What can overshadow the life of a future mother? In the early stages – this is toxicosis, the threat of miscarriage, later – polyhydramnios, gestosis and more.
Why do you have to suffer, endure unpleasant tests while waiting for the baby, what are the causes of polyhydramnios and other problem states?
Pregnancy is a natural process for every woman, when not only her appearance, but also her worldview changes. There is so much excitement, concern, anxiety and reason to rejoice, for example, the first stirring of the baby. But, unfortunately, sometimes there are problems associated with this interesting situation.
When there is a lot of water…
Almost every woman knows what amniotic fluid is – this is the fluid that surrounds the baby in the womb for almost the entire pregnancy. Their number ranges from 20-30 to 1200, less often up to 1500 ml, depending on the term.
What problems can be associated with amniotic fluid?
- Low water.
- Polyhydramnios.
- Amniotic fluid infection.
Polyhydramnios is an excess of amniotic fluid. This problem can occur at any time and it is extremely important to find out and eliminate the cause.
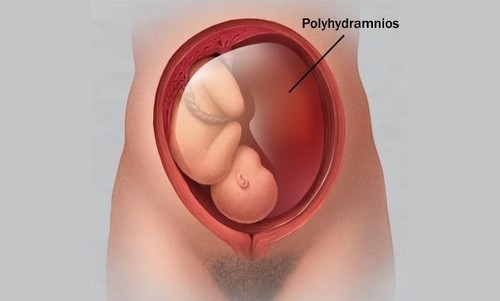
Something is wrong…
In most cases, a moderate increase in amniotic fluid has almost no effect on the well-being of pregnant women or they simply think that it should be so (especially if the pregnancy is the first). What are the symptoms?
- Excessively large abdomen, not appropriate for the size and duration of the fetus.
- Drawing pains in the lower abdomen, a feeling of muscle fatigue due to overload.
- Tachycardia, feelings of lack of air, heartburn and nausea – all this develops due to the higher standing of the uterus, which in turn compresses the stomach and disrupts the movement of the chest (diaphragm).
- Often after polyhydramnios, edema develops, more often than legs.
If these symptoms appear, consult a doctor without waiting for a planned visit.
Causes
The causes of polyhydramnios are diverse, but it is customary to single out the most common.
From the future mother:
- hormonal disorders in the mother’s body, for example, diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism, adrenal insufficiency;
- infectious diseases of the urinary and reproductive systems (specific and non-specific);
- general infectious diseases (bacterial, viral);
- parasitic diseases;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system and their exacerbation during pregnancy;
- various pathologies of the kidneys and urinary system;
- immunological conflicts on the Rhesus factor and blood type.
From the fetus:
- multiple pregnancy;
- overweight of the fetus;
- pathology of the gastrointestinal tract;
- pathology of the urinary system;
- congenital endocrine pathology, in particular hypothyroidism;
- gene and chromosomal diseases;
- dysfunction of the membranes and uteroplacental circulation.
Hormones – body conductors
The hormonal system is a very delicate structure that includes many direct and feedback mechanisms. That is why violations of one link, the pathology of one endocrine gland leads to a gross malfunction throughout the body. This also applies to the process of bearing a child.
With diabetes in the mother, the process of glucose uptake by the cell is disrupted in the body, and as a result, a large amount of this substance remains in the bloodstream, amniotic fluid. Almost all sugars have the ability to attract water. Thus, the increased content of glucose in the blood, amniotic fluid contributes to the attraction of additional fluid to restore the proper concentration of substances. By the way, this is the most common cause of polyhydramnios.
A similar mechanism and with reduced functional activity of the thyroid gland, otherwise with hypothyroidism. This endocrine organ produces substances responsible for metabolism and energy. A reduced amount of thyroid hormones leads to metabolic disruption and, as a result, glycosaminoglycans can accumulate in tissues and amniotic fluid, which in turn, like glucose, attract a large volume of water. Usually in these cases, pregnant women have dense swelling of the skin and subcutaneous fat.
Similar troubles can arise with the pathology of any part of the endocrine system responsible for the metabolism and water in the body.
Local and General Infections
Any infectious process is stress for the body. Local infectious diseases are usually divided into non-specific (microbes and viruses of any strain and class) and specific, for example, gonorrhea and syphilis. The latter are extremely dangerous for the unborn child, not only the development of polyhydramnios, but also the formation of severe congenital pathology, up to malformations. Nonspecific infections, as a rule, can cause infection of the amniotic fluid, then the placenta, and as a result have a toxic effect on the vessels, which will become more permeable. The latter directly leads to an increase in amniotic fluid.
As for common infectious diseases, it can be viruses, bacteria, fungi. The harder the disease for the mother, the worse for the future baby. Influenza, measles, chickenpox, and herpetic infections that arose for the first time are especially dangerous. All of them synthesize toxins into the bloodstream and contribute to the production of inflammatory substances, antibodies, immune complexes that negatively affect the vessels of the placenta, increasing their permeability, and the future baby. Secondary infection of the placenta, amniotic fluid, and the baby may also develop, which can lead to the development of polyhydramnios.
Any stress, including infectious, can cause an exacerbation of chronic diseases of the mother.
Extragenital pathology
This is a group of diseases that is not associated with the reproductive system, but can have an adverse effect on the development of pregnancy, for example, diseases of the cardiovascular system.
Hypertension or other pathology, accompanied by an increase in blood pressure, with decompensation in pregnant women is almost always accompanied by excessive amniotic fluid and edema. It is also a threat of premature placental abruption and a violation of the normal course of labor.
Diseases of the urinary system, unfortunately, are not uncommon in our time and are one of the main causes of problem states during pregnancy, including increased water formation. Most often, pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis and other types of nephritis lead to the latter with impaired renal excretory function.
Exacerbations and reactivation of systemic problems, which most often affect the small vessels of the kidneys, placenta, are extremely dangerous.
When immunity becomes an enemy
Our immune system is designed to protect the body from foreign genetic information – these are transplants, infections, foreign bodies. And the couple is the unborn child. After all, he only half has the genetic material of a woman, the other half from his father.
Most often, the immune system rebels against the child, if there are some differences in the blood group and Rh factor, although there are other incompatibilities. Such conflicts lead to acute inflammation, which in turn causes an increase in amniotic fluid.
Child
Amniotic waters, processes in the placenta are regulated by both the expectant mother and the child. Therefore, there is some pathology or deviation from the norm on the part of the fetus, contributing to the development of polyhydramnios.
For a person, the bearing of one fetus is considered the norm, in other cases this is already a deviation from the norm. The female body undergoes tremendous stress during pregnancy. Around each baby, especially if they are heterogeneous, an amniotic fluid is formed that performs protective, nourishing and training functions. Therefore, a multiple pregnancy is almost always accompanied by an excess of amniotic fluid.
If a child develops endocrine pathology in the womb, accompanied by metabolic and water disorders, then there will be more amniotic fluid. Unfortunately, the baby suffers from this, usually such congenital diseases are accompanied by deviations in neuropsychic development and an increase in body weight (often due to edema) and individual organs.
Amniotic fluid, among other things, serves as a trainer, that is, the child swallows, digests and excretes. Partially assimilation of water with dissolved substances occurs and, accordingly, its amount is controlled. If the child has a pathology of the gastrointestinal tract, for example, atresia, membranes in the lumen, the child will not be able to swallow the fluid, reducing its amount around itself.
Polyhydramnios due to gene and chromosomal abnormalities in the fetus is one of the most unpleasant. The mechanism of water increase in Down, Edwards disease has not been fully studied, most likely this is associated with combined organ pathology.
Quite often, the cause of polyhydramnios remains unclear, then the treatment is symptomatic.
Effects
The danger of polyhydramnios is determined, first of all, by the reason why it arose. Indeed, in some cases, an increase in the volume of amniotic fluid is far from the most terrible symptom and consequence.
An increase in amniotic fluid in itself is dangerous for premature birth. A woman’s uterus can only increase to a certain size and, unfortunately, sometimes this is not due to the normal size of the baby.
Treatment
How to avoid polyhydramnios? It is best to start with prevention, which means that pregnancy should be planned in order to tidy up your body and compensate for chronic diseases of the endocrine, cardiovascular and genitourinary systems.
Most often, the deviation in the normal volume of the intrauterine fluid is ascertained by the results of ultrasound examination. Then you need to establish the true problem. Only treatment for a causative disease will allow you to get a lasting result.
Symptomatic treatment is allowed only if the cause is not established.



