Often the disease proceeds secretly without obvious symptoms, so it is almost impossible to determine glaucoma itself. Non-specific complaints are sometimes possible, which are characteristic of many eye diseases.
Therefore, for differential diagnosis, laboratory and instrumental examination for glaucoma will be required.
It is important to establish the diagnosis of glaucoma as early as possible, since the frequency of complete loss of vision from this disease reaches 14%. And with early treatment, there are good chances to save the visual apparatus.
Primary reception
At the first visit, the doctor asks a number of questions, finds out the presence of chronic diseases, and clarifies the hereditary features. Then conducts an external examination of the ocular organ. After that, the ophthalmologist proceeds to special methods for the diagnosis of glaucoma.
Diagnosis of an acute attack is not difficult, because there are characteristic specific complaints. During an acute attack, a person’s vision deteriorates sharply, his eyes and head are very sore, especially in the forehead and temples. Eyeballs turn red, hard to the touch. Common disorders are possible: nausea, vomiting, impaired consciousness.
And with a hidden flow of complaints, it may not be at all. Then instrumental examinations will come to the rescue.
Tonometry
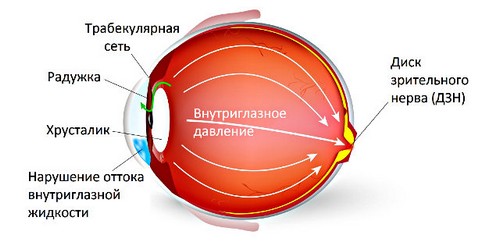
The main diagnostic criterion for glaucoma is the level of intraocular pressure. It can be measured by tonometry.

There are contact and non-contact methods for measuring IOP.
- The classical method is the measurement of IOP according to Maklakov. For this, special weights are installed on the cornea of each eye, the so-called. Maklakov tonometer. Then they are transferred to paper and the IOP level is judged by the diameter of the print.
- More advanced contact measurement techniques are electrotonography and IOP measurement with iCare. With electronic tonography, sensors are installed that record the obtained indicators (outflow of aqueous humor, IOP level). In the second case, the IOP measurement occurs when the apparatus is instantly touched to the cornea.
- There are special devices for non-contact IOP measurement. They can even be used on their own, this helps to determine glaucoma at home. The principle of their action is to feed the air stream and assess the change in its shape (pneumotonometry) or by touching the device to the eyelid (IGD devices, TVGD).
Gonioscopy
Another diagnostic method that an ophthalmologist conducts is gonioscopy. Gonioscopy for glaucoma allows you to examine the anterior chamber of the eye, identify violations of the outflow paths of aqueous humor, and study individual anatomical features.

The diagnostic method involves examination with a special device – a gonioscope. In fact, this is a mirror lens that allows you to clearly examine the small details of the anterior segment of the eye.
Perimetry
A method that allows you to study the features of the boundaries of the field of view – perimetry. More often it is computer perimetry. Since glaucoma leads to a narrowing of the visual fields, loss of areas, then perimetry is required in the diagnosis of this disease.
A person is located in front of the device, one eye closes, and the second looks at the mark. The computer gives signals – light points flash, and a person registers what he sees with the help of a button.
Classical perimetry differs from computer perimeter in instrument. For classical perimetry, a perimeter apparatus is used. The principle of diagnosis is no different.
Ophthalmoscopy
With glaucoma, an ophthalmoscopy is performed – examination of the fundus using an ophthalmoscope. Such a deep examination allows you to determine changes in the optic disc, the presence of excavation (deepening), which often develop with long-term glaucoma.
Biomicroscopy
Examination of the eyes in a slit lamp – biomicroscopy – allows you to study in detail the front of the eye, especially the anatomy.
Ultrasound of eyeballs
Ultrasound is popular because of the painlessness and accuracy of the results. With ultrasound of the eyeballs, you can study in detail the structure, size, location, blood flow and other important characteristics of the eyes.

With glaucoma, an ultrasound is an auxiliary examination method, which is not mandatory.
Optical Coherence Tomography
An auxiliary method such as OCT is required to determine the characteristics of the optic nerve head.

Allows you to assess the level of changes in the fundus.
Early diagnosis
It is worth thinking about early diagnosis if you notice a deterioration in vision, namely:
- flies before the eyes;
- blurred gaze;
- rapid fatigue of the visual apparatus;
- decreased visual acuity;
- lacrimation
- pain in the eyeballs.

Having come to the doctor with such complaints, the ophthalmologist will conduct an examination and examinations to determine the diagnosis. For early diagnosis of the disease with an increase in IOP, even minimal examinations, such as tonometry, tonography, gonioscopy, perimetry, may be sufficient. For a more detailed diagnosis, auxiliary examination methods are prescribed.
The effectiveness of early diagnosis of glaucoma depends on the quality of examinations, as well as their repeated repetition. It is not possible to establish a diagnosis of glaucoma by measuring IOP only once. Repeated diagnosis is required, the assessment of results in dynamics.
An ophthalmologist needs to undergo a routine examination annually. And with the onset of symptoms of open-angle or angle-angle glaucoma, you need to get to the doctor as soon as possible.
Watch a video about the early diagnosis of high IOP:
Treatment of pathology can be either medication (drops to reduce IOP) or surgical (laser: iridectomy, iridotomy, trabeculoplasty; surgical: trabeculoectomy, bypass surgery). This is decided individually on the basis of the diagnostic results.