Bartonellas – a group of diseases caused by bacteria of the genus Bartonella that occur with a primary lesion of endothelial cells and erythrocytes.
Clinical manifestations may range from mild and local (rash, lymphadenopathy, conjunctivitis) to common systemic disorders (fever, anemia, septic bacteremia, endocarditis, meningitis, myelitis).
Diagnosis of bartonellosis is based on the detection of the pathogen and its antigens and antibodies in the blood of the patient. Therapy is by antibiotics (tetracyclines, macrolides, fluoroquinolones), according to testimony, supplemented by symptomatic treatment (antipyretics, detoxification therapy).
Bartonellosis
Group bartonellosis includes felines, trench fever, carrión’s disease, bacillary angiomatosis, bartonellosis syndrome with bacteremia and endocarditis, pelisky hepatitis/splenitis, chronic lymphadenopathy. Chronologically the first among the variety of clinical variants of the infection we studied the disease carrión, therefore, bartonellosis is usually associated with it. Endemic areas for the disease are the northwestern territory South America.
This is due to the habitat of vector species of bacteria of phlebotomus mosquitoes. The peak incidence of bartonellosis falls on the rainy season, when mosquitoes are particularly active. Other forms of infection do not have a clear geographical location, which is due to the widespread prevalence of Bartonella on the planet.

Causes of bartonellosis
Bartonella are gram-negative aerobic rods. Can cause bacteremia in the host organism persistiruut inside the red blood cells. Die quickly under the influence of common disinfectants. The causative agent carrión – B. bacilliformis. In addition, pathogenic for humans are B. henselae (causes felines, bacillary angiomatosis), B. quitana (leads to the development of trench fever, the bacillary angiomatosis, bacteremia, and endocarditis), B. vinsonii and B. elizabethae (cause bacteremia, endocarditis), B. grahamii (causes neuroretinitis), B. washoesis (contributes to the development of myocarditis).
In the human body bacteria penetrate through the bites of mosquitoes, ticks, lice or microdamages of the skin. The reservoir of infection is a person with severe, asymptomatic or bacillicarrier. The frequency of bacteremia in asymptomatic carriers of infection reaches 50%. Susceptibility to bartonellosis among residents of endemic areas is high. Unsanitary conditions, overcrowding contribute to increased frequency of infection.
Pathogenesis
To the point of entry of the pathogen formed primary affect papules, vesicles or pustules. Next, the flow of lymph, the pathogen enters the lymph nodes – lymphadenopathy develops. When you overcome the lymphatic barrier, the pathogen enters the bloodstream – bacteremia occurs. Most sensitive to Bartonella are erythrocytes and endothelial cells of blood vessels, bone marrow, heart valves. Active multiplication of the pathogen in the red blood cells and their destruction causes the development of hemolytic anemia.
In acute processes in endothelial cells is dominated by necrotic changes of the vascular wall infiltered leukocytes and macrophages with formation of granulomas, the phenomenon of proliferation is expressed slightly. In the mucous membranes, the skin appear small hemorrhages. For chronic course of bartonellosis characterized by the formation of new small vessels with formation of angioectasia. When the consistency of the immune system produce antibodies with subsequent elimination of the pathogen. In the case of immunodeficiency is chronic process with long-term persistence of Bartonella in the blood. The lack of treatment in this situation can lead to death. Recovered patients formed a strong immunity.
Classification
Bartonellosis is a group of diverse diseases. Uniform classification of diseases no, because Bartonella remain incompletely understood bacteria, new information on injuries caused by them; in addition, some forms may flow through to other.
To date the following diseases caused by Bartonella:
- Carrión Disease. Anthroponoses infection with the transmissible mechanism of transmission, occurring as acute or chronic form. Characterized by fever, lymphadenopathy, headache, myalgia, arthralgia, petechial rash on the skin and mucous membranes.
- Disease cat scratch (felines, benign lymphoreticulosis, the granuloma Mollard, lymphoreticular Caesars). The typical clinical picture represents the presence of primary affect, fever, enlarged regional lymph nodes. It is also possible atypical course: Parrino syndrome (fever, lymphadenopathy, and follicular conjunctivitis), CNS (meningitis, encephalitis, polyneuritis) and various organs (pneumonia, myocarditis, abscesses of the spleen).
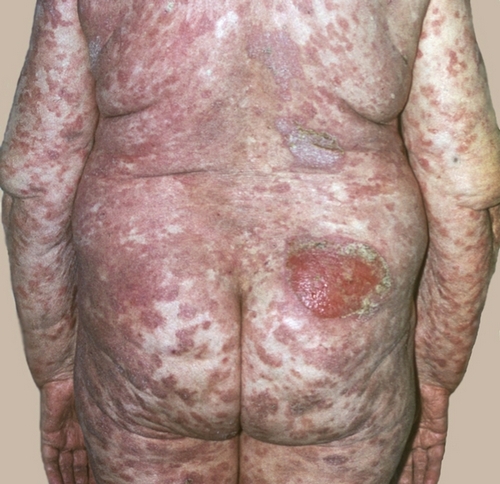
- Bacillary (epithelioid) angiomatosis. Characteristic lesions of the skin and internal organs. At this skin, subcutaneous angioma are formed, which are easily injured and bleed. In case of involvement of internal organs fever, vomiting, sweating, loss of weight, develop pneumonia, abscesses of the spleen, lesions of bone marrow.
- Trench fever (tibiala or five-day fever). Patients complain of severe headaches, back pain, neck, bones, especially the tibia (tibiala fever). In some patients the rash appears rosealina. Characteristic rise in temperature every five days (five-day fever). The prognosis is favorable and, if chronic, may develop endocarditis.
- Hepatic and splenic purpura (purple bacillary hepatitis, hepatitis pelisky). Is a form of bacillary angiomatosis with predominant involvement of the liver or spleen. Characterized by the formation in the bodies of multiple cavities filled with blood. Clinically defined fever, nausea, vomiting, congestion in the liver due to the compression of the newly formed cavities of the vessels.
- Bacteremia, endocarditis. Typical symptoms and signs of bartonellosis, no. Clinically severe intoxication, lesions of various organs and tissues (spleen, liver, Central nervous system), development of DIC. Endocarditis appears when the noise of various kinds, develops decompensation of the cardiovascular system
Symptoms of bartonellosis
Carrión disease is stage process. Can occur in acute (fever the Seating area, which) or chronic phase (Peruvian wart). The simultaneous development of the clinic both stages. In the classic version of the chronic stage follows the acute 1-2 months.
The incubation period of bartonellosis from 10 to 120 days (on average about 2 months). When deployed clinical picture appears, the fever of the wrong type, the rise in temperature to 39-40°C accompanied by chills, and the reduction – sweating, resembling malaria. Patients complain of headaches, malaise, abdominal pain, joints and muscles. Characterized by severe pallor due to anemia. You may experience various symptoms of impaired neurological status until the development of coma. On the skin, mucous membranes there are small hemorrhages. Increased liver, spleen, lymph nodes. The favorable outcome of the disease, the person recovers, however, without treatment the mortality ranges from 40 to 90%.
While maintaining the pathogen in the organism of bartonellosis enters a latent stage, with subsequent reactivation and development of the chronic phase Peruvian wart. The temperature rises again. On the body appears papular rash that eventually transformirovalsya in nodules between 3 mm to several centimeters in diameter. Most often, a rash localized on the face, neck, limbs. There is a loss of mucous membranes of the mouth, vagina, gastrointestinal tract, etc. Nodes can bleed and ulcerate with the accession of secondary infection. With a favorable course in 1-2 months. recovery occurs, nodes are resolved without a scar.
The most common complication is the addition of a secondary Salmonella infection. In the case of septic form of the disease dramatically increases the lethality. It’s also possible infection of ulcerated lesions in the Peruvian wart, in this case, the wounds heal with a scar. With the defeat of the mucous membranes occur bleeding. Bacteremia and multiple organ lesions contribute to the development of sepsis, which is usually accompanied by DIC-syndrome. Regurgitation of high degree heart valve leads to the failure of compensatory abilities of the heart that requires surgical valve replacement. CNS lead to neurologic deficit, bacillary angiomatosis contributes to the oppression of the liver.
If you suspect that bartonellosis should consult a physician, infectious disease specialist, a dermatologist, in case of defeat of the nervous system – a neurologist, development of purulent complications surgeon. During the physical examination is marked pallor of the skin – the primary affect with regional lymphadenopathy, palpation – enlarged liver, spleen.
The diagnosis uses the following laboratory and instrumental methods:
- Examination of the blood. In General and biochemical analysis of blood observed hemolytic macrocytic normo or hypochromic anemia, inflammatory markers (CRP, procalcitonin, increased levels of globulins), ESR acceleration. Leukocytosis may not be thrombosis of the observed reduced fibrinogen, increased D-dimers.
- Direct detection of the pathogen. By microscopy of blood smears, stained by Romanovsky–Giemsa, pathogenic microorganisms are detected inside and outside blood cells. Also as the drug can be used biopsy material from lymph nodes or lesions. The blood cultures of pre-judging the presence and degree of bacteremia is possible in 3 days, finally – after 7-10 days. DNA of the pathogen identificeret by PCR.
- Serological methods of diagnosis. Carry out the determination of antibodies (IgM and IgG) in the serum of the patient by the method of the reaction of hemagglutination, complement, indirect immunofluorescence, ELISA. For detection of antigens of Bartonella perform Western blot sections, Western blotting.
- Ultrasound examination of abdominal cavity. Ultrasound OBP is not specific method of detection of bartonellosis. During the procedure, determined by the enlargement of the liver, spleen, intra-abdominal lymph nodes. Possible detection in parenchymatous organs cavities filled with fluid, foci of proliferation. A similar pattern can resemble many other diseases.
Differential diagnosis of bartonellosis is carried out with a skin form of tuberculosis, an angiosarcoma, a tumor of the skin, in particular myeloma. More common nosology – felinos – it is necessary to delineate with atypical mycobacteriosis, syphilis, tularemia, lymphoma. Getdiagnostic of bacillary angiomatosis must be Kaposi’s sarcoma, angiom, squamous cell and basal cell cancer. Endocarditis and bacteremia must be distinguished from similar diseases caused by other pathogens.
Treatment of bartonellosis
The treatment is carried out in the infectious hospital. You must comply with bed rest. Conducted etiotropic therapy of antibacterial drugs. Because it is possible to further accession secondary salmonellosis, rational use of ciprofloxacin or chloramphenicol in combination with β-lactam antibiotic. Reserve drugs are macrolides, tetracyclines, rifampicin. If necessary, appointed symptomatic treatment (detoxification therapy, antipyretic drugs, hepatoprotectors, red blood cell transfusions). On the infected skin after washing with antiseptic bandage with antibacterial ointment.
Prognosis and prevention
In the acute phase in the absence of comorbidities and time begun treatment the prognosis is favorable. However, immunosuppression with massive bacteremia may develop of bacillary angiomatosis, lesions of the nervous system, cardiac decompensation due to hitting the valves. Under Peruvian warts fatal cases is almost not described, the mortality associated with the accession of infection. Specific prevention of bartonellosis has not been developed. Individual protection measures include the use of repellents, mosquito nets.


that’s a reasonable viewpoint you have!
Never knew this, thank you for letting me know.
Don’t wear seat belts lest you drown in you own urine?
I was wondering if you ever considered changing the layout of your site? Its very well written; I love what youve got to say. But maybe you could a little more in the way of content so people could connect with it better. Youve got an awful lot of text for only having one or 2 pictures. Maybe you could space it out better?
Hallo The bookmaker is simply a middle-man who operates on a small revenue margin and ideally likes to see a fair overround, assuring a revenue. thanks
You seem a bit out of touch-can you add some detail?