Treatment of vasculitis do, primarily, specialists rheumatologists, but the diversity of clinical manifestations often require examinations by doctors of other specializations.
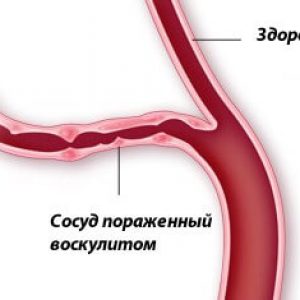
“Vasculitis” is a General term that covers a number of diseases characterized by inflammation of the vascular walls. With such pathologies constricts blood vessels, and nutrition and supply of oxygen to tissues deteriorates.
The result is often tissue death and a sharp decline in the functional activity of individual organs, until complete failure.
Classification
According to the adopted classification, there are primary and secondary varieties of inflammatory lesions of the vascular walls.
Depending on the type of vessels affected by the inflammatory process, vasculitis, divided into:
- arteriitis (suffer large vessels – arteries);
- anteriority (affected arterioles);
- phlebitis (inflamed veins);
- kapillyarity (the affected small blood vessels).
To the group of vasculitis include the following diseases:
- hemorrhagic vasculitis (syndrome of Henoch-Schonlein purpura);
- Takayasu’s disease (nonspecific aortoarteritis);
- microscopic polyangiitis;
- Kawasaki disease;
- mixed vasculitis;
- polyarteritis nodosa;
- allergic vasculitis of the skin;
- Behcet’s disease;
- the disease of Horton (giant cell vasculitis);
- Wegener’s granulomatosis;
- cryoglobulinemic vasculitis.
Why develop vasculitis?

Primary vasculitis is considered by specialists as an independent nosological form. The exact causes of this disease to date, remain unclear.
Secondary lesions of the vascular walls develop on the background of different pathologies.
Possible causes of secondary vasculitis:
- infections (both acute and chronic);
- individual reaction to the introduction of the vaccines (serums);
- contact with chemical substances or biological poisons;
- genetic factors (hereditary predisposition);
- the thermal factor (overheating or overcooling of the body);
- skin burns (including on the background of long-term exposure);
- trauma of various Genesis and localization.
Important: vasculitis often develops in individuals who have had hepatitis.
Any of these factors, as well as a combination of two or more of them, able to change the antigenic structure of the body’s own tissues, in this case the walls of blood vessels. The immune system begins to perceive them as alien and activates antibody production, further damaging the blood vessels. Thus starts the autoimmune reaction, in which target tissues develop inflammatory and degenerative processes.
Symptoms of vasculitis
Common to all the symptom of vasculitis is considered to be more or less severe febrile reaction. The fever is a typical reaction to a serious inflammation of any localization.
Hyperthermia can be fickle; to inflammation of blood vessels are rather characteristic daily fluctuations of temperature. At the height of its increase often develop skin reaction such as rashes.Clinical manifestations of pathologies of this group is largely dependent on the nature of the disease, i.e. specific nosological forms. Some vasculitides affect only the skin, causing the patient to only minor discomfort. Other cause multiple lesions of internal organs leading to death.
Among other symptoms, often observed in patients with vasculitis include:
- weakness;
- severe physical and mental fatigue;
- nausea;
- vomiting;
- pallor of the skin;
- myalgia (typical for nodular form);
- paresthesia (numbness);
- the decline in visual acuity.
- periodic loss of consciousness (fainting);
- headaches;
- deterioration or lack of appetite;
- sleep disorders;
- nervous and mental disorders;
- conjunctivitis;
- frequent inflammation of the oral mucosa;
- swelling in the temporal region (characteristic of the disease of Horton);
- the appearance is not associated with the infection of ulcerative lesions on the genitals (with behçet’s syndrome).
Typical clinical manifestations of vasculitis include bleeding small area with primary localization on the skin of various parts of the body. As the progression of the process, they appear in muscle tissue, the articular cavities and in areas of nerve endings.
Depending on which vessels are affected, mainly suffers from a specific organ. If the affected renal vessels, often develop glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis and infarcts of the kidney. When the localization of inflammation in the coronary arteries, high risk of cardiac complications (up to caused by ischemia, infarction). When the affected blood vessels that feed the joint tissues first develop symptoms of arthritis and other symptoms may appear only after several weeks or even months.
Please note: for arthritis, due to impaired nutrition and oxygenation of tissues, characterized by the development of pain syndrome that is not associated with increased physical exertion or injuries. On the background of vasculitis usually develops inflammation in large joints.
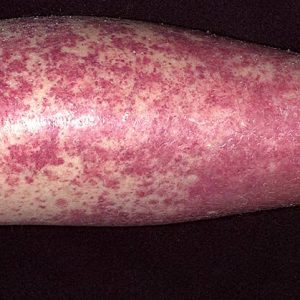
A characteristic symptom of one of the most common vasculitis – hemorrhagic – palpable purpura is. This skin rashes in the form of small hemorrhages preferentially localized at the joints of the limbs. Often reveals abdominal syndrome, which is characterized by intense pain in the abdomen.
With the defeat of coronary vessels appear cardialgia, shortness of breath and irregular heart rhythm.
For Wegener’s granulomatosis peculiar to predominant lesion of paranasal sinuses with discharge of blood and pus from the nasal passages.
For any of the pathologies of this group is typically a protracted chronic course with an inevitable progression in the absence of treatment. They also suffer recurrent exacerbations, during which the severity of clinical symptoms increases.
In the course of laboratory diagnostics in the blood is often determined by the decrease hemoglobin levels (anemia) and a moderate increase in the number of leukocytes and platelets.
In the urine are determined blood cells (leukocytes and erythrocytes), i.e. microhematuria; often found and protein.
Clinical symptoms are mostly nonspecific, therefore, diagnosis requires a number of laboratory tests (for confirmation of inflammatory and autoimmune process) and hardware methods of investigation – ultrasound, fluoroscopy, computed tomography and MRI. If necessary, biopsy of tissues.
The treatment of vasculitis, prognosis and prevention
Therapeutic approach is tailored to each patient individually. When the treatment plan is taken into account a form of vasculitis, the severity of the process and the presence of comorbidities.
The main tasks of therapeutic measures in vasculitis:
- remission;
- preventing recurrence;
- warning of irreversible lesions of organs and tissues;
- reducing the likelihood of complications;
- increasing life expectancy and improving the quality of life of the patient.

The treatment of vasculitis is pharmacotherapy. The patient is assigned drugs that reduce the sensitivity of tissues and reduces the synthesis of antibodies. In particular, it is shown glucocorticoid hormones. Is hormonal therapy allows for a short time to suppress the abnormal activity of the immune system. If complicated course of the disease fails to achieve positive results with the help of glucocorticoids, shows chemotherapy using cytotoxic drugs.
If diagnosed hemorrhagic pathology, a prerequisite for successful treatment becomes rational antibiotic therapy.
Good therapeutic effect in most cases possible to achieve with the help of blood purification by means of methods of plasmapheresis and hemosorption.
In mild course of the disease and in remission help the drug from the group of NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs). Patients, in particular, are assigned Voltaren and Indomethacin, allowing, in particular, to reduce the intensity of pain.
Vasculitis shown drugs that reduce the permeability of vascular walls and inhibiting thrombogenesis.
Please note: treatment vasculitis, allergic Genesis, which revealed only minor skin lesions, possible without the use of pharmacological agents. In this case, in the foreground, the elimination of contact of the patient with the alleged allergen.
Forecast
The prognosis largely depends on the location and severity of inflammation of blood vessels, and the number of affected organs.
Prevention
To prevent inflammation of the blood vessels are recommended tempering treatments. One of the important preventive measures is to reduce the influence of adverse external factors on the organism and normalization of sleep and rest. Should not take drugs without medical supervision or to undergo vaccination without the need. All vaccines people should get in accordance with the National vaccination calendar.