Contracture of the knee joint is called a pathological condition in which decreases the volume (amplitude) of his movements. This can suffer as flexion and extension. The severity of contractures can vary greatly – from barely noticeable to complete immobilization of the joint.
Due to the anatomic peculiarities of the knee joint – the structure is quite delicate, so it contracture develops faster than contracture of other joints.
As the knee joint is involved in the process of moving of the person, his contracture is a very unpleasant condition. Methods of diagnosis and treatment of diseases brought to perfection, but often the treatment is delayed.
General data
Knee flexion contracture is a fairly common pathology of the different forms of contracture affects about 15-25% of all patients diagnosed with pathology of the knee joint. In 13-15% of all cases the contracture of the knee joint causes violations of disability and disability of the person.
Most of these are common in working age – from 25 to 45 years, men are affected more often than women.

Reasons
The main groups of causes of contracture of the knee joint is a:
- prolonged immobilization;
- congenital anomalies;
- traumatic damage to the structures that make up the fragments of the knee or involved in its activities – the bones, ligaments, capsules and muscles;
- degenerative-dystrophic process;
- diseases of inflammatory nature.
The most frequent reason of development of contractures of the knee joint is injuries and degenerative processes. The last cause osteoarthritis – the destruction of the structures of the knee joint.
For gonarthrosis contracture occurs because:
- changes of all structures of the joint, which inevitably progressing;
- critical changes to the shape of the articular surfaces of the femur and tibia.
The cause of contractures of the knee when the injury is the direct injury of the joint that triggers such violations as:
- change the shape of the joint;
- with intraarticular fractures scarring in the soft tissues;
- fractures of the femur, tibia and fibula – shortening of the quadriceps muscles due to prolonged stay of the limb in the position of extension;
- violation of the structure of articular cartilage due to prolonged immobility.
Knee flexion contracture can develop with immobilization for three weeks. These rapid changes arise because of the following reasons. Each week muscle strength of the lower limbs is reduced by 20%, and for three weeks the stiffness of the joint capsule is increased by approximately 7-8 times. This means that for making a normal movement in the knee joint the patient is required to exert a lot more effort – despite the fact that muscle arrays significantly weakened.
On the second place among the reasons for the development of contractures of the knee joint – purulent arthritis and extensive burns, due to which the formation of massive scars, skin tightening.
Several less likely to cause movement limitation in the knee are the scars that emerged after deep lacerations and wounds Radosavlevich in such locations as:
- knee joint area;
- front and back of the thigh;
- the back of the leg.
Of all congenital malformations of the knee joint most often the perpetrators of contractures of the knee are congenital dislocation of the knee joint, hypoplasia (underdevelopment) and aplasia (absence) of the tibia.
The development of the pathology
There are many varieties of contractures of the knee joint, so in the clinic, they are for convenience klassificeret on different grounds.
This pathology is:
- congenital – develops due to a failure of the fetal development, the child is born with a contracture of a knee joint;
- acquired – occurs in the postnatal (after birth) period due to the impact on the joint of any pathological factors.
Also knee flexion contracture may develop in the postnatal period on the background of congenital changes in the tissues that form the joint. This contracture also refers to acquired.
Depending on the mechanism of occurrence there are two large groups of contractures of the knee joint:
- active (also called neurogenic);
- passive (also called structural).
Neurogenic contractures of the knee joint are due to innervation (nerve support) muscles – their functionality is affected, and the muscles are not able to bring the knee joint in motion.
Disorders in which there is this kind of described pathology is:
- paresis – partial immobilization of muscles due to innervation;
- paralysis – complete functional failure, which occurs when there is complete cessation of the innervation of the muscles that move the knee joint;
- some mental disorder.
Depending on the cause, which led to the development of neurogenic contractures of the knee joint, they are divided into:
- Central neurogenic – they can occur on the background of any lesions of the brain and spinal cord (injuries and illnesses);
- peripheral neurogenic – such contractures develop any damage to the peripheral nerves;
- psychogenic – a special form of contractures of the knee joint that occur during an attack of hysteria (especially prolonged).
In turn, peripheral neurogenic contractures of the knee joint can be:
- traumatic;
- non-traumatic.
Also there is a clinical classification of peripheral neurogenic contractures – they are:
- pain;
- reflex;
- irritative-paretic – arise from the violation of metabolism in the peripheral nerve branches.
A special form of peripheral neurogenic contractions – those that occur in disorders of the autonomic innervation of the vessels supplying the structures of the knee joint.
Structural contractures develop because of an obstacle that does not allow the knee joint to perform flexion and/or extension movements. Such an obstacle can be:
- the shortening of the muscles – observed in their trauma, certain diseases, and also due to a failed surgery on this area;
- joint “mice” – the presence in the cavity of the knee joint cartilage or bone fragments that were formed as a result of the pathological process (for example, by metabolic disorder in cartilage and the formation of conglomerates of salts), or injury (fragments of cartilage or bone may break away and migrate into the joint cavity).
Depending on the location of the lesion and joint contractures are also divided into the following types:
- arthrogenic – develop in disorders that are observed directly from the side of the knee joint (this deformation, birth defects, etc.);
- myogenic – observed in the pathology of the muscles that provide the movement of the knee joint (most often the shortening of the muscles that occurs for a variety of reasons);
- diskogennye is contractures that develop due to the formation of connective tissue scars, adhesions, ties;
- dermatogenic – are formed when the scarring of the skin that directly covers the knee joint structure of lower extremities that is within the joint (femur and tibia);
- immobilization – their occurrence should be wary of prolonged restriction of mobility of the limbs (regular or plaster bandages).
Of all contractures dermatogenic are less common, but the occurrence of contracture of the knee joint can cause scarring of the skin, which start in the region of the hip or ankle and stretch to the knee joint.
Immobilization contractures – some of the most common contractures of the knee joint from the category of the structural. They are preceded by a long skeletal drawing, complex operations on the knee joint, a long stay in a cast about of fractures and other severe injuries of the lower limbs that require prolonged immobilization and stay of the lower limb in the stimulated stationary state.
Depending on what type of limitation of movement occurred in the knee joint, there are the following types of contractures:
- flexion – joint is reduced in persistent flexion position;
- extension – joint is reduced in the persistent position of the extension.
Symptoms of contractures of the knee joint
The main symptom indicating the development of contractures of the knee joint is the limitation of his flexion or extension. Other features are minor, their presence in this pathology is optional. It can be:
- deformation of the joint;
- swelling;
- violation of the support;
- pain in the joint;
- shortening of the lower limb;
- its a forced situation.
By itself, the deformation of the joint can be reduced visually observed deformation of the entire limb.
Edema can develop as a reaction of the periarticular soft tissue, or occurs as a symptom of pathology that has led to contracture of the knee joint.
Breach of support is that people can not rely on the affected limb at any location.
Characteristics of pain in the joint:
- localization – cover the entire joint;
- widespread irradiation as such is not typical, but pain can radiate into the neighboring structures caused by disease, which led to the development of contractures of the knee joint;
- nature – often nagging, aching less;
- the expression is often tolerable, but careless movement of the patient or when you try to force the joint to bend/stretch can be intense and even unbearable;
- on the origin – arise depending on whether the violation led to the development of contractures.
Shortening of the lower limb when the knee flexion contracture is observed in the case of flexion contractures of the thigh and lower leg are taking against each other forced situation.
These are just the main symptoms that may be accompanied by contracture of the knee joint. Other symptoms that can develop, fickle, since they depend on the specific disease or pathological state, which led to the development of described pathology.
The continued existence of contractures of the knee joint in many cases develops the clinical picture of osteoarthritis – non-inflammatory destruction of the joint with a gradual erosion of its institutions (primarily the articular cartilage).
Diagnosis
Contracture diagnosis put on the basis of complaints of the patient, anamnestic data (history of disease) and results of inspection.
More important (and sometimes difficult) is to identify causes that could lead to the development of contractures of the knee joint. Therefore, it is necessary to attract the complex of additional methods of examination, instrumental and laboratory. Often for rapid accurate diagnosis is necessary to attract to the diagnostic process related specialists and vascular surgeon, neurosurgeon. If you suspect a neurogenic contracture, to detect lesions of the peripheral nerves, brain or spinal cord will need to consult a neurologist and neurosurgeon. Hysterical type of contracture is necessary to consult a psychiatrist or psychotherapist. After examination of the patient, the experts will put a preliminary diagnosis and narrow the range of necessary methods of inspection.
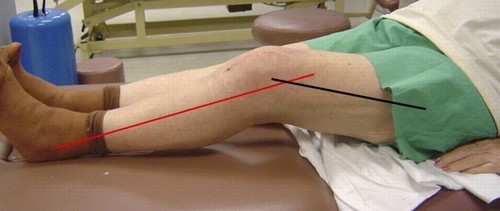
Important is the clarification of details of the history. For this, the patient must answer the following questions:
- when there is a contracture;
- was it seen as its progression;
- what are the diseases of musculoskeletal system preceded the appearance of contractures of the knee joint.
The physical examination evaluated the following parameters:
- when inspecting the position of the limb, its shortening of the visual (if any), condition of the skin covering the knee joint, and muscle (visible tension, which can be seen in well-developed muscular tracts of the lower limbs);
- palpation (feeling) to the presence or absence of pain syndrome and edema.
For analysis of the severity of the contractures it is necessary to conduct measurements of range of motion:
- passive – the patient is in the supine position, the doctor takes the injured limb in his hands and holds flexion/extension in the affected knee joint. Such testing should be conducted on the principle of “to stop”, but without violence, the doctor must stop testing when the patient reports pain or any expressed discomfort in the affected joint;
- active – being in different positions (standing, sitting, lying), the patient has flexor and extensor movements of the knee joint.
Instrumental methods of examination that are most informative in the diagnosis of contracture of the knee joint is:
- radiography of the knee joint is the most affordable method, with which in any clinic will be able to establish the approximate causes contractures of the knee joint;
- computed tomography (CT) – computer sections will identify the changes that led to the contracture of the knee joint and that cannot be detected by radiographic examination;
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is its ability the same as the possibilities of computed tomography. But an MRI will help to better examine the soft tissue changes which could lead to the described pathology;
- arthroscopy the cavity of the knee joint introduce the arthroscope (type of endoscope with an optical system and lighting), visually determine changes in it.
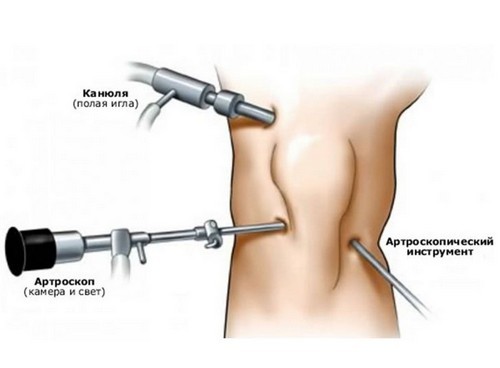
Laboratory methods for the diagnosis involved diseases that could lead to the development of contractures of the knee joint. Often, the most important are:
- General analysis of blood;
- rheumatology test;
- biochemical analysis of blood – the greatest practical value has determination of sodium, potassium, calcium, chlorine, which depends on the amount of motor activity of muscles, “move” the knee joint, and functionality of nerve endings, providing the work of these muscles.
Differential diagnosis of
Differential diagnosis is carried out between those diseases which could lead to the development of contractures of the knee joint.
Complications
The main complication is contracture of the knee joint is the reduced functional ability of the affected lower extremity until the complete inability to make the movements. In advanced cases, prolonged immobilization may lead to muscle atrophy.
It should also be borne in mind that the pathology that caused the contracture, can lead to several other complications, so the development of contractures of the knee joint should be a kind of signal for wide diagnostics.
The treatment of contractures of the knee joint
The treatment of contractures of the knee joint is carried out using both conservative and operative methods. In any case, it is conducted in a hospital – in the emergency room (rarely), or casualty Department (usually).
The treatment is very different and depends on the cause of contractures. But in any case effective are the following methods:
- bloodless correction of position of the limb;
- physiotherapy;
- Exercise;
- massage.
Bloodless correction of position of the limb is as follows. Knee joint lead to physiological state gradually, with the laying on plaster, in this position, the joint is some time.
Surgical correction of contractures of the knee joint is carried out if:
- conservative treatment is ineffective;
- contracture progresses;
- got complications in the form of atrophy.
The operation is performed:
- open access;
- with the help of the arthroscope.
The basic manipulation, which are most commonly performed during surgical intervention to eliminate the contractures of the knee joint is:
- to restore the normal form of the articular surfaces;
- the carving scar tissue;
- lengthening of the muscles.
If the articular surface is significantly destroyed, and restore them not succeed, but the muscles of the femur and tibia is preserved, carry out the knee replacement. In some cases, the anatomical features do not allow the endoprosthesis, therefore, perform arthrodesis of the joint in a functionally advantageous position – the joint itself is removed, the remaining fragments of the lower limbs are fastened together into a unified whole.
In any case, after surgery prescribe physiotherapy exercises and physiotherapeutic treatment methods. With their help:
- tone up your muscles, prevent their atrophy;
- improve blood flow to the affected limb.
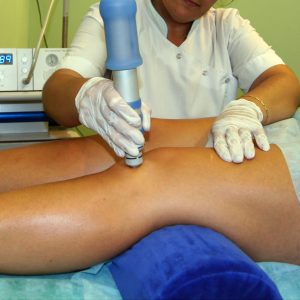
Neurogenic contracture go, if you assigned adequate treatment of a neurological disease, which led to it.
If due to cerebral or spinal paralysis developed flexion contracture of the knee joint, straightening the affected limb to impose the tires or straighten it using special equipment with weights.
Hysterical contractures require psychiatric treatment, or apply various psychotherapeutic techniques.
Prevention
The most important methods of prevention of contractures of the knee joint are:
- avoidance of prolonged immobilization of the lower limb instead prefer surgical methods of treatment;
- if necessary, immobilization – previously, the appointment of therapeutic physical training;
- protect knee joint from trauma (use of special equipment when Biking, rollerblading, skateboarding, traumatic sports);
- prevention, early detection and treatment of pathologies that lead to the development of contractures of the knee joint – first and foremost, neuro-trophic.
Forecast
The prognosis of contracture of the knee joint are different, often complex. It depends to a large extent on:
- of the disease;
- the neglect of pathological changes in the joint and tissues that are in the neighborhood.
Fresh immobilization contractures are well treated, if treatment is assigned earlier.
In long-standing contractures of any origin, the prognosis worsens over time in the joint develop scars not only damaged but also healthy tissue.


This is nice!
There are some interesting closing dates in this article however I don’t know if I see all of them heart to heart. There may be some validity however I will take maintain opinion till I look into it further. Good article , thanks and we would like extra! Added to FeedBurner as well