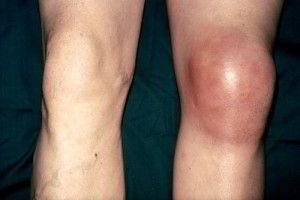
Arthritis of the knees includes several dozen varieties of articular pathology. Each of them proceeds slowly and has constant progressive signs. If, at an early stage, it is not possible to identify the causes and treatment, the disease takes a chronic form, which causes unbearable pain in the patient and leads to disability.
Knee arthritis is a pathology based on a slow but constantly progressing process that affects the musculoskeletal system of the body. By its nature, the disease is divided into primary and secondary types.
The primary form is caused by inflammation of the joint itself, and with secondary arthritis, negative changes occur as a result of other diseases.
However, not only these causes provoke gonarthritis. Any malfunction in the basic functions of the body or various external influences lead to the emergence of this insidious disease.
Causes and Risk Factors
The causes of knee arthritis are manifold.
- after strong physical exertion on the knee joint;
- with overweight. In this case, the reasons lie in the increased load on the knee joint;
- in case of metabolic disorders;
- in frequent hypothermia of articular joints.
In addition to the most common factors, there are other causes of the disease:
- infection. Arthritis of the knees can be a consequence of serious infectious diseases (syphilis, tuberculosis, gonorrhea) or as a complication after infection of the genitourinary or digestive systems. Every second case is caused by the appearance of streptococcal bacillus or occurs as a result of angina infection. At the same time, not only the joints are affected, but also the work of the kidneys and heart;
- injury. Post-traumatic arthritis of the knees develops after bruises, ruptures of the knee capsule and hemorrhages arising in the cavity of the knee joint;
- age. Risk factors include the age category of men and women who have reached the age of 60;
- floor. Most often, knee arthritis is found in women during menopause.
- birth defects in the knee joint. Gonarthritis occurs against the background of different leg lengths, flat feet and joint hypermobility.
Symptoms of the disease
It is not difficult to diagnose knee arthritis, because the symptoms of the disease have a pronounced characteristic. First of all, the affected area differs from a healthy joint in its size. In the affected area there is swelling, swelling and redness. Symptoms of the disease also appear as an increase in temperature at the site of joint damage. Characteristic features in later stages are already manifested as a deformation of the knee joint.
Symptoms in a patient at the initial stage begin to arise in the form of pain during physical exertion. Then they become permanent. Relief usually occurs in a bent position of the leg. In the final positions, pain reaches its maximum value.
Symptoms characteristic of any type of arthritis:
- stiffness of movements after a night’s sleep;
- discomfort in the knees is expressed in aching and burning pain;
- acute pain may periodically occur in the affected joint. If this is gouty arthritis of the knees, then especially often they bother the patient at night;
- signs of an advanced stage, as well as gouty and purulent gonarthritis, are characterized by partial loss of motor function and knee deformation.
Main forms
Reactive arthritis
The reasons why this type occurs, most often lie in the untimely diagnosed and cured infectious diseases. Reactive arthritis of the knee joint in most cases occurs in women and men whose age category is in the range of 20-40 years.
Its symptoms can be seen a month after the infection in the body. The signs that accompany reactive gonarthritis are expressed as inflammation of the prostate in men and genitals in women. Frequent urination may occur, accompanied by burning and pain.
The treatment of the disease is primarily aimed at the destruction of the infection that provoked it. The patient is prescribed antibacterial agents and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Rheumatoid arthritis
The reasons for the development of this type of disease are not fully established. But the basis of pathological changes is the presence of autoimmune damage to the connective tissues of the articular membrane. Rheumatoid arthritis of the knee joint, for the most part, develops symmetrically in both limbs.
Symptoms are manifested not only in morning stiffness for an hour, but also in the form of wave-like attacks, followed by remission. Further progression of the disease contributes to the destruction of cartilage, capsule joints, stretching of muscles and tendons.
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis of the knee joint most often develops against a background of metabolic disorders that cause slow circulation in the joints and bone tissues. Such dysfunctions gradually lead to the destruction of cartilage in the joint. It loses its natural color, becomes thinner, exfoliates, and cracks. The destructive process affects bone tissue. They form growths, spikes and seals, gradually deforming and bending the joint.
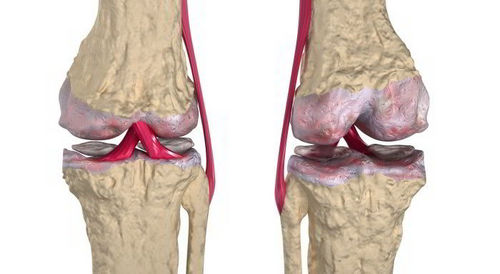
An exacerbation of the disease can acquire a purulent type, a complication of which is sepsis. The main symptoms that cause a person to see a doctor are pain and stiffness of movements, especially in the morning after a night’s sleep.
Polyarthritis
Polyarthritis of the knee joint occurs with simultaneous inflammation of several joint joints at once, or this process proceeds sequentially. Most often, such knee arthritis is a consequence of another disease that is difficult to diagnose. Especially difficult is gouty polyarthritis, which occurs against the background of an increased content of uric acid in the body.
Arthritis of the knees of this type at an early stage is almost not palpable. Its first signs are the high sensitivity of articular joints to weather changes. With further progression of the disease, the patient’s appetite and body weight may decrease. And if such arthritis of the knees becomes acute and becomes purulent, high body temperature is added to the above stated symptoms. Untimely treatment started threatens to result in visual impairment, damage to the skin, as well as a violation in the functioning of internal organs and the circulatory system.
Antibacterial therapy and the use of anti-inflammatory non-steroid drugs are necessarily included in the treatment of polyarthritis. Also, the introduction of corticosteroids into the cavity of the affected knee joint is also required. In some cases, the patient is prescribed a course of plasmapheresis. Basic therapy for polyarthritis can last more than one year.
Infectious Arthritis
Purulent arthritis of an infectious type is usually caused by microorganisms that enter the joint cavity through blood or lymph fluid passing through the foci of infection. Also, infectious inflammation is caused when pathogenic microbes from the external environment get into an open injury or when an inept medical intervention in the internal cavity of the joint (puncture, arthrotomy) occurs. Its occurrence can provoke diseases such as measles, mumps, rubella, hepatitis and influenza. The main causative agents of infection are staphylococci (80%), as well as streptococci, pneumococci and meningococci (20%).
Infectious arthritis of the knees of a purulent form in a patient causes very severe pain. Because of this, he cannot move, and the limb is forced to be in a bent position. With inflammation in the joint cavity, an effusion (fluid) is formed, which fluctuates slightly upon palpation of the knee.
Treatment of the disease includes eliminating the infection from the body, relieving inflammation, prescribing painkillers. Purulent arthritis may require complete immobilization of the joint after puncture and washing of its cavity with antiseptic solutions.
Gouty arthritis
Gouty gonarthritis is usually associated with metabolic disorders. A similar pathology causes an increase in uric acid in the body and the deposition of salt crystals in the joint. The disease is unpleasant, but with timely and accurate diagnosis can be cured.
Gouty arthritis is triggered by the following factors:
- an unbalanced diet that contains excessive amounts of meat products and alcohol;
- the use of drugs (aspirin) including diuretics;
- overweight;
- diabetes;
- high blood pressure
- weakened kidney function.
Gouty arthritis at the initial stage is almost not palpable. Episodic pain attacks at later stages can happen quite often, but their duration usually is no more than 3 hours. The knee joint swells, reddens and limits the possibility of movement.
The treatment of the disease is based on diet therapy, which provides for the rejection of products that increase the concentration of uric acid salts in the body. Anti-inflammatory and analgesic drugs may also be prescribed. As you can see, arthritis is far from a safe disease. Therefore, at the first signs it is recommended to contact specialists. Be healthy!