominal aorta, internal and common iliac arteries. In the lower part, from branches of the internal iliac artery (uterine, vesical, umbilical, rectal branches). Vascular bundle in the ventral portion passes in front of the ureter and in the pelvis behind him.
Venous blood flow is formed by the same name veins arranged parallel to the arteries. From the bottom of the division for him, the blood flowing in the branches of the internal iliac vein and from the top – ovarian (testicular).
Lymph flow is on its own vessels to the internal iliac and lumbar lymph nodes.
Features of innervation
Functions of the ureters are controlled by the autonomic nervous system through the nerve ganglia in the abdominal and pelvic cavity.
Nerve fibers are part of the ureteric, renal and lower podshivnogo plexus. To the top of the suitable branch of the vagus nerve. The lower one is the innervation of the pelvic organs.
The reduction mechanism
The main objective of the ureters – push urine from the pelvis to the bladder. This function is provided by Autonomous contractile ability of the muscle cells. In ureteropelvic segment is the driver of the rhythm (pejjsmeker), which specifies the desired rate reductions.

The rhythm can change depending on:
- horizontal or vertical body position;
- the rate of filtration and urine formation;
- the “instructions” of the nerve endings;
- the status and readiness of the bladder and urethra.
Pushing urine is due to the activity of muscle cells
Proven direct effect on the contractile function of the ureter calcium ions. The concentration in the cells of smooth muscles of the muscular layer depends on the force of contractions. Inside of the ureter pressure, exceeding a similar indicator in the pelvis and bladder. In the upper part of it is equal to 40 cm of water. article, closer to the bladder, it is up to 60.
Such pressure can “pump” the urine at a rate of 10 ml per minute. General innervation of the ureter with the adjoining portion of the bladder creates the conditions for co-ordination of muscular effort of these bodies. The pressure in the bladder “adjusts” to the ureteral, so in normal conditions warned back urine reflux (vesicoureteral reflux).
Avilable in childhood
Newborn length of ureter is 5 to 7 cm It has a convoluted shape in the form of “knees”. Only at the age of four length grows to 15 cm Intravesical portion gradually grows from 4-6 mm in infants up to 10-13 mm to 12 years.
In the renal pelvis of the ureter extends under an angle of 90 degrees, which is associated with the formation of the renal pelvis in the first year of baby’s life.
The muscle layer in the wall is poorly developed. Elasticity is reduced due to the thin collagen fibers. However, the mechanism of reduction provides a rather large evacuation of urine, the rhythm of contractions constantly frequent.
Congenital anomalies are:
- atresia – complete absence of the ureteric tube or outlet holes;
- megaloureter – marked extension diameter throughout its length;
- ectopia – disturbed location or connection of ureter, includes a message from the bowel entering the urethra, bypassing the bladder, the connection with the internal and external genitalia.
Research methods structure of the ureter
To detect the pathology of the way, revealing the characteristic pattern of defeat.
To do this, use:
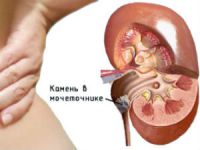
Removal of stones from the ureter in males
- the elucidation of the history of illness and complaints;
- palpation of the abdomen;
- x-ray examination;
- instrumental techniques.
Most often, the pathology of the ureters is accompanied by symptoms of pain.
They are typically:
- character – constant aching or paroxysmal colic;
- irradiation – in the lower back, abdomen, groin and external genitals, in the navel area.
Distribution can be judged on the localization of pathological process:
- if the violations are in the upper third of the ureter, the pain coming in the iliac region (the upper quadrant);
- middle division in the groin;
- of the bottom third in the vulva.
Patient complaints of cramps during urination and more frequent urination occur with pathology in the pelvic and intramural part of the body.
Palpation experienced doctor will determine the muscle tension in the anterior abdominal wall in the course of the ureter. For a more detailed palpation of the lower section of the approach used bimanual (two-handed). One hand with two fingers introduced into the rectum, vagina in women, the other making a counter movement.
Laboratory in the analysis of urine find many leukocytes and erythrocytes, which may indicate a lesion in the lower urinary tract.
Cystoscopy by inserting a cystoscope through the urethra into the bladder to inspect the orifice (mouth) of the ureters on the inside. Matter the form, localization, secretion of blood, pus.
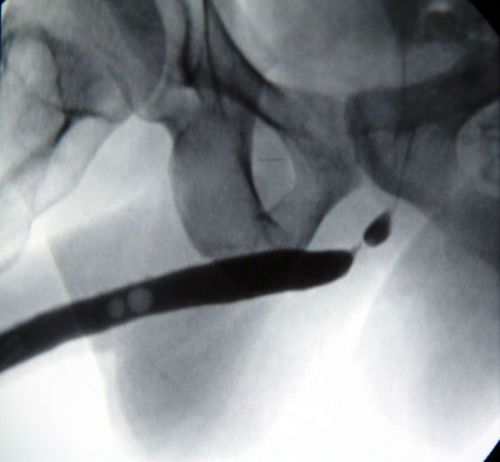
With cystochromoscopy with a preliminary introduction into the vein of the colorant compare the rate of discharge from each hole. Thus it is possible to suspect the presence of a unilateral obstruction (stone, pus, tumor, blood clot).
Catheterization of the ureter is carried out a thin catheter through the opening in the bladder to the level of the detected obstacles. A similar approach with retrograde ureteropyelography allows you to test radiographic anatomy of the ureters, the presence of the patency of the bottlenecks, izvietota.
Overview programme does not show the ureters, but in the case of existing stone (shadow stones) it is possible to suspect its localization.
The contours show the physiological narrowing and the condition of the segments between them, in this case the violation of the passage of the contrast until the complete obturation of the lumen
The most revealing excretory urography. The series of images after intravenous contrast allows us to trace the course of the ureters and to detect pathology. The shadow has the form of a narrow strip with clear, smooth boundary. The doctor radiologist determines the location relative to the vertebrae. In the pelvic cavity are observed 2 bending: first, to the lateral side, then on the approach to the bladder toward the center.
Protomognathus spend when you doubt the value of defeats from the neighboring organs and tissues. The layered images allow us to separate them from the ureter.
Motor skills learning with the help of wreckovery. The method allows to identify reduced or increased tone in the muscle wall. Modern devices make it possible to display reduction in different departments of the ureter, explore the electrical activity of the cells.
Knowledge of the structure and location of the ureter necessary for the diagnosis of diseases of the urinary system, comparative pathology, accompanied by urinary retention. Every surgical intervention in operative urology needs to take into account the anatomical age features of the approach to the neurovascular bundles. In medical language they are called topography.



What a data of un-ambiguity and preserveness of valuable experience concerning unpredicted emotions.
There is certainly a great deal to know about
this subject. I really like all of the points you’ve made.