Blastomycosis – a disease from the group of systemic mycoses occurring with a primary lesion of the lung and hematogenous dissemination of fungal infection in internal organs, bones and skin.
Blastomycosis can occur in different forms: pulmonary (pneumonia), skin (rash, ulcers of the skin, subcutaneous abscesses), bone (osteomyelitis, arthritis), urogenital (prostatitis, epididymitis).
The Diagnosis of blastomycosis is confirmed by isolation of the causative agent – the fungus Blastomyces dermatitidis by microscopy, culture-study biopsy. Treatment of blastomycosis is with antifungal drugs (Itraconazole, amphotericin); may be shown drainage and debridement of abscesses.
Blastomycosis
In the medical literature describes different types of blastomycosis: North American (disease Gilchrist), South American (paracoccidioides), European (cryptococcosis) and keloid disease (Lobo), the greatest prevalence of which has North American type. North American blastomycosis – a fungal disease characterized by Multisystem lesion with the development of purulent granulomatous processes in the lung, skin, skeletal, genitourinary tract.
Leaflets distributed in the United States and Canada; in the form of sporadic cases found in Latin America, Africa, Europe, Australia, and India. During epidemics the incidence of blastomycosis in more vulnerable children and young people up to 20 years. The issues of treatment and prevention of blastomycosis located at the intersection of different clinical disciplines: Mycology, pulmonology, dermatology, urology, etc.
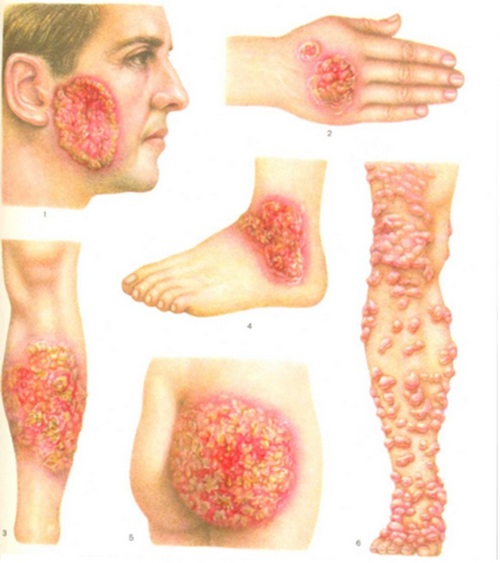
Causes blastomycosis
North American blastomycosis is called dimorphic (diphasic) saprophytism fungus Blastomyces dermatitidi that live in the soil. In the human body fungus is ingested by inhalation of dust inhalation of fungal spores with dust particles. The main pathways of the pathogen are hematogenous and lymphogenous. Possible sexual transmission of blastomycosis. The causative agent of blastomycosis can exist in two forms: mycelial and yeast. In mycelial form of the fungus exists at temperatures below 30°C, and in the affected organism (at t 37°C) it goes into a yeast phase.
Once in the lungs, microconidii of the fungus pass into the yeast phase and cause the development of primary infiltrative foci of inflammation. At later stages in the foci formed granulomas with areas of suppuration and necrosis. Skin lesions and internal organs is secondary and occurs as a result of introduction of infection from the lungs. Development blastomycosis contribute to comorbidities: diabetes, tuberculosis, blood diseases, immunodeficiency States (e.g. HIV infection). Groups at risk on the incidence of blastomycosis include growers, farm workers and other people, often in contact with soil containing spores of blastomycetes, and persons living in endemic areas.
The symptoms of blastomycosis
Distinguish the following clinical forms of blastomycosis: pulmonary, skin, bone, urinary and other (CNS, pericardium, liver, spleen, thyroid, adrenal). Systemic (disseminated) blastomycosis may develop years after the primary lesion of the lungs.
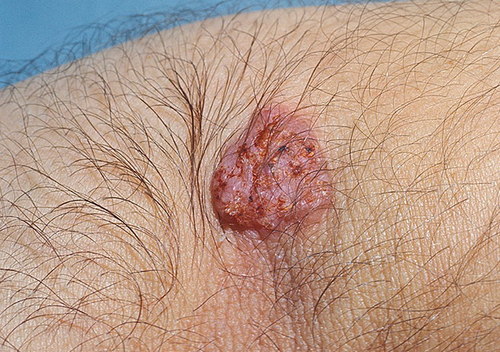
Pneumonic blastomycosis is 60-90% of all cases of fungal infection and occurs in the form of bronchopneumonia. The average incubation period is 30-45 days. The onset is acute or subacute; in the initial period prevails intoxication syndrome: subfebrile or febrile temperature, chills, muscle and joint pain. Rarely blastomycosis from the start develops as a primary chronic, without severe clinical symptoms. Cough (initially dry, then with purulent sputum), hemoptysis, chest pain, shortness of breath. An objective study rales are heard, pleural friction RUB; x-ray revealed upper lobe infiltrates, sometimes cavity. For surrounding patients with pulmonary blastomycosis-contagious.
Among extrapulmonary lesions the most common cutaneous blastomycosis (40-80% of cases). Cutaneous blastomycosis occurs with vesiculo-papular or papular-pustular eruptions that transformirovalsya in ulcers, covered with abundant granulation tissue. Discharge from sites of ulceration is bloody or purulent. Ulcers may extend to the mucous membrane of the oral cavity, pharynx and larynx. Healing of ulcers takes place with the formation of the thin soft cicatrix. The formation of subcutaneous abscesses.
The share of bone shape accounts for 25-50% of cases of extrapulmonary blastomycosis localization. Occurs mainly in the form of osteomyelitis of long tubular bones, spine, ribs. In the affected area are often formed abscesses surrounding soft tissues, fistulous passages, arthritis of nearby joints.
Urogenital form of blastomycosis (10-30% of cases) is more often diagnosed in men. The clinical picture corresponds to orchitis, epididymitis, prostatitis; may be hematuria and pyuria. Infection of women with urogenital blastomycosis is sexually transmitted and rare. With disseminated blastomycosis can affect internal organs with the development of liver abscesses, pericarditis, adrenal insufficiency, etc. With involvement of the CNS arise brain abscesses, meningitis.
Diagnosis of blastomycosis
First of all, blastomycosis should be suspected in patients arriving from endemic areas and with signs of lesions of the lungs, skin, bones, genitourinary system. Therefore, the assessment of such patients, except for specialists (pulmonologist, dermatologist, urologist, etc.) should be involved infektsionisty mycologists.
The diagnosis of blastomycosis is confirmed by detection of B. dermatitidi in biological material: sputum, purulent discharge from the fistula and abscesses, urine, cerebrospinal fluid, biopsy material. Most often used microscopic examination and microbiological culture. To get sample material is puncture of the abscess and aspiration of their content, excisional biopsy of tissue. Serological diagnosis of blastomycosis is carried out by methods IFA, RSK, RIA. Skin-allergic tests with blastomycosis have low sensitivity and specificity. With the aim of identifying changes in the internal organs conducted additional tests: chest x-ray, bone scan, CT scan of the brain and spine.
Pulmonary blastomycosis must be differentiated from other chronic lesions of the lungs: bacterial pneumonia, tuberculosis, tumors, and lung abscess, empyema, pulmonary aspergillosis, histoplasmosis. Cutaneous excludes pyoderma, other ringworm, squamous cell carcinoma of the skin. Genitourinary blastomycosis should be distinguished from bacterial prostatitis and orchiepididymitis, prostate cancer, syphilis. Bone blastomycosis requires the differential diagnosis with tuberculosis of bones and bacterial osteomyelitis.
Treatment of blastomycosis
Acute pulmonary blastomycosis can result in the recovery without special treatment. In all other cases, the basis of treatment of various forms of blastomycosis are antifungal therapy. In mild course of the disease is assigned to Itraconazole or ketoconazole orally for 6 months; in severe – amphotericin b intravenously. According to the testimony of antifungal therapy supplemented by surgical debridement with drainage of the pleural cavity, opening of abscesses of the skin, necrectomy, etc.
Adequate and timely treatment for localized forms of blastomycosis allows to achieve recovery in 90% of cases. In disseminated forms in the absence of treatment with a high probability of death. To avoid infection with blastomycosis is recommended personal hygiene, respiratory protection when loosening the soil and other farming activities in disadvantaged areas, the use of barrier methods of contraception during casual sex


I must voice my interest for the kindness in support of individuals that actually need guidance on this one issue. Your special dedication to getting the solution up and down became extremely invaluable and contains continuously made associates similar to me to reach at their ambitions. The helpful help and advice means so much a person like me and especially to my mates. Many thanks; from everyone folks
Wow! Thank you! I permanently needed to write on my blog something like that. Can I include a part of your post to my site?
Just wish to say your article is as amazing. The clarity in your post is just nice and i could assume you are an expert on this subject. Well with your permission allow me to grab your RSS feed to keep up to date with forthcoming post. Thanks a million and please continue the enjoyable work.
I will immediately snatch your rss feed as I can not to find your email subscription hyperlink or newsletter service. Do you have any? Please permit me recognise so that I could subscribe. Thanks.
Hello! This is my first comment here so I just wanted to give a quick shout out and say I genuinely enjoy reading through your blog posts. Can you recommend any other blogs/websites/forums that deal with the same topics? Thank you so much!
Its like you read my mind! You seem to grasp so much about this, like you wrote the e-book in it or something.
I feel that you just can do with some percent to power the message home a bit, but other than that, this is excellent
blog. A fantastic read. I’ll certainly be back.
It’s really a nice and useful piece of information.
I am satisfied that you shared this helpful information with us.
Please keep us up to date like this. Thank you for sharing.
I all the time emailed this web site post page to all my friends, because if like to read it afterward my links will too.
I truly appreciate this post. I have been looking all over for this! Thank goodness I found it on Bing. You have made my day! Thanks again
Thank you, I’ve just been searching for information about this topic for ages and yours is the greatest I have came upon so far. But, what about the conclusion? Are you certain about the supply?