Rheumatoid arthritis is a systemic disease of connective tissue with a lesion mainly of peripheral joints, and internal organs. According to statistics rheumatoid arthritis affects approximately 1% of people around the globe. The average age of onset of disease, forty-fifty years. More common in women than men.
Causes
The nature of rheumatoid arthritis very challenging. The basic cause of the pathology considered an autoimmune process, when the immune system perceives its own cells are foreign and attacks them. It is assumed that this abnormal activity of the immune system due to genetic predisposition.
The factors that trigger the disease include:
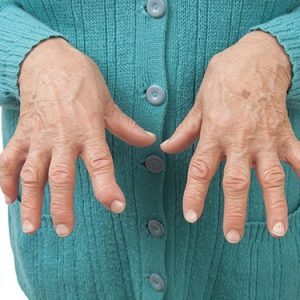
Symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis occurs with a lesion of joints, and internal organs.
The severity of the clinical picture of the disease depends on the degree of activity of pathological process:
- I – Low degree of activity;
- I I – Moderate;
- III – High;
- 0 – in Remission.
The disease first manifests itself in the form of General, nonspecific symptoms. The man said that he was getting tired easily and feels weak. Periodically, the temperature rises slightly, seemingly for no apparent reason, appears sweating. Marked muscle pain, body aches. Often the disease develops slowly, the clinical signs and symptoms takes place over several months, and sometimes years. At this time begin to show signs of joint damage. Much less frequently the disease develops acute or subacute.

Joint pain
Rheumatoid arthritis has several features that can accurately differentiate it from other diseases. In most cases the disease is manifested by arthritis (defeat more than three joints), rarely with oligoarthritis (with the defeat of two joints) or monoartrit (defeat only one joint).
In rheumatoid arthritis joints are affected symmetrically, that is, if the affected joint of a finger on his left hand, his right hand was also observed in the inflammation of the same joint.
Most often affects the following joints:
- Metacarpophalangeal (with the exception of the big toe joint);
- Proximal interphalangeal;
- Metatarsophalangeal;
- Knee;
- Wrist;
- Elbow;
- Ankle.
A characteristic feature of rheumatoid arthritis – the occurrence of morning stiffness. This symptom is characterized by the fact that after waking up, people noted the difficulty of mobility and increased pain in the joints. This symptom develops due to the fact that the night in the cavity of the affected joint inflammatory exudate accumulates, which limits joint function. This condition lasts for more than an hour. Gradually, the stiffness disappears and the person begins to feel more comfortable, joint mobility is restored. In General, rheumatoid arthritis is characterized by constant aching pain in the joints.

Rheumatoid arthritis progresses in three stages. On the first stage of developing swelling of the synovial Bursa of the joint and producing an inflammatory exudate, which is manifested outwardly by swelling of the joint, a local increase in skin temperature, pain. In the second stage the connective tissue cells actively divide, which is sealed by a synovial sheath.

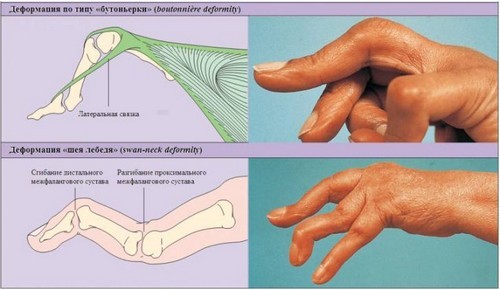
In the third stage, the inflamed cells is produced by a special enzyme, which leads to deformation of the joints, increased pain and loss of motor function. Depending on the localization of the pathological process can be observed such deformation of the brush, as spindle-shaped fingers, neck of a Swan, the type of buttonhole.
Extra-articular symptoms
Since rheumatoid arthritis is a system disease, many patients developed lesions on many internal organs.
Often affects organs such as:
- Skin;
- Heart;
- Light;
- Kidneys;
- The organ of vision;
- Nervous system.

Have 20-50% of patients have subcutaneous rheumatoid nodules. They represent a dense subcutaneous painless education with a diameter of two centimeters. Often, the nodules occur in the elbow, Achilles tendon, over the small joints of the hand.
Rheumatoid nodules can also occur in internal organs, like the lung. Often patients with rheumatoid arthritis affects the pleura of the lungs with the development of pleural effusion and interstitial tissue with the development of interstitial pneumonia. It is believed that the mortality from lung disease among patients with rheumatoid arthritis is twice than in the General population.
The vascular lesions is manifested in the form of vasculitis, which is the basis of diseases of many organs. On the skin appears hemorrhagic vasculitis rash.
Rheumatoid arthritis may experience a loss of any layer of the heart: endocardium, pericardium, myocardium. Most often observed in pericarditis – inflammation of the pericardium, sometimes accompanied by effusion. It is worth noting that patients with rheumatoid arthritis already at a young age is observed atherosclerotic vascular disease.
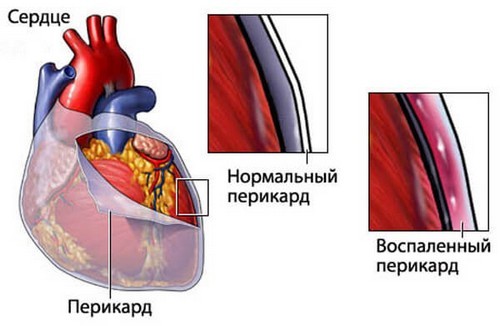
Serious life-threatening is of a kidney disease. When inflammation of the glomeruli develop glomerulonephritis, which may cause renal failure. Patients with long current form of rheumatoid arthritis can occur renal amyloidosis is a pathological deposition of amyloid protein.

In addition, when the disease can affect the organ of vision in the form of dry keratoconjunctivitis, nervous system in the form of neuropathy, loss of muscle in the form of muscle weakness and pain.
Diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis
Diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis is very extensive. To detect the disease can be used non-specific, specific and auxiliary methods.
Non-specific diagnostic methods
First of all, there are traditional clinical research. In the clinical analysis of blood determines the increase in the number of white blood cells, ESR acceleration, reduction of hemoglobin.

In the biochemical study of blood can be detected increase in the level of fibrinogen, sialic acid and C-reactive protein, haptoglobin. However, these changes are nonspecific and can occur in various diseases.
Specific methods of diagnostics
To confirm the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis allows the identification of specific markers of rheumatoid process. In particular, approximately 60% of patients in the blood is found rheumatoid factor. The autoantibodies to their own immunoglobulin G. High titers of factor correlate with the severity, rapid progression of the pathological process. If the patient failed to detect rheumatoid factor – doctors say about seropositive rheumatoid arthritis, if the factor is not detected – seronegative.
One of the most sensitive methods, can be used in the diagnosis of the disease at an early stage of the disease, is the definition anticitrulline antibodies (ACCP). Citrulline is an amino acid which is formed during inflammation. Cells containing citrulline recognized by the immune system the alien, which produces antibodies to them. With rheumatoid arthritis test positive ACCP approximately 80% of cases.
Auxiliary methods of diagnostics
Auxiliary method of diagnosis is the study of synovial fluid. In the liquid are able to detect changes such as decrease its viscosity, increase of leukocytes and neutrophils, color change, transparency. By and large, similar changes are observed in other inflammatory diseases of the joints. Reliably confirms the presence of rheumatoid arthritis detection in the synovial fluid of rheumatoid factor.
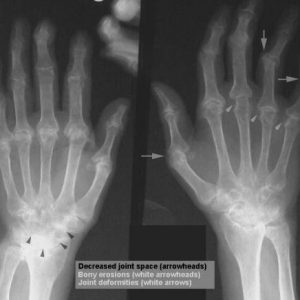
For studies of the affected joints use an x-ray examination and arthroscopy. Early x-ray signs are periarticular osteoporosis, blurred contours of the joint, erosions on the articular surfaces.
Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis
Patients with rheumatoid arthritis need to undergo treatment in the rheumatological patient. In therapy using the following groups of medicines:
- Symptom-modifying drugs;
- Disease-modifying (basic) Antirheumatic drugs;
- Disease-controlling drugs.
Symptom-modifying drugs
The purpose of this group of drugs is the rapid decrease in local inflammation, pain, yet will not affect the basic agent. This group of drugs include NSAIDs and glucocorticoids.
NSAIDs have anti-inflammatory, antipyretic and analgesic effects. Anti-inflammatory effect is due to inhibition of the enzyme cyclooxygenase involved in the synthesis of inflammatory mediators. It has two isoforms: ЦОГ1 and ЦОГ2. Respectively distinguish NSAIDs mainly acting on ЦОГ1 or ЦОГ2. The former include Ibuprofen, Diclofenac, Indomethacin, to the second – Meloxicam, Celecoxib. And those and others have anti-inflammatory effect. However, the blockers ЦОГ2 not have aggressive effects on the mucosa of the gastrointestinal tract, unlike blockers ЦОГ1.
Significant anti-inflammatory effect corticosteroids have. Low doses of glucocorticoids used as “bridge therapy” until, until it begins to have an effect of basic Antirheumatic agents. In some cases, injected large doses of glucocorticoids for several days, which is called “pulsterapii”. Glucocorticoids also applied locally – by injection into the affected joint. However, in this case it is possible to suppress local inflammation.
Basic anti-rheumatic drugs
Are drugs that have an effect not immediately, but at the expense of their ability to intervene in the immune mechanisms of the disease, they can lead to long-term remission.
To the basic drugs include:
- D-penicillamine;
- Gold preparations;
- Salasanoja;
- Cytostatics;
- Quinoline derivatives.
The principle of therapy DMARDs: initially administered high doses to suppress the inflammatory process. Further dose gradually reduce and reach a therapeutic dose, which should be consumed for a long time. If after four to six months of treatment those or other basic drug positive result can not be achieved – so is it necessary to change medication.
Disease-controlling drugs
The effect of these medicines (also called biological agents) aimed at the inhibition of the synthesis anti-inflammatory cytokines – TNF-a and IL-1. It is a modern medicines and genetic engineering that allow to recover patients with resistance to other drugs.
This group includes the following drugs:
- Remicade;
- Humira;
- Rituxan;
- Kinneret;
- Umbrella.
Despite their undeniable effectiveness of disease-controlling drugs have disadvantages. The main drawback is the high cost of drugs. Because treatment of these drugs need long-term, it appears that such treatment can afford not everyone.
Non-drug therapy
Non-pharmacological treatment plays a lesser role than treatment with medicines. Therefore, patients with rheumatoid arthritis need to stick to a diet that is described in the article “Diet in rheumatoid arthritis”. Wishing to recover, you need to stop Smoking because it worsens the disease.
The patient shows moderate (not excessive!) gymnastic exercises, massage. Favorably affect the course of the disease Spa treatment and physiotherapy (balneotherapy, mud cure, laser therapy, magnetic therapy, UHF, electrophoresis). Physiotherapy is carried out after remission of an acute inflammatory process. Correctly used can improve joint mobility and reduce pain.



Don’t let US stop you..