Balantidia – protozoal intestinal infection, caused by the ciliated infusorians – balantidiasis. Clinical symptoms of balantidiasis are a reflection of the inflammatory and ulcerative processes in the large intestine, characterized by abdominal pain, tenesmus, frequent loose stools mixed with blood and pus, weight loss, intoxication syndrome.
For the diagnosis of “balantitis” the importance of clinical and epidemiological data, the results of sigmoidoscopy, detection of balantidium in the faeces and smears.
Etiotropic therapy is balantidiasis metronidazole, tinidazole, tetratziklinovykh antibiotics, monomitsin.
Balantidia
Balantidia (diatomaceous dysentery) – protozoal zoonotic infection, occurring with symptoms of ulcerative hemorrhagic colitis and systemic intoxication. Outbreaks of balantidiasis more frequently occur in the southern regions, however, sporadic cases of infection are also registered in rural areas with developed pig production industries. Balantidia is characterized by severe, while later the beginning of treatment, high mortality due to intestinal complications, cachexia, joining of sepsis.
The distribution of balantidiasis contributes to the lack of alertness on the part of health professionals to the disease, low level of sanitary culture of the population, the highest invazirovannost rural population (4-5%).
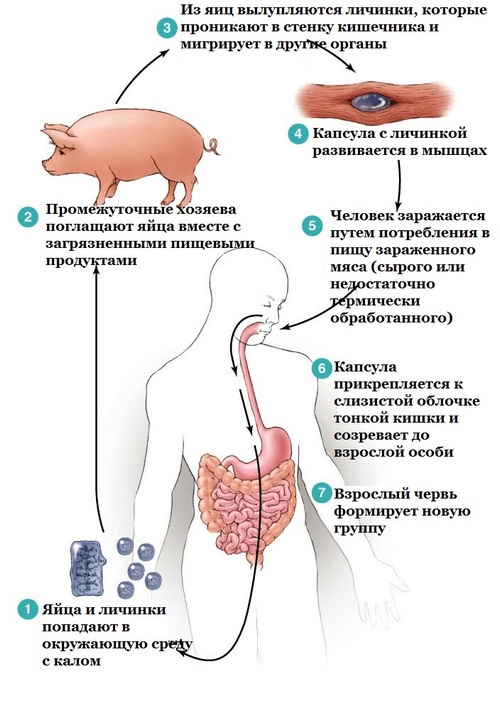
Causes of balantidiasis
The etiologic agent of balantidiasis acts ciliary ciliate Balantidium coli. Balantidia are the largest members of the intestinal protozoa, parasitic in the human body. Their life cycle is 2 stage – tistou and autonomic. Cysts ʙalantidij have a diameter of about 50 microns, a rounded shape and can remain viable outside the host organism for 3-4 weeks. The length of the vegetative forms of parasites – 30-150 microns, a width of 30-100 microns; a surface covered with cilia, by which the traffic moves. In the external environment vegetative forms are less stable, you die in 3-5 hours.
The main reservoir of pathogens balantidiasis serve pigs, among which the infestation reaches 60-80%; less often the source of protozoal infection is a man. The mechanism of infection by balantidiozom – fecal-oral. Transfer ʙalantidij (often cistych forms) occurs through dirty hands, contaminated water, fruits, vegetables. Often balantidiozom sick workers of pig farms, slaughterhouses, meat shops. In the human digestive tract from cysts formed the vegetative form, which are parasitic in the tissues of the blind, sigmoid and rectum.
In the place of their introduction in the lining of the colon, formed areas of hyperemia and edema, which further transformirovalsya in erosions and ulcers. Defects of the mucous membrane have a crater shape, jagged edges, covered with necrotic masses the bottom. Ulcerative-destructive changes in the gut, absorption of toxic substances, as well as the nutrition of parasites at the expense of its owner form the basis of the pathogenesis of balantidiasis and determine its clinical manifestations.
Symptoms of balantidiasis
From the moment of infection to the manifestation of balantidiasis is a 1-h weeks. According to the severity of the clinical manifestations are asymptomatic (subclinical) and manifestou form balantidiasis, according to the nature of the flow – acute, chronic and recurrent; severity – mild, moderate and severe.

In the subclinical form bowel dysfunction and toxicity do not exist, and balantidia recognized on the basis of the endoscopic picture and laboratory findings. The symptoms of acute symptomatic form resembles dysentery balantidiasis. Patients complain of progressive weakness, headache, febrile fever, nausea and vomiting. At the same time develop signs of colitis: cutting pains in abdomen, diarrhoea, tenesmus. Chair becomes liquid, Muco-purulent, then bloody; quickens to 15-20 times a day; the stools have a putrid smell. In severe balantidiasis there is a rapid loss of body weight, up to cachexia.
Chronic balantitis flows with weakly pronounced intoxication syndrome, palpitations (up to 2-5 times a day) loose stools, flatulence, pain caecum and ascending colon on palpation. Continuously acute and chronic balantidiasis can lead to the development of intestinal and extraintestinal complications: bleeding, perforation of ulcers of the colon, of rectal prolapse, peritonitis, abscesses of the liver, hypochromic anemia. No specific causal treatment for acute balantidiasis is a very high risk of death. Extremely severe balantidiasis is celebrated when it is combined with helminth infections and acute intestinal infections.
Diagnostics and treatment of balantidiasis
Patients with suspected balantidia sent to the infectious disease. The disease can be suspected on the basis of positive epidemiological history and clinical manifestations; final confirmation and verification of the diagnosis is possible after carrying out endoscopic examinations of the bowel and laboratory tests.
In the acute stage balantidiasis with sigmoidoscopy or colonoscopy detected focal infiltrative-ulcerous changes of the bowel wall; in chronic catarrhal-hemorrhagic or ulcerative lesions. The true proof of balantidiasis is the presence of vegetative forms ʙalantidij in freshly isolated feces or scrapings from the affected areas of the colon. Identification of cysts indicates a transient carriage of protozoan infection. In the course of diagnosis balantidia differencebut with bacterial dysentery, amebiasis, giardiasis, cryptosporidiosis, bacterial overgrowth, ulcerative colitis.
Patients with confirmed balantidiozom be hospitalized in the infectious hospital. As a causal treatment is assigned antibacterial (monomitsin, oxytetracycline, ampicillin) or Antiprotozoal drugs (metronidazole, tinidazole). Usually performed 2-3-day cycle of therapy. Systemic drug therapy may be supplemented by enemas with colloidal-dispersion salt norsulfazola. At the same time shows a detoxification therapy, vitamin therapy, adherence to a rational diet.
The media treatment of protozoal infections are also a must. Criteria of healing balantidiasis is considered a lack kriticheskogo syndrome, negative coprological study on balantidia, no ulcerative changes of the intestinal wall.
Prognosis and prevention of balantidiasis
Used at present methods of specific treatment of balantidiasis contribute to the recovery of patients. In the case of late begun or inadequate treatment, the fatality rate may reach 10-12%. Balantidiasis prevention consists of observance of measures of personal security (personal hygiene, boil water, wash vegetables and fruits, etc.), as well as protecting the external environment from faecal pollution (protection of water bodies, improvement of hygienic conditions the pigs, disposal of manure, etc.). Specific prevention balantidiasis is not developed.



I have been browsing online more than three hours today, yet I never found any interesting article like yours.It’s pretty worth enough for me. Personally, if all website owners and bloggersmade good content as you did, the internet will be muchmore useful than ever before.
The media treatment of protozoal infections are also a must. Criteria of healing balantidiasis is considered a lack kriticheskogo syndrome, negative coprological study on balantidia, no ulcerative changes of the intestinal wall.