There is a great variety of infectious diseases, and at all times they were the main enemies of man. History knows many examples of the devastating effects of smallpox, plague, cholera, typhoid, dysentery, measles, flu. No wonder infectious disease is called “morovich diseases.”
So, in 737, the smallpox became extinct more than 30 % of Japan’s population (the death rate in densely populated areas reached 70 %.
In the XVII-XVIII centuries, this disease killed millions of people in Europe every year were infected with smallpox on average, approximately 10 million people, of whom about 1.5 million died. The most ominous in the history of Western Europe, the pandemic of plague broke out in 1346-1348 years: the black death claimed a third of the population – died over 25 million people.
Starting in 1600-ies of the European tuberculosis epidemic known as the Great white plague, raged for more than 200 years, died every seventh infected person. During an epidemic of influenza – the famous “Spanish flu” in 1918-19 was carried out 20-40 million (and by some estimates even more) human lives.
IN THE HISTORY OF MANKIND, INFECTIOUS DISEASES HAVE INFLICTED MORE DAMAGE THAN THE BLOODY WAR.

THE RATIO OF KILLED AND DIED OF DISEASE DURING THE WAR
Despite the sanitary well-being, advances in modern medicine, it is naive to believe that humanity has conquered infectious diseases, and each of us is at risk. Now in a world of rampant epidemics – AIDS, tuberculosis, malaria, measles, Ebola, whooping cough, influenza, and other diseases.
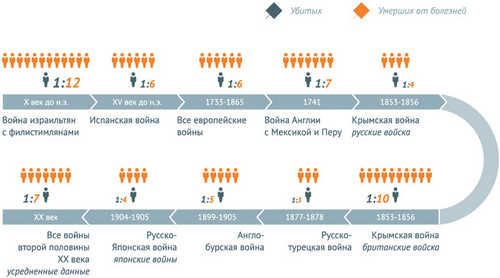
In the mid 1960-ies there was even a special term – “microbial unification of mankind.” This phenomenon, which was first recorded in the 14th century, when Eurasia and North Africa was swept by a plague epidemic called “black death”.
The meaning of the “microbial unification” lies in the fact that life and health depend on the health and life of each person. The emergence of new diseases in every corner of the globe threatens the rest of the people. Epidemics are impossible to hide. In addition, the epidemic have implications that spread into many other areas of human life.
Now, according to the world health organization, about 50% of the population lives under the constant threat of epidemics.
- Infectious diseases do not recognize international boundaries or sovereign States.
- The disease may occur everywhere in the world and quickly spread to other regions.
For the development of infectious diseases there are several objective conditions.
First, this is the active development of tourism. Around the world from country to country, along with people travel and infectious diseases. Every year the number of tourists increased by about 6% per year. By 2020 their number will amount to 1 billion 600 million people. Especially dangerous from the point of view of the spread of infectious diseases tourism in developing countries. They represent an attractive tourist destination, and more than 80 million tourists from developed countries annually visit developing countries where low standard of living , maintained a high level of infectious diseases. And experts estimate that by 2030, developing countries will annually visit the more than a billion tourists.
Second, is the growth of migration processes. To date, the Russian Federation ranks second in the world in the number taken on their territory of migrant workers, second on this indicator only the USA. A characteristic feature of labour migration in Russia is a significant number of migrants with irregular status or working without permits. They do not undergo any medical control, which of course makes it difficult to control the spread of infections.
According to the Federal migration service on the territory of our country are 10.2 million foreign citizens, including citizens of Uzbekistan (23%), Ukraine (13.3%) and Tajikistan (10%). According to Rospotrebnadzor, for the period 2007-2013 have passed a medical examination more than 7.4 million foreign citizens. Total found 56 206 patients with infectious diseases, including HIV – 11358 (20,2%) with tuberculosis – 20881 (37,2%), patients with sexually transmitted infections – 23967 people (42.6 per cent). In addition, registered 2909 cases of other infections, including typhoid fever, acute intestinal infections of various etiologies.
Third, a growing number of re-returning and re-emerging diseases.
At any time in any place of the planet could start an epidemic or outbreak caused by infectious pathogens:
- new;
- returned or moved to new territories.
You can highlight several reasons why again today and are there new diseases. Currently, there is an acceleration of the evolution of infectious diseases. The infectious agents quickly evolyutsioniruet that allows them to improve the survival and sustainable existence. For example, flu vaccines are updated annually. Infection spread to new areas. People master them to stay, invading the space of the natural habitat of vectors and reservoirs of infection. The expansion of human contacts with animals that are sources and carriers of pathogens of several infectious diseases.
Climate change, urbanization and degradation of habitat is also affected by the fact that infectious diseases come back or spread to new areas. Many pathogens have learned to develop resistance, i.e. immunity to antibiotics. Moreover, we are incorrectly using antibiotics, accustom them to the medication – taking these drugs without prescription, disrupting the modes of reception and dosage, if not unnecessarily. The big danger is the use of antibiotics in poultry and farm animals – meat every day we eat hundreds of millions of people worldwide, thereby accustoming of pathogens to drugs.
Humanity is still not enough studied viruses, not all infectious agents are identified. For example, in the late 20th century proved the relationship of human papilloma virus (HPV) with cervical cancer. Today, the share of known pathogenic viruses is 4% of the total estimated their number, and proportion of the known pathogenic bacteria – 12%.
Constantly there are new, or first identified infectious diseases. Since the 1970-ies annually, at least one new infectious disease.
In 2012, the taxonomic database of the U.S. national center for biotechnology information (NCBI) presented 17 600 described bacteria, and about 150,000 waiting for their annotations. In the body of a man discovered almost 10 000 species of bacteria, and only 500 of them studied.
Functioning genes of the microbiome described at about 8 million, which is 360 times the number of genes of the person.
Today the world knows more than 1.5 thousand of infectious diseases, but people learned to prevent only a small but the most dangerous from the point of view of epidemics, some of them with the help of vaccinations.
Of these, 15-17 infections, which most often sick children around the world, included in the National calendars preventive vaccination countries of the world. Russian vaccination calendar today includes vaccination against 12 diseases. 16 from the list of dangerous diseases included in the national calendar of immunization on epidemiological indications.
THE NUMBER OF PREVENTABLE VACCINATION DISEASES WORLDWIDE AND THE DISEASES INCLUDED IN THE COMPULSORY NATIONAL IMMUNIZATION SCHEDULES IN DIFFERENT COUNTRIES

Today all over the world successfully use vaccines to prevent more than 30 diseases have developed about 500 new vaccines


Great wordpress blog here.. It’s hard to find quality writing like yours these days. I really appreciate people like you! take care
When I initially commented I seem to have clicked on the -Notify me when new comments are added- checkbox and now every time a comment is added I get 4 emails with the exact same comment. There has to be a means you are able to remove me from that service? Thanks.