One of the most serious diseases not only respiratory tract, but also the entire body, especially in children during the first three years of life is pneumonia. It can, without timely recognition and active treatment, cause death from respiratory disorders and metabolic disorders.
It often occurs as a complication of SARS or childhood infections, flu or some somatic pathologies, may be formed as a weakened and stagnant long-term lying in the hospital, toddlers and even infants as a result of intrauterine infection.
What treat pneumonia, what drugs, and activities are included in the standards of care and what is important to know parents?
What is meant by the term “pneumonia”
Pneumonia (or as it is called – pneumonia) is an acute process involving microbial, viral or rarely fungal, non-infectious origin. Usually inflammation pneumonia localized in the alveoli and the terminal branches of the bronchi, the place of transition in their lung tissue.
The alveoli of the lungs is the most important of their functional unit, they designed to to perform continuous gas exchange and deliver to the cells of the body oxygen through the circulatory system while relieving the body from the resulting cellular respiration carbon dioxide. If the inflammation is formed in the region of lung tissue, where these lie the alveoli, impaired gas exchange process and naturally suffers the metabolism, is formed by tissue hypoxia and impairment of cell respiration and produces energy for life.

In children pneumonia is usually secondary infectious origin, as a complication of colds and other diseases. Rare variants can be primary pneumonia and noninfectious lung disease.
How dangerous is pneumonia in children
A particular danger is pneumonia in children, especially early age – infants and breast, due to the fact that they have inflammation rarely separated one segment or a lobe of the lung, they usually have inflammation prone to rapid and extensive dissemination to the tissue of the lungs due to the imperfections of immune system and weak defense mechanisms. Extensive damage to the lung tissue leads to loss of its functioning because of the swelling and inflammation that threatens severe hypoxia, particularly dangerous for the nervous tissue (and brain in particular), as well as the heart and kidneys.
According to statistics, pneumonia in children under one year are particularly common, they suffer up to 20 kids out of a thousand, and by the age of three years, this number is reduced to 4-6 per 1,000 children.
Pneumonia is life-threatening, so it is always important to monitor children for colds, in case of any doubts or complications immediately consult a doctor to determine signs of inflammation in the lung tissue and immediately conduct a full diagnosis.
In case of confirmation of the diagnosis requires complete and proper treatment according to protocols and standards that will allow as soon as possible to recover.
What to consider in the treatment of pneumonia
In pneumonia in children can not do only one or two drugs, you need a comprehensive treatment that is emerging as medicines, and additional influences (mode, nutrition, fluid intake, physical therapy, physical therapy, etc.). The younger the child, the more carefully should be carried out all the activities out of drugs and treatment, often infants and children with atypical forms of pneumonia are treated stationary.
Pneumonia community-acquired origin in children after three years of allowable treatment at home under the watchful supervision of a physician. Treatment is divided into certain groups, and is based on the cause, severity and the presence of certain symptoms. Let’s talk more about all medical events, groups of preparations and techniques in therapy.
Usually selected a set of medicines and activities on the basis of:
- The causative and precipitating factors,
- Possible complications
- The localization process
- Age and condition of the child.
All products are strictly calculated on the weight and age of the crumbs, taking into account the portability and compatibility among themselves, data about allergies and other conditions, not to cause harm to a large number of medicines.
Treatment of bacterial pneumonia in children
The most common and frequent is bacterial pneumonia which is usually caused by opportunistic or pathogenic flora, which has frequent contact with the child. The most common of the reasons are coccal forms of germs or bacilli, Haemophilus influenzae.

To suppress their activity and harmful effects on children’s lungs antibiotics. Such microbes can be sensitive to one type and resistant to others, so the selection should be conducted in ideal according to the culture and determine the individual sensitivity to antibiotics of a particular microbe.
But it may take a few days, during which pneumonia may reach a critical current, and will endanger the child, so the starting sputum is taken for culture and antibiotic treatment empirically (based on experience of doctors and the most common pathogens), and carefully check the effectiveness of treatment. If it is not very efficient and has already arrived, the planting data, the antibiotics are changed already to those to which reliably sensitive microbe that caused the inflammatory process, defined according to the analysis.
The most commonly prescribed such medications as protected penicillins (clavulanate), macrolides or cephalosporins of the last generation.
When antibiotics are taken into account the child’s age and the severity of his condition, used such forms as solutions, syrups or suspensions, tablets and capsules, or drugs injection.
To date, in connection with the emergence of a large number of oral forms of contemporary powerful and effective antibiotics in community-acquired (home of pneumonia mild or moderate severity) no benefits injections before taking antibiotics. Excellent job with inflammation medicines, syrups and tablets, suspensions and injections – this is unnecessary mental and physical trauma, stress in children, undermining the immune system.
Injectable form shown children who are unable for objective reasons to take oral form – they are in a serious condition, there are serious pathology of digestion, for which antibiotics via the mouth under a ban, or at the confluence of special circumstances, with the transition at the first opportunity for the period of treatment already in oral form.
Treatment of viral and fungal pneumonia in children
Can form pneumonia some virus is typical of adenovirus, parainfluenza and influenza infection. Treatment of viral pneumonia complicated and often quickly joins secondary microbial component. In this case, the applicable anti-influenza gamma-globulin and antibiotics of the same type as in microbial pneumonia.
If this is pneumonia as a result of infection with influenza type A (especially swine and avian strains), shows the use of antivirals new generation is Tamiflu or relenza. Treated similar to pneumonia because of their high risk and the propensity for complications only in a hospital. Drugs need to enter during the first two days of onset of disease, then they can provide in relation to the virus effect.
In the presence of pneumonia of viral origin, which provoked the chickenpox or cytomegalovirus, prescribers Acyclovir injections to achieve fast results and maximum concentrations. Complement the treatment of interferon preparations and inducers of its synthesis of endogenous.
Dangerous for children atypical pneumonia agents which becomes a specific flora. This group will carry Mycoplasma and chlamydial infection, as well as legionelleza pneumonia. These agents have a specificity in the development of pneumonia and during infection, are intracellular parasites, which difficulty the impact on them of antibiotics. So often in their treatment prescribe specific antibiotics group, which is applicable for severe pneumonia, in combination with immunomodulatory, antiviral and anti-inflammatory drugs.
The treatment is carried out, forcing the agents to leave the affected cells, then exposing them to antibiotics. The treatment is carried out in the hospital, often supplementing it with chemotherapeutic drugs intravenously and monitor efficiency, adjusting treatment as needed.
Fungal pneumonia and Pneumocystis (the fungi belonging to the group of pathogenic or opportunistic pathogens) are treated through the use of medications of antifungal activity, antibiotics, under these types of inflammation are prohibited, they will only worsen the situation. Apply solutions specific powerful antifungal agents in combination with inhibitors of folic acid administered clindamycin.
Parasitic pneumonia caused by infection with helminths are treated comprehensively with the use as the basis of antiparasitic drugs in the age dosages, in addition, use immune-boosting and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Special forms of inflammation
Perhaps in rare cases, the development of allergic pneumonia, in which inflammatory process caused by exposure to allergens – pollen, feather, feathers, medicines, fungal spores, etc. In this case, shows the separation with the allergen and receiving antihistamines, hormonal agents and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory therapy.
In the treatment of chemical pneumonia, provoked by the inhalation of different chemical compounds, toxins and poisonous substances, gases and symptomatic anti-inflammatory therapy in combination with total body detoxification (the use of antidotes that bind and detoxifying).
Aspiration pneumoniacaused by inhalation of oropharyngeal contents, amniotic fluid with meconium and liquids, shows a complex treatment with application of antibiotics injections and anti-inflammatory treatment, immune drugs, common security measures and a proper diet, drinking.
Mechanisms of development of pneumonia and treatment principles
Origin of pneumonia are divided into primary and secondary, the effect of such a division can vary considerably and mechanisms of treatment, types of prescribed drugs and tactics regarding a sick child. So, the primary pneumonia is a result of the penetration threat of microbial flora in the respiratory tract and lung tissue directly, or brought into the area of the alveoli with the flow of lymph or blood. In this pneumonia treatment will focus on reducing directly by the pathogen, it requires active suppression of all inflammatory processes inside the body.
Secondary pneumonia occur as a complication of certain infections – acute or exacerbation of chronic, it is necessary to guide treatment, primarily to eliminate the root causes of pathology.
Therapy of pneumonia, based on the localization and size of lesions
Pneumonia may be focal, in this case formed inflammatory areas in the lung tissue approximately 1-2 cm in this form of the disease requires the selection of antimicrobial therapy depending on the type of pathogen. In addition, this pneumonia may be cough and shortness of breath, which disappears with decreasing of the inflammatory process and inhibition of microbial activity. So there is no need antispasmodic and eliminate bronhoobstrukcia drugs, symptomatic tools. This pneumonia in the prognosis and treatment are much more favorable, weeks the rest.
Segmental or polysegmental options pathology – with them an inflammatory lesion within one or more segments of the lung, but less than one share as a whole. They must be sure the appointment of antibiotics according to the results of crops, as well as the applicable oxygen therapy – the use of mixtures with enriched oxygen, improving pulmonary ventilation and blood oxygen saturation applicable inhalation drugs to expand the bronchi (bronchiodialator and bronhodilatiruty means).
In the inflammatory process in the pulmonary region, a proportion is formed of lobar pneumonia, it is very heavy, in addition to massive antibiotic therapy when it shows the use of inhalation drugs, relieving the obstruction of the bronchi, is sometimes necessary the use of forced pulmonary ventilation and electrophoresis with analgesic and bronchiodialator drugs. Also important is the localization of the inflammatory lesion in the apex of the lung or its Foundation, as well as the age of the baby and the severity of the condition.
The course of the disease and adjustment of treatment
If it is not complicated by bacterial pneumonia, which occurs according to classical laws, applicable antibiotic penicillin (protected – Amoxiclav) or semi-synthetic penicillins (flemoksin, Augmentin). Can also be applied cephalosporin drugs (Suprax, SACEP, Zinnat), macrolide medicines (Sumamed, Klacid, Macropen).

If it’s pneumonia with complications of lung abscesses, pleurisy, or bronhoobstruktive syndrome, on the background of anemia or risk of sepsis, pulmonary edema applicable combination of two antibiotics – usually the funds with aminoglycosides, imipenem (the drug Tienam).
Treatment of hospital and community-acquired forms of pneumonia
In the case of the treatment of community-acquired pneumonia using medication, macrolides or penicillins, cephalosporins. In hospital of pneumonia, you need antibiotics reserve, who carefully select for more resistant to the usual treatment of flora – can apply combinations of their latest generations of cephalosporins and aminoglycosides, fluoroquinolones.

In the treatment of congenital pneumonia, when a child gets an infection in the womb or during childbirth, applicable macrolide antibiotics of new generations.
General principles of treatment of pneumonia in children
The duration of treatment for pneumonia will depend on the type and comorbidities, the age of the little patients and many related conditions, certain symptoms and degree of disorders of metabolic processes. All of this will be considered the attending physician in prescribing and dosages, taking into account data of external examination, listening to light, temperature and x-ray pictures.
Strictly prohibited any attempts to treat this disease at home, it can not only improve the condition, but also lead to serious and fatal complications, the transition of inflammation into a chronic form and disability of the baby.
The average, uncomplicated cases the treatment lasts about 8-10 days, undertaking necessary rehabilitation, up to three months. Atypical types of pneumonia, treatment can take from two weeks to a month, but it is believed that even ordinary uncomplicated pneumonia treated home about month after you start taking antibiotics.
You should know that without the antibiotics pneumonia is not cured, none of the traditional methods and drugs will not eliminate microbial inflammation, and the prognosis is favorable only when carrying out a full complex therapy. Without the help of doctors possible fatal outcomes or serious complications.
To treat pneumonia can be both at home and in the hospital, the decision on where it will be accepted by the doctor based on certain criteria and characteristics:
- the age aspect. For children up to three years this is by far the inpatient treatment, as needed round the clock medical observation, the probable complications that develop quickly and rapidly.
- General condition of the child. After three years it is possible home treatment of uncomplicated forms of pneumonia, in the absence of chronic pathologies and at a relatively satisfactory condition, positive dynamics in treatment.
- the form of pneumonia. In the presence of focal forms is possible home treatment where you don’t need the injections and droppers, with extensive lesions and the need for invasive manipulations, inhalation and oxygen therapy are placed in a hospital.
Symptomatic drugs in the treatment of pneumonia
In addition to prescribing antibiotics in order to alleviate the condition of the baby, to help him to actively cope with the disease and quickly go on the amendment, applicable symptomatic medication.
These include several groups of substances and drugs:
- for high fever reduce malaise and improve the condition applicable antipyretics based on paracetamol or ibuprofen (preferred). They are used in increasing numbers on the thermometer is above 38.5℃, and for infants up to three months – above 38.0℃.
- preparations for the liquefaction and separation of sputum, relieve cough, easier expectoration from the bronchi its. Drugs can be used orally in the form of solutions and syrups, drops, and also used in the form of solutions for inhalation with a nebulizer.
- drugs bronholiticeski and bronhodilatiruyuschego number – expand the lumen of the bronchi and relieve bronchial smooth muscle spasm, helping to improve and make breathing easier used in the form of inhalation or drops, tablets and syrups inside. Can also be applied electrophoresis with aminophylline.
- antihistamines to reduce swelling of lung tissue and enlargement of the bronchi complications of pneumonia and an allergic component of inflammation. Used in the form of drops, solutions and tablets.
- local anesthetics are shown with caution if breast pain during coughing and breathing, are used in the form of electrophoresis.
Can also be applied absorbable drugs, multivitamin means and physiotherapy, electrophoresis with various drugs.
Prohibited in the presence of pneumonia jars with mustard plasters, baths, and any warming up procedures. They only increase the inflammation and spread germs.
The use of oxygen, aerotherapy in pneumonia
All children with pneumonia suffer from hypoxia, and the harder the process, those more expressed metabolic disorders. Shows the use of oxygen therapy (breathing humidified oxygen) or aerotherapy (breath mix with the air in predetermined proportions).
Also shown on the stage of treatment of the salt caves and “mountain air”, additional physiotherapy and a walk in the fresh air, sleep with the window open. Can also be used oxygen baths, oxygen tents, it all depends on the age of the patient and his condition. During rehabilitation used in rehabilitation treatment the five sessions of oxygen therapy with a change in pressure rates up to 10 treatments.
Gymnastics, physiotherapy, massage
In order to avoid congestion and improved aeration of the lung fields applicable respiratory gymnastics and special exercises, which gradually normalize lung function. Under a moderate load, the child activates the metabolism, is struggling with weakness and relieves cough, develops the lungs. A specific set of exercises will select the doctor of physical therapy office, where the baby will send a doctor. The parents and the child will be taught correct breathing exercises and exercises for home treatment.
To improve the sputum and promote expectoration shows drainage massage, which carried out courses of 10 sessions lasting no more than 6-8 minutes. This tapping vibration movement over the surface of the chest and massage the skin. After such drainage massage phlegm easier to cough and moves away, babies need to put pressure on the tongue to stimulate the after the massage the cough reflex.
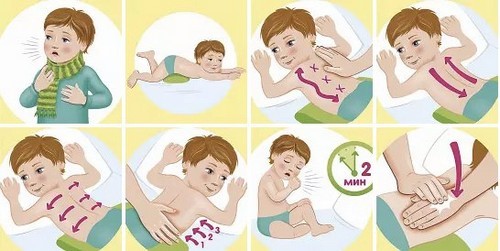
Drainage massage allowed only if there is wet productive cough. On the background of fever and dry cough it is prohibited.
General care of a sick baby
Important strict bed rest at the time of fever and feeling sick and the entire acute period of the disease. With the improvement of the child will periodically need to raise bed, change its position to acceslevel sputum, and there was stagnation.

If there is no fever and the condition is relatively satisfactory, in the supine position to conduct classes in physical therapy in order to facilitate expectoration of sputum. This will help to improve the ventilation of the lungs and deliver it to the blood more oxygen. In the room where the baby needs constant wet cleaning in the morning and evening with disinfectants, the air must be constantly wet and often ventilate for oxygen.
Should drink plenty of liquids in order to reduce the intoxication syndrome and to withdraw products of metabolism and toxins, germs and residues of drugs. Useful water and vegetable broths, compotes and fruit drinks, broths of dried fruits and mineral water without gas, in a serious condition the solutions injected into a vein. Shown table No. 15 with a warm, distressed and non-irritating meals, salt in the diet restricted, it is important to consume more protein and vitamins, carbohydrates for recuperation, refusing fatty foods and heavy meals.




100 the best private proxies with major discounts + Super fast proxy serrvers!