Lipoma of the ear is called benign tumor, which is mainly localized in the outer ear (often on the lobe of the ear) and very rarely in the middle or inner ear.
This is a slow-growing tumor, which mainly causes an aesthetic inconvenience. But we should remember that the lipomas are classified as those tumors that are often malignities (become malignant). Therefore, the required DC cancer control, and in the case of the fast-growing tumors without signs of malignant transformation, which were confirmed by laboratory methods – radical (complete) removal.
More common name of disease, but is practised more often among patients – Wen ear.
General data
Lipoma ear is more common in patients of middle and old age, although repeatedly described cases the development of this benign tumor in young people up to 20-25 years and even in children.
Accurate statistics are contradictory, as often Wen the ear, having small dimensions, without disturbing the patient’s discomfort and not increasing for a long time, simply ignored, and the majority of patients (especially in the regions) do not seek medical help. It is often an accidental finding during routine medical checkups or examinations regarding any other disease which brought the patient to the office specialist.
Women and men suffer from about the same frequency. In malignant degeneration of the tumor, this pattern disappears: liposarcoma is found in male patients are approximately 4 times more often in female patients.
Fatty tumors of the inner ear it is almost nonsense, but due to the fact that, overall, oncological processes unpredictable, you should be aware of the possibility of lipoma in the structures of the middle and inner ear.
Causes and development of disease
The appearance of liposarcoma of the ear occurs under the influence of the factors that provoke surplus growth and reproduction of cells in subcutaneous adipose tissue of the outer ear. However, the immediate causes of lipoma ear is not established – is the “white spot” in the knowledge of clinicians and scientists concerns and other tumors.

Highlighted a number of factors that are regarded as such, which contribute to the formation of lipomas ear. They are not specific – this means that such factors can lead to the initiation and further progression of not only Wen the ear, but any other tumor entities.
All of them can be divided into the following groups of factors:
- physical;
- chemical;
- inflammatory;
- chronic skin disease;
- system;
- vascular;
- endocrinology.
Physical factors, on the background of the action which the lipoma of the ear occurred more frequently in turn can be divided into:
- mechanical;
- heat;
- radioactive.
Mechanical factors contributing to the formation of lipomas of the ear, can be any mechanical effect on the tissues of the outer ear that can cause the rapid growth and excessive development of fat cells.

Lipomas mainly occur after the ear:
- permanent mechanical effects provoked by the wearing of tight hats that put pressure on the ear;
- surgery on the outer ear – their share in the composition of all surgical interventions on the structures of the ear is quite small, most often it is plastic surgery to correct the shape of ears;
- the habits of the patient to act mechanically on the ear. Meet emotionally labile patients who are in stressful situations, teasing his own ears. Also some patients tend to squeeze all sorts of pimples and retention cysts (small cystic structures formed when a blockage of the ducts of the sebaceous or sweat glands) – this mechanical stimulus also contributes to the development of lipomas ear;
- the impact of a traumatic nature – it can be sliced, chopped, bitten, broken and other wounds.
Heat factors that can cause the formation of lipomas of the ear, is the temperatures:
- high;
- low.
This factor begins to “work” in the case that such exposure is regular. In other words, a short stay in an extremely low temperature somewhere in the Kola Peninsula, or in high desert conditions are unlikely to trigger the formation of lipomas ear. On the other hand, permanent residence expressed in terms of minus or plus temperatures is fraught with zapuskaem the cancer process.
Radioactive impact, causing lipoma ear, can be:
- chronic;
- sharp.
It is observed in the following cases:
- a course of radiation therapy;
- contact with radioactive substances because of the specificity of labor activity in this matter a violation of the principles of labor protection;
- unauthorized access to radioactive substances is not associated with any therapeutic action or work.
A separate factor can distinguish the role of excessive ultraviolet radiation that affects the body in such cases as:
- sunbathing in natural conditions at the beach;
- sunbathing in artificial conditions in the Solarium.
Chemical factors that can cause the transformation of normal fatty tissue lipoma ear, can be any aggressive chemical compounds:
- production;
- agricultural;
- household.
A tendency to stimulation of oncological processes are characterized by:
and others.
Lipoma of the ear can occur on the background of dushirovanie of granulation tissue (the specific tissue formed in the wound) with a solution of nitrate of silver.
This tumor can develop after the transfer in any location of the ear inflammatory and purulent-inflammatory processes. It can be:
- dermatitis – specific or non-specific inflammation of the skin (in this case the auricle);
- abscess – limited ulcer;
- phlegmon – diffuse purulent inflammation
and others.
Of all the infectious lesions of the external ear most often the role of non-specific infectious lesions, often they are triggered by such pathogens as:
Nonspecific pathogens lead to the development of infectious process in tissues of the ear, which would be a precipitating factor for the development of lipomas, extremely rare.
Chronic skin disease that tends to provoke the development of lipomas of the ear, most often marked with:
- psoriasis is a chronic non-contagious affection of the skin characterized by the appearance of lesions reddish-pink in color and peeling;
- eczema – an acute or chronic noncontagious inflammatory skin lesions manifesting a variety of rashes, burning sensation, itching and a tendency to relapse (re-emergence).
Systemic diseases, which increases the chance of the formation of lipomas of the ear, secrete systemic lupus lupus – diffuse (widespread in the body) immune complex connective tissue and its derivatives.
Disease, which can cause circulatory disorders of the subcutaneous fatty tissue of the outer ear with the subsequent formation of lipoma ear, can be:
- various vasculitis – lesion inflammatory nature of the vascular wall and its subsequent destruction;
- DIC (disseminated intravascular coagulation) pathology, in which the small blood vessels throughout the body are formed of multiple small blood clots that prevent blood flow to the tissues and, as a result, can cause their reaction in the form of development of oncologic process
and some others.
Of endocrine abnormalities that promote the formation and development of the Wen’s ear, mostly plays the role of a diabetes – the metabolism of carbohydrates, which occurs due to the lack of the hormone insulin. As a result, develops diabetic damage to small blood vessels, blood flow is suffering, the tissues react in the form of launching the cancer process.
Symptoms
Lipoma of the ear in the overwhelming scenario develops in the outer ear, the most often in the earlobe.
For such tumors are common the following characteristics of the pathological process:
- slow growth;
- long asymptomatic.
The most significant signs of lipoma ear is:
- the physical presence of tumors;
- pain.
The characteristics of tumors:
- shape – round;
- size – from 0.1-0.2 cm in diameter or larger;
- the consistency is smooth.
In most cases the pain syndrome occurs when the lipoma ear is located on the top edge of the curl the ear – it is this location of the outer ear characterized by relatively high sensitivity.
Lipoma ear, resulting in ear canal, can block its lumen and to provoke the development of conductive hearing loss – hearing loss due to the violation of zvukoprovodnost.
If the lipoma ear is in close proximity to the eardrum, increasing in size, it can put pressure on it – this process is accompanied by the development of phenomena such as:
Characteristics of the ear noise in this case is the following:
- the expression is quite intense, if the lipoma ear flush “closer” to the eardrum and puts pressure on it;
- the occurrence is periodic with a small amount of the lipoma or constant when large amounts of tumor;
- nature – rustling, fluttering.
Lipoma ear in the middle ear is found casuistically rare. Increasing in size, it begins to push on the eardrum, as well as to limit the movement of auditory ossicles.
This is accompanied by such symptoms as:
- the noise in the ear of a continuing nature;
- hearing loss in conductive type (i.e., out of frustration of sound transmission).
Cases where lipoma is the ear inside the tympanic cavity, are also found casuistically rare.
In this case, it is able to exert pressure on the eve of the labyrinth – as a result, there are vestibular disorders that manifest in the form:
- bouts of dizziness system;
- balance disorders;
- coordination disorder;
- appearance of nystagmus (rolling of eyeball movement).
If the lipoma ear is the tympanic cavity, though it is a benign tumor, but malignant is manifested in the growth of the can, pushing on the eardrum and walls of the tympanic cavity, to destroy them.
When this occurs, the tumor invasion into anatomical structures that are in the neighborhood. This:
- large vessels;
- structures of the inner ear;
- the cavity of the skull.
And the clinical symptoms are very similar to that for malignant neoplasms. If shattered eardrum, in this case, the tumor mass can be seen when inspecting the auditory canal of the ear stands out bloody discharge.
If the lipoma grows in the ear the Eustachian tube and the nasopharynx develops the picture, which is a characteristic of benign tumors of the pharynx. The symptoms are the following:
- voice changes – it becomes agriplan or husky;
- frequent coughing.
If the ear lipoma reaches a large size and spreads to posterior cranial fossa, it leads to damage to IX, X, XI cranial nerves, causing the violation:
- the sound production;
- swallowing.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of lipoma of the ear is put on the basis of complaints of patient, anamnesis (history) of the disease, the data inspection. The localization in the middle or inner ear require instrumental methods of research. To clarify the nature of the tumor and the differential diagnosis may require laboratory methods.
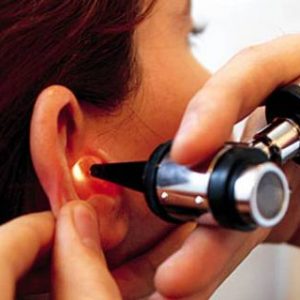
Diagnosis of lipoma of the ear, which is located on the ear, carried out jointly by an otolaryngologist, a dermatologist and a skin oncologist.
The results of the physical examination the following:
- during the examination the tumor may be visualized as a round, like a ball or a hemispherical education;
- on palpation the tumor to the touch, painless, often welded with the surrounding tissues, smooth.
Instrumental methods of diagnostics are used in the presence of a lipoma ear deep in the ear canal or if you suspect its presence in the middle or inner ear.

Used:
- otoscopy – inspection of the external auditory canal with ear mirrors. If the tumor has formed in the tympanic cavity, during otoscopy is defined by a bulge of the eardrum;
- pharyngoscope – inspection of the pharynx in cases of suspected large size of the lipoma of the ear and its distribution in the structure of the throat;
- radiography of the skull in the region of the temporal bone – the distribution of the lipoma ear, based in the middle or inner ear, can be detected by the destruction of bone walls of the tympanic cavity;
- computed tomography of the skull in the region of the temporal bone – it is carried out with the same purpose as x-rays, but computer sections data are more informative;
- audiometry – study of hearing acuity of the patient in the presence of a lipoma in the middle or inner ear. Used if you suspect a conductive type of hearing loss;
- the study of hearing tuning fork is held in the same case, and audiometry, in order to establish the kind of hearing loss;
- acoustic impedancometry – in the case of lipoma growths in the middle ear allows to detect the violation of the mobility of the auditory ossicles;
- otoacoustic emission is the study of the responsiveness of the ear on sound signals. During a survey in the ear canal place the probe in which is mounted a microphone;
- biopsy – a fragments Wen ear with subsequent study under a microscope.

Laboratory methods that can be used is:
- General blood analysis – performed for suspected malignant degeneration of Wen ear. This may signal anemia and reduction in the number of erythrocytes and haemoglobin and a significant increase in ESR;
- histological study – the study under a microscope biopsy for the presence of malignant tissue;
- cytological examination of smears from the surface of the lipoma ear under the microscope, studying the cellular structure of the tumor in terms of its malignant transformation.
Differential diagnosis of
Differential (distinctive) diagnosis of lipoma of the ear carried out with such diseases and pathological conditions, such as:
The tumor, which carried a differential diagnosis of lipoma ear, can be:
- benign;
- malignant.
Differential diagnosis of lipoma ear often carried out with such benign tumors, such as:
- fibroma – tumor of connective tissue;
- sebaceous cyst – tumor formation, which occurs as a result of blockage of sebaceous glands and is a cavity filled with cheesy contents;
- angioma – a tumor that grows from the wall of the vessel.
Lipoma of the ear, located in the tympanic cavity, must be differentiated from neoplasms such as:
- cholesteatoma – a tumor-like cavity formation surrounded by connective tissue capsule, within which are necrotic epithelial cells and a mixture of some biological substances (keratin, cholesterol);
- otitis media – inflammation of middle ear structures;
- labyrinthitis – inflammation of the labyrinth, which is a structure of the inner ear;
- Meniere’s disease – purulent lesions of the internal ear, which amplifies the volume of the endolymph (the fluid of the labyrinth) and increases inner labyrinthine pressure, which leads to bouts of deafness and vestibular disorders (disorders of coordination, balance, and so on);
- cochlear neuritis – damage to the auditory nerve, which causes hearing loss and introduces noise in the ears.
Malignant neoplasms, which should be carried out differential diagnosis of lipoma ear is:
- liposarcoma is formed from fat;
- fibrosarcoma is formed of connective tissue;
- angiosarcoma is formed from the tissues of the vascular wall
and others.
Complications
Lipoma ear most often may be accompanied by such complications as:
- malignant degeneration;
- infection and suppuration – occurs when the penetration of infection in the tissue lipoma in case of violation of their integrity, hematogenous (through the blood) or lymphatic (lymph flow) by.
Treatment
To get rid of lipomas ear can only surgically. Any impact of the conservative nature in the form of lotions and compresses are ineffective and Vice versa can lead to negative consequences – is:
- accelerated development and growth of the lipomas;
- its malignant degeneration.
Lipoma ear be surgical removal:
- a hearing;
- cosmetic purpose;
- to prevent malignant transformation.
Removal of fatty lipoma ear is carried out routinely in the clinic. Often such a patient hospitalityat in a surgical hospital (regional hospitals) or in the Oncology clinic.
Type of anesthesia when removing depends on:
- the size of the tumor;
- the pain threshold of the patient.
Please note:
Small lipomas can be removed under local anesthesia, in other cases, intravenous anesthesia.
Removal methods may include:
- surgical (or operative) – removal of the tumor with a scalpel;
- removal with laser – tumor tissue is exposed to a laser beam;
- radiowave method of tissue lipoma is exposed to radio waves with a predetermined frequency;
- cryosurgery is used to remove liquid nitrogen.
Removal of lipoma of the middle or inner ear is technically challenging manipulation, so should be done by an experienced physician when using a clinical microscope.
Keep in mind the following nuances:
- if the lipoma ear does not extend beyond the tympanic cavity, then its removal is carried out by tympanotomy (opening the tympanic cavity) and atticoantral (opening nabraboogo space and the cave of the mastoid process);
- when tumors that go in the ear canal, apply mastoidectomy – opening of the mastoid process of the temporal bone.
Prevention
As direct causes of lipoma ear is unknown, specific prevention methods to be developed.
To reduce the risk of developing the tumor can be, resorting to such actions as:
- avoidance of trauma to the ear;
- prevention of ear diseases of any nature and in their development – early diagnosis and treatment;
- a healthy way of life.
Forecast
The prognosis of the lipoma ear generally favorable. But be aware of the possibility of malignant transformation at any time, which will significantly worsen the prognosis for health and life.




My followers on Twitter would get a lot from your blog. Would it be ok if I promote it to them?
Thanks, I think.
Yes- we shouldn’t take this for granted problem any more. Suggestions?
This is quite interesting. Would it be ok to ask a question?
For most recent news you have to visit world wide web and on the web I found this web site as a best web page for latest updates.
Do you mind if I quote a few of your posts as long as I provide credit and sources back to your website? My website is in the exact same area of interest as yours and my users would truly benefit from some of the information you present here.
Please let me know if this ok with you. Thanks!
Question is that leather or rubber on the toe above the sole that wraps around?
Wonderful work! That is the type of information that should be shared across the
internet. Disgrace on Google for now not positioning this put up upper!
Come on over and seek advice from my web site . Thank
you =)
Good business!
It agree, very good piece
I am sorry, that I can help nothing. I hope, you will be helped here by others.
I consider, that you commit an error. I can prove it. Write to me in PM, we will talk.
Your opinion is useful
Usually if you have a lipoma, it does not cause any symptoms but you notice a painless lump. Lipomas grow very slowly. Sometimes a lipoma under the skin can be unsightly if it grows to be several centimetres across.
For example, if they occur on the face. Occasionally, a lipoma needs to be removed if it is causing symptoms – for example, by pressing on another part of the body. Sometimes if the diagnosis is not clear, a lipoma is removed to look at under the microscope.