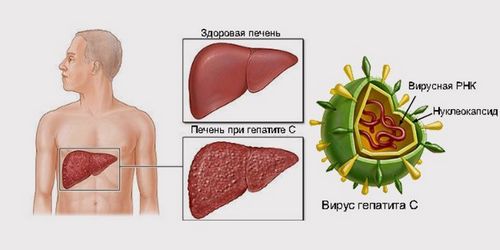
Hepatitis C is a viral infectious disease of the liver, transfusion transmitted, wherein light, often subclinical, rarely moderate course in the phase of primary infection and a tendency to chronicity, cirrhosis and malignancy. In most cases, hepatitis C has Busselton oligosymptomatic beginning.
In this regard, it may remain undiagnosed for several years, and is detected when the liver was developing cirrhosis or malignant transformation occurs in hepatocellular carcinoma.
The diagnosis of hepatitis C is considered to be sufficiently justified in identifying the blood viral RNA and antibodies to her as a result of repeated studies by PCR and serological reactions.
Viral hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is a viral infectious disease of the liver, transfusion transmitted, wherein light, often subclinical, rarely moderate course in the phase of primary infection and a tendency to chronicity, cirrhosis and malignancy. Hepatitis C virus, called RNA-containing virus of the family Flaviviridae. The tendency of this infection to chronicity is caused by the ability of the pathogen to remain in the body for a long time without causing intense manifestations of the infection. As the rest of the flavivirus, hepatitis C virus capable of multiplying, forming quasistable with a variety of serological variants that prevent the body forming adequate immune response and allows you to develop an effective vaccine.
Hepatitis C virus is not propagated in cell cultures, which makes it impossible to examine its stability in the environment, but we know that he’s a bit more stable than HIV dies upon exposure to ultraviolet rays and can withstand heat to 50 °C. a Reservoir and source of infection are sick people. The virus is contained in blood plasma of patients. Contagious as suffering from acute or chronic hepatitis C, and persons with asymptomatic infection occurring.
The mechanism of transmission of hepatitis C virus is parenterally, mainly spread through blood, but can sometimes cause the contamination and contact with body fluids: saliva, urine, semen. A prerequisite for infection is direct contact with a sufficient amount of the virus in the blood of a healthy person.
In the majority of cases currently, the infection occurs when sharing intravenous drug use. The spread of the infection among drug addicts reaches 70-90%. Persons who use drugs are the most dangerous in epidemiological terms, a source of viral hepatitis C. in addition, the risk of infection increases in patients who received medical care in the form of repeated blood transfusions, surgical interventions, parenteral injections and punctures with non-sterile instruments are reusable. The transfer may be carried out in the tattooing, body piercing, cuts during a manicure and pedicure, manipulations in dentistry.
In 40-50% of cases could not track the method of infection. In medical professional groups, the incidence of hepatitis C is not greater than that in the General population. Transmission from mother to child is when the mother’s blood builds up high concentration of the virus or with the combination of hepatitis C virus with human immunodeficiency virus.
The possibility of developing hepatitis C with a single ingestion of a small quantity of the pathogen in the bloodstream of a healthy person is small. Sexual transmission infection seldom realized, primarily in persons with concomitant HIV infection, are prone to frequent change of sexual partners. Natural sensitivity to hepatitis C virus largely depends on the dose of the pathogen. Post-infectious immunity is not sufficiently studied.
Symptoms of viral hepatitis C
The incubation period of viral hepatitis C ranges from 2 to 23 weeks, sometimes puffing up to 26 weeks (due to one way or the other). The acute phase of infection in the majority of cases (95%) manifested severe symptoms, leaking in Busselton subclinical. Later serological diagnosis of hepatitis C may be associated with a probability of “immunological window” – a period when, despite the infection, the antibodies to the pathogen is absent or the titer of their infinitesimally small. In 61% of cases of viral hepatitis laboratory diagnosed after 6 months or more after the first clinical symptoms.
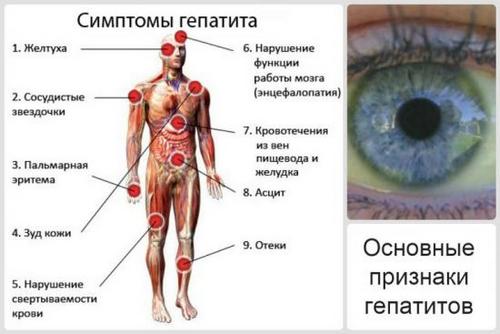
Clinically manifestation of viral hepatitis C can manifest in the form of common symptoms: weakness, lethargy, decreased appetite, rapid saturation. May experience local symptoms: the severity and discomfort in the right hypochondrium, dyspepsia. Fever and intoxication in viral hepatitis C are quite rare symptoms. Body temperature if it rises, then to subfebrile values. The intensity of those or other symptoms often depends on the concentration of virus in the blood, the General state of immunity. The symptoms are usually minor and patients don’t tend to give it value.
In the blood in acute hepatitis C often noted decreased content of leukocytes and platelets. In a quarter of cases there is transient mild jaundice (often limited to the ikterichnost sclera and biochemical manifestations). In the future, if chronic infection with episodes of jaundice and increase of activity of hepatic transferases accompany exacerbation of the disease.
Severe course of viral hepatitis C is not more than 1% of cases. This may develop autoimmune disorders: agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia, neuritis of peripheral nerves. In this period of probable death in geanticlinal period. In ordinary cases of viral hepatitis C develops slowly, without obvious symptoms, years remaining nediagnostirovanne and manifesting, even at a significant destruction of the liver tissue. Patients are often first diagnosed with hepatitis C, where already there are signs of cirrhosis or hepatocellular carcinoma of the liver.
Complications of viral hepatitis C is cirrhosis and primary liver cancer (hepatocellular carcinoma).
Diagnosis of viral hepatitis C
Unlike hepatitis b, where it is possible to highlight viral antigen, clinical diagnosis of viral hepatitis C is performed using serological methods (IgM antibodies to the virus are determined using ELISA and RIBA), as well as the definition in the blood of viral RNA using PCR. While PCR is carried out twice, because there is a chance of false-positive reactions.
In identifying antibody and RNA can suggests adequate reliability of the diagnosis. The serum IgG can mean the presence of the virus in the body, and previous infection. Patients with hepatitis C are assigned for biochemical tests of the liver, coagulation parameters, liver ultrasound, and in some difficult diagnostic cases – liver biopsy.
Treatment of viral hepatitis C
Therapeutic tactics in case of hepatitis is the same as in viral hepatitis b: prescribed diet №5 (restriction of fats, especially refractory, the normal ratio of proteins and carbohydrates), the exclusion of foods that stimulate the secretion of bile and liver enzymes (pickled, fried, canned food), the saturation of the diet lipoliticeski active substances (cellulose, pectin), large amounts of fluid. Completely eliminated alcohol.
Specific therapy of viral hepatitis is interferon in combination with ribavirin. The duration of the therapeutic course – 25 days (when resistant to antiviral therapy variant of the virus possible extension rate up to 48 days). In the prevention of cholestasis in the complex of therapeutic measures include drugs ursodeoxycholic acid, and as an anti-depressant (because the psychological state of patients often affects the effectiveness of treatment) – ademetionine. The effect of antiviral therapy depends on the quality of interferon (degree of purification), the intensity of therapy and the General condition of the patient.
According to the testimony of basic therapy can be part of oral detoxification, antispasmodic, enzymes (Mezym), antihistamines and vitamins. In severe hepatitis With intravenous detoxification shown by solutions of electrolytes, glucose, dextran, if necessary, Supplement the therapy with prednisolone. In the case of complications the course of treatment is complemented by appropriate measures (treatment of cirrhosis and liver cancer). If you want to produce plasmapheresis.
The prognosis of viral hepatitis C
With proper treatment recovery ends 15-25% of cases. Most often, hepatitis C becomes chronic, contributing to the development of complications. Death With hepatitis C usually occurs due to cirrhosis or liver cancer, the mortality is 1-5% of the cases. Less favorable prognosis of co-infection with hepatitis viruses b and C.
Prevention of viral hepatitis C
General measures prevention of hepatitis C include careful observance of sanitary regime in medical institutions, quality control and sterility transfused blood, as well as the sanitary supervision of institutions providing services to population with the use of traumatic techniques (tattooing, piercing).
Among other things, conducted educational activities among young people advertised individual prevention: safe sex and refusal of drugs, conduct medical and other traumatic procedures in certified institutions. Among drug users apply disposable syringes.